Test 2 2014 2nd sem

Test 2 Inorganic 3
Good luck!! Hope you all do very well in the test.
25 September 2014
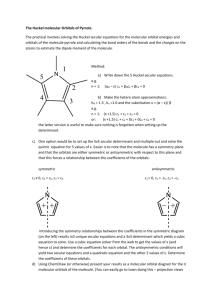
1 Discuss the three factors causing theoretical bond length to deviate from predicted bond length (6)
2
1 Multiple bonds √ : Multiple bonds are shorter than single bonds √ . Double and triple bond radii can also be defined. (N
2
triple bond 1.10 Å; N2 double bond 1.25 Å and N2 single bond
1.45 Å.
2 Hybridisation √ : Hybridisation can also affect the covalent radius since s orbitals are more contracted than p orbitals. The radius will decrease with an increase in the s character √ .
C(sp 3 ) 0.77 Å ; C(sp 2 ) 0.73 Å ; C(sp) 0.70 Å.
3 Electronegativities √ : When there is great difference in electronegativities of two atoms, the bond length is usually less than the sum of the covalent radii √ . E.g. Si-F predicted distance
1.17 Å + 0.64 Å = 1.81 Å but actual distance is 1.54 Å. C-F predicted distance 0.77 Å + 0.64 Å
= 1.44 Å but actual distance is 1.32 Å
Why is the bond angle (XAX) smaller for NF
3
than for NCl
3
as shown below? (1)
Due to the higher electronegativity of F
3 Consider the molecule, IF
2
and answer the questions:
3.1 Draw the Lewis structure of IF
2
(2)
3.2 What is the molecular geometry of the structure? (1)
1
linear
3.3 How many charge clouds are there? (1)
5
3.4 What is the hybridisation of the central atom, iodine? (1) dsp3
3.5 Is the molecule IF
2
polar or non-polar? Explain your answer by indicating the direction of the dipoles. (2)
Non polar
Arrows to be drawn from F to I and from I to the lone pairs.
Dipole moments cancel each other therefore the molecule is non polar
3.6 Is the molecule IF
2
a saturated, unsaturated, electron deficient molecule or a hypervalent molecule? Why? (2)
Hypervalent molecules: Can acquire more than an octet of electrons due to availability of dorbitals. The valence shell expands.
It can also be a saturated molecule since it does not have double bonds
4 Which two molecules, CO, or O
2
or NO are isoelectric and explain your answer. (2)
CO 4+6 = 10
O
2
: 6+6=12
NO : 5+6+1 =12
O
2
and NO - are isoelectric.
5.1 Draw the molecular orbital diagrams of NO and NO + . Show both the atomic and molecular orbitals. Remember to label the orbitals. (8)
2
5.2 Use the molecular orbital diagrams and calculate the bond orders and then predict which molecule of NO and NO + is the most stable.(3)
3
NO = 2.5
NO+= 3
5.3 Use the molecular orbital diagrams and predict for each molecule if the molecules are paramagnetic or diamagnetic. (2)
NO = paramagnetic
NO+= diamagnetic
6.1 Draw the molecular orbital diagrams of HCl. Show both the atomic and molecular orbitals.
Remember to label the orbitals. (4). non-bonding different energy levels no of electrons; filling and labels
7
6.2 Use the molecular diagram and calculate the bond order (1)
(2-0)/1=1
Why do molecules like HF and HCl have non-bonding orbitals in their molecular orbital diagrams where molecules like H
2
, Cl
2 and F
2
have only bonding and anti-bonding orbitals?
(2)
4
Electronegativity of H and halogen differs a lot, therefore orbitals have large difference in energy.
Due to the large difference in the energies of the orbitals, the s orbital of H does not overlap with s orbital of F and Cl. s orbital of H overlap with p orbitals of halogen.
8 What is an organometallic compound?
An organometallic compound contains one or more metal-carbon bond. Sometimes components containing also semi-metal-carbon bonds are also considered to be organometallic compound.
9 What is the commercial use of Triethylaluminium?
Triethylaluminium is used in the Ziegler-Natta polymerisation catalyst.
Ziegler–Natta catalysts are used to polymerise 1-alkenes
10 Why is organotin compounds added to poly vinyl chloride (PVC)?
Organotin compounds is to stabilise poly vinyl chloride (PVC)
5