Overview Interactions of Life
advertisement

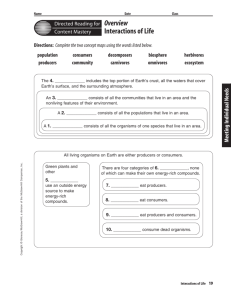
Name Date Directed Reading for Content Mastery Class Overview Interactions of Life Directions: Complete the two concept maps using the words listed below. consumers community decomposers carnivores biosphere omnivores herbivores ecosystem The 4. _____________ includes the top portion of Earth’s crust, all the waters that cover Earth’s surface, and the surrounding atmosphere. An 3. _____________ consists of all the communities that live in an area and the nonliving features of their environment. A 2. _____________ consists of all the populations that live in an area. A 1. _____________ consists of all the organisms of one species that live in an area. Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All living organisms on Earth are either producers or consumers. Green plants and other There are four categories of 6. ____________, none of which can make their own energy-rich compounds. 5. ____________ use an outside energy source to make energy-rich compounds. 7. ____________ eat producers. 8. ____________ eat consumers. 9. ____________ eat producers and consumers. 10. ____________ consume dead organisms. Interactions of Life 19 Meeting Individual Needs population producers Name Date Section 1 Section 2 Directed Reading for Content Mastery ■ ■ Class Living Earth Populations Directions: Circle the word listed below in the puzzle. Then complete the sentences by writing the words in the appropriate spaces. habitat community carrying limiting biosphere size ecologists A H R X population biotic Z A R Y F W P C A R R Y I N G Y G A Meeting Individual Needs D B I O S P H E R E C L I M I F B H T W C S D E Y D S I T I N G I Y A S M G F R E R R O J T S N H J T Y T F T P O P U L A T O N I U H X E L K S H D F C C O M M U N I Y W F R P C Z I T Y E C H U I D E C O L O G I S T S E 1. The part of Earth that supports life is called the ____________________. 2. ____________________ are scientists who study the interactions of organisms and their environments. 3. All the people living in one area make up that area’s ____________________. 4. All the animals and plants living in an area make up a ____________________. 5. The desert is a tarantula’s ____________________. 6. Competition limits a population’s ____________________. 7. Anything that restricts the number of individuals in a population is a ____________________ factor. 8. ____________________ capacity is the largest number of individuals of one species that an ecosystem can support over time. 9. The highest rate of reproduction for a population is its ____________________ potential. 20 Interactions of Life Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. U U L O T Y E H U G H Name Date Directed Reading for Content Mastery Section 3 ■ Class Interactions Within Communities Directions: Write the word that completes each sentence in the correct space in the puzzle. The answers are listed below. The letters in the dark, vertical box spell the answer to question 7. consumer commensalism symbiosis mutualism niche producer Meeting Individual Needs 1 2 3 4 5 G Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 6 1. A ______ refers to how an organism survives, including its habitat, how it obtains food and shelter, and how it avoids danger. 2. A ______ is an organism that cannot make its own energy-rich molecules. 3. A ______ is an organism that uses an outside energy source to make energy-rich molecules. 4. A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit is called ______. 5. ______ is a symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is not affected. 6. ______ is any close relationship between species. 7. ______ is the study of interactions among organisms and their environment. Interactions of Life 21 Name Date Directed Reading for Content Mastery Class Key Terms Interactions of Life Directions: Select the term from the following list that matches each description. biosphere ecology mutualism carrying capacity ecosystem parasitism commensalism habitat population community limiting factor producer consumer niche symbiosis 1. how an organism survives, including its habitat, how it obtains food and shelter, and how it avoids danger Meeting Individual Needs 2. the place in which an organism lives 3. all the organisms in an ecosystem that belong to the same species 4. all the populations in an ecosystem 5. all the organisms living in an area and the nonliving features of their environment 7. anything that restricts the number of individuals in a population 8. the largest number of individuals of one species that an ecosystem can support over time 9. the study of interactions that occur among organisms and their environment 10. organisms that use an outside energy source, such as the Sun, to make energy-rich molecules 11. organisms that cannot make their own energy-rich molecules 12. any close relationship between species 13. a symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit 14. a symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is not affected 15. a symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits but the other is harmed 22 Interactions of Life Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 6. the part of Earth that supports life, including the top portion of Earth’s crust, all the waters that cover Earth’s surface, and the surrounding atmosphere