colegio agustiniano ciudad salitre area de ciencias naturales y
advertisement
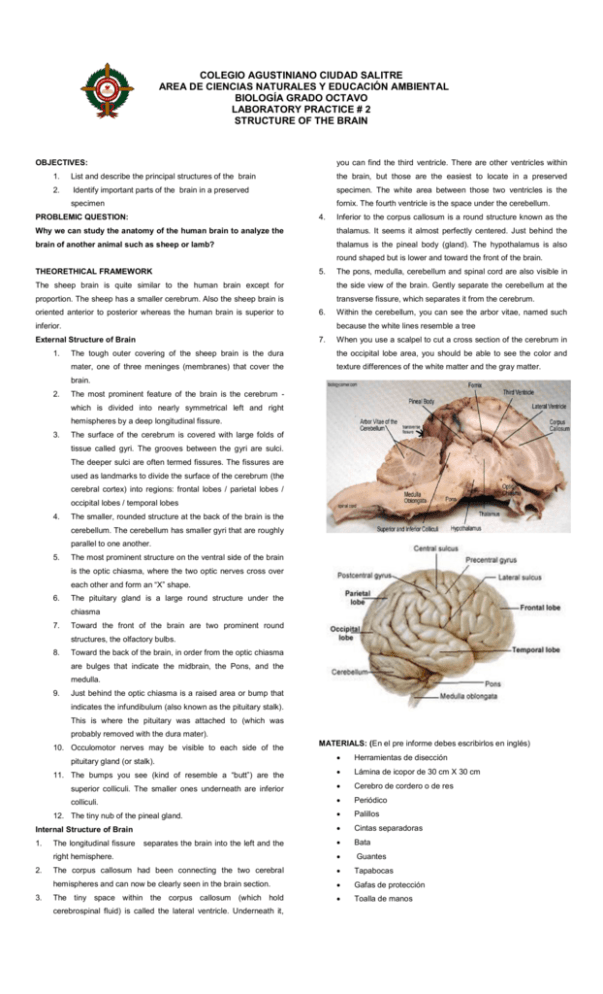
COLEGIO AGUSTINIANO CIUDAD SALITRE AREA DE CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EDUCACIÓN AMBIENTAL BIOLOGÍA GRADO OCTAVO LABORATORY PRACTICE # 2 STRUCTURE OF THE BRAIN OBJECTIVES: you can find the third ventricle. There are other ventricles within 1. List and describe the principal structures of the brain the brain, but those are the easiest to locate in a preserved 2. Identify important parts of the brain in a preserved specimen. The white area between those two ventricles is the specimen fornix. The fourth ventricle is the space under the cerebellum. PROBLEMIC QUESTION: 4. Inferior to the corpus callosum is a round structure known as the Why we can study the anatomy of the human brain to analyze the thalamus. It seems it almost perfectly centered. Just behind the brain of another animal such as sheep or lamb? thalamus is the pineal body (gland). The hypothalamus is also round shaped but is lower and toward the front of the brain. THEORETHICAL FRAMEWORK 5. The sheep brain is quite similar to the human brain except for the side view of the brain. Gently separate the cerebellum at the proportion. The sheep has a smaller cerebrum. Also the sheep brain is oriented anterior to posterior whereas the human brain is superior to transverse fissure, which separates it from the cerebrum. 6. inferior. Within the cerebellum, you can see the arbor vitae, named such because the white lines resemble a tree External Structure of Brain 1. The pons, medulla, cerebellum and spinal cord are also visible in 7. When you use a scalpel to cut a cross section of the cerebrum in The tough outer covering of the sheep brain is the dura the occipital lobe area, you should be able to see the color and mater, one of three meninges (membranes) that cover the texture differences of the white matter and the gray matter. brain. 2. The most prominent feature of the brain is the cerebrum which is divided into nearly symmetrical left and right hemispheres by a deep longitudinal fissure. 3. The surface of the cerebrum is covered with large folds of tissue called gyri. The grooves between the gyri are sulci. The deeper sulci are often termed fissures. The fissures are used as landmarks to divide the surface of the cerebrum (the cerebral cortex) into regions: frontal lobes / parietal lobes / occipital lobes / temporal lobes 4. The smaller, rounded structure at the back of the brain is the cerebellum. The cerebellum has smaller gyri that are roughly parallel to one another. 5. The most prominent structure on the ventral side of the brain is the optic chiasma, where the two optic nerves cross over each other and form an “X” shape. 6. The pituitary gland is a large round structure under the chiasma 7. Toward the front of the brain are two prominent round structures, the olfactory bulbs. 8. Toward the back of the brain, in order from the optic chiasma are bulges that indicate the midbrain, the Pons, and the medulla. 9. Just behind the optic chiasma is a raised area or bump that indicates the infundibulum (also known as the pituitary stalk). This is where the pituitary was attached to (which was probably removed with the dura mater). 10. Occulomotor nerves may be visible to each side of the Herramientas de disección 11. The bumps you see (kind of resemble a “butt”) are the Lámina de icopor de 30 cm X 30 cm superior colliculi. The smaller ones underneath are inferior Cerebro de cordero o de res colliculi. Periódico Palillos Cintas separadoras pituitary gland (or stalk). 12. The tiny nub of the pineal gland. Internal Structure of Brain 1. 2. 3. MATERIALS: (En el pre informe debes escribirlos en inglés) Bata right hemisphere. Guantes The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral Tapabocas hemispheres and can now be clearly seen in the brain section. Gafas de protección The tiny space within the corpus callosum (which hold Toalla de manos The longitudinal fissure separates the brain into the left and the cerebrospinal fluid) is called the lateral ventricle. Underneath it, PROCEDURE:(En el pre informe lo escribes en forma de diagrama de You need to know the difference between a nerve and a flujo “Flowchart”) tract. On this screen also note the longitudninal fissure and the cranial nerve called the oculomotor (III) nerve which 1. 2. Before beginning the dissection of the sheep brain you will helps control eye movements. need to know the terms used to specify the location and Find the medulla (oblongata) which is an elongation below relative location of various brain structures .Read carefully the pons. Among the cranial nerves, you should find the very the information of the following link: (IMPORTANT: Print large root of the trigeminal nerve. one file per group) From the view below, find the IV ventricle and the http://psych.hanover.edu/classes/neuropsychology/Syllabus/ cerebellum. Labs/DISSECTION.pdf From the view below, you can see both the superior The procedure is divided into three main sections: colliculus(i) and inferior Examination of the Exterior of the Brain, Examination of the colliculus(i). The superior and inferior colliculi are part of the Mid-Sagittal Plane of the Brain, Examination of two Frontal midbrain and collectively known as the Tectum. Cuts. Note the large gyrus called the Uncus. Posterior to the uncus Examination of the Exterior of the Brain. find the Hippocampal gyrus so named because the The first portion of the dissection will be a detailed hippocampus lies dorsal to it. In the middle of the brain you examination of the brain surface. No actual cutting of the will find the Mammilary Bodies which are part of the limbic brain is required for this portion of the dissection. As you system and play a role in memory. Also find the Rhinal proceed to identify the listed parts of the brain, note their Fissure which defines one boundary of the limbic system. structure and how they are related to other parts of the brain. Now find the four lobes of the cerebrum: frontal, parietal, First examine the exterior of the entire brain. You may be able temporal, and occipital. The Frontal Lobe is bounded by the to see one or two of the three layers of the meninges, the Ansate Sulcus and the Pseudosylvian Sulcus. The Parietal dura mater, the arachnoid layer, and the pia mater. The Lobe is bounded by the Ansate Sulcus, the Suprasylvian meninges are the protective coverings, which enclose the Sulcus, and the Lateral Sulcus. The Temporal Lobe is brain and spinal cord. The dura mater, the tough outer layer, bounded by the Pseudosylvian Sulcus and the Suprasylvian will have been mostly removed when the brains were Sulcus. The Occiptial Lobe is inside the Lateral Sulcus. prepared for the dissection; however, some of the dura mater Examination of the Mid-Sagittal Cut may remain near the base of the brain. The arachnoid layer, Do not proceed to the next step before checking with the lab the middle layer, and pia mater, the inner layer, are still likely instructor No you will make a mid-saggital cut. Hold the to cover the brain. The pia mater follows the gyri and sulci brain level and flat and cut along the longitudinal fissure. On and most likely is still on your specimen and may be this screen you can find the lateral ventricles (and septum indistinguishable from the brain. Blood vessels are between pellucidum), third ventricle, the cerebral acqueduct (which the arachnoid layer and the pia mater. These vessels and the connects the third and fourth ventricle), and the tegmentum, arachnoid layer will obscure your view of the sulci making the the other part of the mid brain. identifications below difficult and confusing. Before Can you find the superior and inferior colliculi on this view? proceeding with the identification of structures on the surface This is a more detailed view of the mid-saggital section. Here of the brain you will need to remove the arachnoid layer and you can find the largest of all of the commisures (a band of the blood vessels. Use your tweezers and be very careful fibers that connects the two sides of the central nervous because the brain is soft and easily damaged. system). This is the corpus callosum. It is so big that Next locate the area referred to as the brain stem. This area different parts of it get different names. So you have the is made up of the pons, medulla, and cerebellum. Find also genu, splenium, and the body of the corpus callosum. In the root where the pituitary gland was attached to your brain. addition note the pineal body famous from our discussion The pituitary gland may have been there when you first of Decarte), the hypothalamus, and the massa intermedia. cleaned your brain. Now you are looking at the cerebellum. Notice the pattern of Examine the ventral surface of the sheep brain. The next grey and white matter. To some it resembles a tree or bush several steps will view this surface of the brain. A pair of and is called as a result the arbor vitae (the tree of life –ok a olfactory bulbs may be seen, one under each lobe of the bit strong). frontal cortex. Several important parts of the visual system are Examination of the Frontal Cuts visible in the ventral view of the brain. Muscles, other nerves Do not proceed to the next step before checking with the lab and fatty tissue may surround the optic nerve on your instructor. specimen. After inspection of these, use a scalpel to cut away Find the putamen, globus pallidus, and caudate nucleus. this muscle tissue, leaving as much of the optic nerve as These structures are collectively known as the Basal possible protruding from the ventral side of the brain. Notice Ganglia. In addition you should see the crossing of the that as the optic nerves from the right and left eyes proceed anterior commissure right above the optic chiasm. While not towards the center of the brain, they meet in the optic labeled see if you can see the corpus callosum and the chiasm (named for the Greek letter chi, C, which it lateral ventricles. resembles). In the optic chiasm, there is a partial crossover of fibers carrying visual information. Any time fibers in a tract or nerve cross the midline of the brain it is called a decussation. After the optic chiasm, visual information proceeds along the optic tract toward the visual cortex. Names:_______________________________________ Class # _____________________________________________ ANALYSIS OF RESULTS. _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Score _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Date:__________________________ Grade: ________ Topic: Lab practice structure of brain RESULTS Match the structure to the description a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. looks like a butt' leathery covering over the entire brain cauliflower, the area toward the back of the brain behind the colliculi, looks like a little nub looks like a "tree" the rounded part of the brain stem shaped like an X large area under the corpus callosum space for fluid between the corpus callosum and the fornix contains nerves, connects to the far front of the brain Organize the description of your observations in the following table, In addition for your lab report, print and paste photos of the brain observed in the lab. 1. ___ Arbor Vitae 2. ___Lateral Ventricle 3. ___Optic Chiasma External structure 4. ___Superior Colliculi of the brain 5. ___Dura Mater 6. ___Cerebellum 7. ___Pineal Gland 8. ___Thalamus 9. ___ Pons 10. ___ Olfactory Bulb Internal structure of the brain Label this brain What conclusions can you make about the brain from this examination? Before you clean up your brain, your teacher will check to make sure you know the structures on this page. You will be given 1-5 items on the list to locate. Alternatively, you may be shown slides a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. p. q. r. s. t. Thalamus Hypothalamus Superior & Inferior Colliculi Arbor Vitae Cerebellum Cerebrum Optic Chiasma Transverse & Longitudinal Fissue Corpus Callosum Lateral Ventricle pineal body pituitary gland fornix spinal cord medulla pons midbrain olfactory bulb sulcus gyrus 1. _________________________________ 1______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________ 3. _________________________________ 4. _________________________________ 5. _________________________________ 3______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________