Glandular Epithelium
advertisement

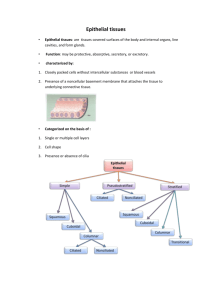
(٢)Glandular • It is a modified type of epithelial tissue specialized in • production of secretions. • It is classified : 1- According to the duct. 2- According to the secretory part. 3- According to nature of secretion. 4- According to mode of secretion. epithelium I- According to the duct * Exocrine glands: possess ducts e.g. salivary glands I- According to the duct * Endocrine glands: have no ducts and the secretion pass directly to the blood e.g. Thyroid G. Pituitary G. Adrenal G. I- According to the duct • * Mixed glands: have the two types e.g. Pancreas (B) Branching of the duct: * Simple glands possess one unbranched duct e.g. intestinal, gastric glands (B) Branching of the duct: • Compound glands have branched duct system • e.g. salivary glands. II- According to the secretory part. (A) Number of cells : • Unicellular glands: formed of a single cell • e.g. goblet cells. II- According to the secretory part. (A) Number of cells : • Multicellular glands: formed of numerous cells e.g. salivary glands, pancreas liver II- According to the secretory part. Shape of the secretory part : • * Tubular glands: have tubular secretory parts e.g. intestinal glands and liver • * Alveolar glands: have alveolar (flask shaped) or acinar (grape like) secretory parts e.g. sebaceous and mammary glands. • * Tubulo-alveolar glands: the secretory part is formed of the two types e.g. salivary glands and pancreas. Branching of the secretory part: • * Simple glands: have unbranched secretory parts e.g. intestinal glands. • * Branched glands: have branched secretory parts e.g. salivary glands, • liver and • pancreas. III- According to nature secretion • * Mucous glands: produce viscid mucous poor in enzymes e.g. goblet cells and minor salivary glands. • * Serous glands: produce watery solution rich in enzymes e.g. Parotid glands and pancreas. • * Mucoserous glands: produce both types of secretions e.g. submanibular and sublingual glands. • Sweat glands of skin produce watery secretion containing some enzymes and waste products • Oily glands: secrete fatty secretion e.g. sebaceous and tarsal glands • Waxy glands: secret waxy secretion e.g. ceruminous glands of the external canal. • Cellular glands: produce cells e.g testis and ovary VI- According to method (mode) of secretion: Merocrine glands : the secretory cells are not destroyed during secretion e.g. salivary glands. VI- According to method (mode) of secretion: Apocrine glands : the apical part of the cells is destroyed during secretion e.g. mammary glands. VI- According to method (mode) of secretion: Holocrine glands: the whole cell is destroyed during secretion e.g. sebaceous glands. (3) NEUROEPITHELIUM • Definition: • A modified type of epithelial tissue specialized for receiving of sensory stimuli. (3) NEUROEPITHELIUM • SITES: Taste buds Olfactory epith. Organ of Corti Crista ampularis Macula sacculi, utriculi