Atoms and Ions Bohr Diagrams
advertisement

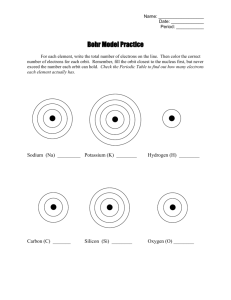
Atoms and Ions Inside the Atom http://www.chemistryland.com/CHM107Lab/Lab5/Filters/Lab5Exp2filters.html Three sub­atomic particles Protons: ­positive charge, heavy, inside nucleus Electrons: ­negative charge, very light, "orbiting" nucleus Neutrons: ­ neutral, heavy, inside nucleus Did you know If you could somehow squeeze all the space out of your body's atoms you would be smaller than a penny but still be as heavy. Bohr­Rutherford Diagrams Bohr Diagrams Ex. phosphorus ­ 31 Steps for drawing Bohr diagrams: Draw a circle for the nucleus and add the symbol • • Draw circles around the nucleus to represent electron orbits. First orbit = 2 electrons Second orbit = 8 electrons Third orbit = 8 electrons (Just Remember 2,8,8) Add dots to each orbit until the • # of electrons = atomic number=# protons. mass # 31 atomic # 15 P # of Protons = atomic number = 15 15 P 16 N # of Neutrons = mass # ­ atomic # = 31 ­ 15 = 16 Atoms are neutral because they have equal numbers of protons (+ve) and electrons (­ve). Charged ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. • Gain of electrons = negative ion = Anion • Loss of electrons = positive ion = Cation n for negative Atoms become stable ions, by gaining or losing electrons until they have 8 valence electrons (stable octet rule). (­only 2 needed for the first orbit). Example: Do not copy What must a sodium atom do to become stable? t looks like a + sign edixo edimorb .gnidne "edi" na teg snoinA :etoN negyxo .xe enimorb Na Protons Electrons +ve ­ve 11 11 Sodium Atom NOTE: Only electrons can be gained or lost, because protons are heavy, and they're stuck in the nucleus. It must either: a) Lose 1 electron or b) Gain 7 electrons Atoms become stable ions, by gaining or losing electrons until they have 8 valence electrons (stable octet rule). (­only 2 for the first orbit). Atoms become stable ions, by gaining or losing electrons until they have 8 valence electrons (stable octet rule). (­only 2 for the first orbit). Example: Example: What must a sodium atom do to become stable? Take this one away Valence electron Na Protons Electrons +ve ­ve 11 11 Sodium Atom It must either: a) Lose 1 electron or b) Gain 7 electrons Na 11 Sodium Atom It will most likely lose 1 electron Protons Electrons +ve ­ve Atoms become stable ions, by gaining or losing electrons until they have 8 valence electrons (stable octet rule). (­only 2 for the first orbit). Example: Draw Bohr diagrams for the following atoms and corresponding stable ions. Magnesium atom Magnesium ion Example: +1 We now have 1 more +ve than ­ve Na 11 Sodium Mg Mg Protons Electrons +ve ­ve 10 Sulfur atom Sulfur ion Ion S Non­metals tend to gain electrons. Metals tend to lose electrons. S electrons electrons + Non­metals tend to gain electrons. Metals tend to lose electrons. ­ 1 ­ + 18 +1 H +1 Li +1 stable 2 13 +2 +3 Be +2 Na Mg +1 K +2 Ca B +3 14 no ion C N no ion Al Si 15 ­3 ­3 P 16 ­2 O ­2 S 17 ­1 He stable Ne F ­1 Cl stable Ar Group 14 elements do not form ions. Noble gases already have 8 valence electrons, so they do not form ions.