Innervation of the GI Tract
advertisement

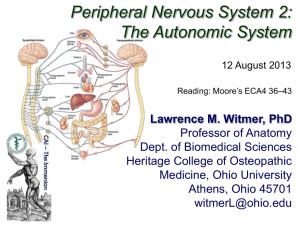
Innervation of the GI Tract GI tract is made of smooth muscle ●innervation is from autonomic system ● parasympathetic (for peristalsis) ● sympathetic (for regulation of blood flow) 88 Posterior vagal trunk L. greater splanchnic nerve Celiac ganglion Lesser and least splanchnic nerves Superior mesenteric ganglion Left sympathetic trunk Inferior mesenteric ganglion Superior hypogastric plexus R and L hypogastric nerves Right inferior hypogastric plexus 89 Greater, lesser, least splanchnic nerves Vagus n. Celiac ganglion T5 -T9 Superior mesenteric ganglion T10 T11 T12 Aorticorenal ganglion L1 L2 S2 S3 Sacral splanchnic n.s Lumbar splanchnic n.s Inferior mesenteric ganglion S4 90 Pelvic splanchnic n.s 91 Nerves (sympathetic, parasympathetic, afferent) Myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus Mesentery Submucosal (Meissner’s) plexus Submucosa Circular muscle 92 Vagus nerve provides parasympathetic innervation up to proximal 2/3 of transverse colon Pelvic Splanchnic Nerves 93 Hirschsprung’s Disease ● Congenital absence of enteric parasympathetic ganglia in distal colon →Absence of peristalsis → Dilation of proximal colon → Constipation, failure to pass meconium, distension of abdomen ● 1 case / 5000-7000 births 94 Motility of the Large Intestine • Haustral contractions – Slow segmenting movements that move the contents of the colon – Haustra sequentially contract as they are stimulated by distension • Presence of food in the stomach: – Activates the gastrocolic reflex – Initiates peristalsis that forces contents toward the rectum 95 Defecation • Distension of rectal walls caused by feces: – Stimulates contraction of the rectal walls – Relaxes the internal anal sphincter • Voluntary signals stimulate relaxation of the external anal sphincter and defecation occurs 96 Defecation External anal sphincter is contracted by voluntary motor stimulation from pudendal nerve 97 Parasympathetic stimulation relaxes internal anal sphincter – which is normally contracted by sympathetic stimulation – when rectum is distended, and prepares for defecation Visceral Afferents and Referred Pain dorsal root ganglion Visceral sensory nerves [GVA] • run with sympathetic & parasympathetic nerves • cell bodies in dorsal root ganglion • nerve ending in viscera Somatic sensation: • conscious, sharp, well-localized • touch, pain, temperature, pressure, proprioception Visceral sensation: • often unconscious; if conscious: dull, poorly-localized 98 • distension, blood gas, blood pressure, cramping, irritants Visceral Afferents and Referred Pain Referred Pain: • Pain originating in a visceral structure perceived as being from an area of skin innervated by the same segmental level as the visceral afferent • Results from convergence of somatic & visceral afferents on the same segmental level of the spinal cord • “Cross-talk” in the dorsal horn somatic afferent www.merck.com 99 visceral afferent convergence & “cross-talk” T10 dermatome = umbilicus 100 Point-Specific Referred Pain Travels Along Sympathetic Fibers Splanchnic Nerves Ganglion Viscera Region of referred pain Greater – T5 – T9 Celiac - Foregut Epigastric Lesser – T10/T11 Sup. Mesenteric – Midgut Periumbilical Least – T12 Aortico-renal Kidneys Lower Thoracic Lumbar – L1/L2 Inf. Mesenteric Hindgut Hypogastric 101 Visceral Afferents and Referred Pain Maps of Referred Pain Grant’s Atlas 11 2005 102 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System Differences between Sympathetic & Parasympathetic Location of Preganglionic Cell Bodies Sympathetic Parasympathetic Thoracolumbar Craniosacral T1 – L2/L3 levels of the spinal cord Brain: CN III, VII, IX, X Spinal cord: S2 – S4 103 Structure of spinal nerves: Somatic pathways dorsal ramus dorsal root ganglion dorsal root spinal nerve dorsal horn CNS interneuron somatic sensory nerve (GSA) ventral somatic ramus motor ventral horn nerve ventral root Mixed Spinal Nerve gray ramus communicans sympathetic ganglion 104 (GSE) white ramus communicans Structure of spinal nerves: Sympathetic pathways dorsal ramus intermediolateral gray column spinal nerve ventral ramus gray ramus communicans sympathetic ganglion 105 white ramus communicans Sympathetic System: Postganglionic Cell Bodies 1. Paravertebral ganglia • Located along sides of vertebrae • United by preganglionics into Sympathetic Trunk • Preganglionic neurons are thoracolumbar (T1–L2/L3) but postganglionic neurons are cervical to coccyx • Some preganglionics ascend or descend in trunk Paravertebral ganglia sympathetic trunk (chain) synapse at same level Prevertebral ganglia • celiac ganglion • sup. mesent. g. • inf. mesent. g. ascend to synapse at higher level descend to synapse at lower level106 aorta Moore’s COA5 2006 Sympathetic System: Postganglionic Cell Bodies 2. Prevertebral (preaortic) ganglia • Located anterior to abdominal aorta, in plexuses surrounding its major branches • Preganglionics reach prevertebral ganglia via abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves Paravertebral ganglia sympathetic trunk (chain) Prevertebral ganglia • celiac ganglion • sup. mesent. g. • inf. mesent. g. abdominopelvic splanchnic nerve aorta 107 Moore’s COA5 2006 Sympathetic System: Summary visceral tissues (organs) Cardiopulmonary Splanchnics: postganglionic fibers to thoracic viscera somatic tissues (body wall, limbs) T1 postganglionics via 31 spinal nerves to somatic tissues of neck, body wall, and limbs sympathetic trunk Moore’s COA5 2006 Abdominopelvic Splanchnics: preganglionic fibers to prevertebral ganglia, postganglionic fibers to abdominopelvic viscera L2 prevertebral 108 ganglia Parasympathetic Pathways Cranial outflow • CN III, VII, IX, X • Four ganglia in head • Vagus nerve (CN X) is major preganglionic parasymp. supply to thorax & abdomen • Synapse in ganglia within wall of the target organs (e.g., enteric plexus of GI tract) Sacral outflow • S2–S4 via pelvic splanchnics • Hindgut, pelvic viscera, and external genitalia 109 Clinical Relevance » Surgery for colorectal cancer puts pelvic splanchnics at risk » Damage causes bladder & sexual dysfunction sympathetic motor fibers Splanchnic Nerves Greater: T5 – T9 2 Lesser: T10, T11 Least: T12 Lumbar: L1,L2 1 Pelvic: S2-S4 3 110 Greater, lesser, least splanchnic nerves Vagus n. Celiac ganglion T9 Superior mesenteric ganglion T10 T11 T12 Aorticorenal ganglion L1 L2 S2 S3 Sacral splanchnic n.s Lumbar splanchnic n.s Inferior mesenteric ganglion S4 111 Pelvic splanchnic n.s Visceral Afferents and Referred Pain Maps of Referred Pain Grant’s Atlas 11 2005 112