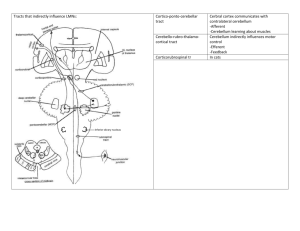
Spinal Cord Tracts
advertisement

ASCENDING TRACTS Receptors and afferents 1st order neuron 2nd order neuron Decussation level Fine touch, pressure, vibration, movement, position, Pain, temperature Highly specialized mechanoreceptors Dorsal root ganglia Fasciculus gracilis (T6 or lower) Fasiculus cuneatus (above T6) Lamina I and V (nuc posteromarginalis, nuc proprius) Cross midline at medulla medial leminiscus VPL (thalamus) Somatosensory cortex VPL Somatosensory cortex Paleospinothalamic tract Dull, poorly localized pain Nerve endings in skin Intralaminar nucleus (thalamus) Cingulate cortex Anterior Spinothalamic tract Crude touch and pressure, poorly localized, nondiscriminative Muscle sense Nerve endings in skin DRG Dorsal horn Cross at each spinal segment ascend in anterolateral fasciculus Cross at each spinal segment ascend in anterolateral fasciculus ascend bilaterally in anterolateral fasiculus VPL Somatosensory cortex Muscle spindles Golgi tendon organs DRG Clarke’s nucleus (C8 and below) External cuneatus (above C8) DC-ML SYS Tract Dorsal column system SPINOCEREBELLAR TRACTS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM Neospinalthalamic tract Dorsal Spinocerebellar tract (DSCT-C8 and below) Cuneocerebellar tract (above C8) Ventral Spinocerebellar tract (VSCT) Function Whole limb muscle sense, mostly lower limbs Highly myelinated SA fibers Nerve endings in skin Golgi tendon organs DRG (via Lissauer’s) *signal edited in lamina II DRG *signal edited in lamina II DRG Lamina IV-VIII Spinal border cells 3rd order neuron Final destination Cerebellum (via ICP) DSCT Do not cross -- Cross VSCT cross again (end up on same side) Cerebellum (via SCP) -- CORTIOCSPINAL DESCENDING TRACTS Tract Lateral corticospinal tract (LCST) Anterior corticospinal tract (ACST) SCS - LAT GROUP Rubrospinal Raphespinal SUBCORTICOSPINAL – MEDIAL GROUP Tectospinal Reticulospinal Lateral vestibulospinal (LVST) Medial vestibulospinal (MVST) Function Voluntary movement Origin Motor and premotor cortex Pathway/Decussation Internal capsulecerebral peduncle pyramids Destination Some interneurons in intermed gray Cross midline in pyramids descend in LCST Voluntary movement *Only upper cervical and upper thoracic levels Motor control, coordination; muscle tone – distal flexors Modulating pain (releases serotonin) Motor: mediates head, eye, postural responses to visual stimuli Modulates spinal reflexes Axial muscle tone, posture Antigravity extensor muscles in lower limbs posture and balance Flexors control head position according to vestibular information (in cervical levels of SC) Motor and premotor cortex Internal capsule cerebral peduncle pyramids alpha motor neurons in distal muscles Axial motor neurons Stay ipsilateral, descend in ACST, cross midline at each level Red nucleus Cross midline at Ventral Tegmental Decussation (VTD) rubrospinal tract *always with LCST Interneurons of ventral horn Dorsal raphe nucleus Cross midline, descend next to RuST, LCST Superior colliculus Cross midline at Dorsal Tegmental Decussation (DTD) Projects bilaterally onto grey matter Reticular formation Pontine reticulospinal tract: uncrossed Medullary RTS: bilaterally medial/lateral funiculus Interneurons and SA in laminae I, II, V Interneurons (anterior horn) and motor neurons (neck, trunk muscles) at cervical levels Interneurons at all levels Lateral vestibular nucleus Don’t cross midline LVST Motor and interneurons of extensors Medial vestibular nucleus Don’t cross midline MVST Interneurons and motor neurons of neck