The Directorate general for civil aviation
advertisement

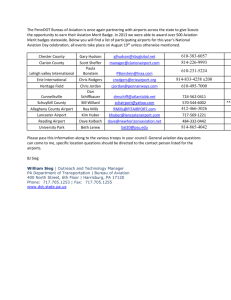
The Directorate general for civil aviation ROLE DGAC, the French Civil Aviation Authority (DGAC) is responsible for ensuring the safety and security of French air transport, as well as maintaining a balance between development and environmental protection. On one hand is a regulatory authority, but it also supervises safety, provides air navigation services and training and it is a partner of key players in the aeronautics industry. It is in charge of financial aid for research in aircraft construction and State industrial policy in this sector. In charge of safety and security Maintaining high safety and security standards in the air transport sector is one of the DGAC’s constant concerns. It is in charge of monitoring industrial players, operators and flight crew. Service provider The DGAC provides services for airline companies and general aviation. It provides air traffic services, through its en-route control centres and air traffic control towers. Market regulator The DGAC plays an active role in economic and social affairs. It acts as France’s air transport regulator. It is the key representative of airline companies, airports and their customers. Partner of the aeronautics industry As a partner of industrial manufacturers and operators, the DGAC closely monitors activity in the aeronautics industry. It implements a policy designed to support this key sector in the French economy thanks to research subsidies and repayable advances. Actions for the Ecologial transition The DGAC takes action to reduce pollution, especially noise and air pollution, generated by air transport. It is involved in minimising pollution and maintains dialogue with local elected officials and the representatives of residents which live in proximity to airports. At the heart of international action The environment of civil aviation is highly international and European. The DGAC is involved in defining and defending France’s position within the international bodies. It plays an active role in constructing the Single European Sky. This project aims at harmonising air traffic management across the whole Europe with a view to improving safety, while reducing costs, delays and CO2 emissions. Ministry of Ecology, Sustainable Development and Energy www.developpement-durable.gouv.fr DGAC ORGANISATION Directorate general for civil aviation Air transport gendarmerie Directorate general for civil Aviation Patrick GANDIL Staff cabinet Flight Control Organisation Deputy director-general Paul Schwach Light, general and helicopter aviation service Directorate for air navigation services 9 metropolitan interregional directorates (7 métropoles) Technical and innovation directorate Directorate for air transport Civil Aviation Technical Department Operations directorate DSAC West Indies-French Guiana 4 CRNA area control centres 9 metropolitan airports regional structures (SNA) SNA West Indies-French Guiana SNA Indian Ocean CESNAC (central air navigation systems operations centre) SIA (aeronautical information services department) SAC Saint-Pierre and Miquelon DSAC Indian Ocean General secretariat Airport Taxes Management department National airport engineering department Modernisation and IT department National School of Civil Aviation SEAC French Polynesia DAC New Caledonia SEAC Wallis and Futuna Directorate general Headquarters Departement with national authority Decentralised units Public establishment Key Figures for the French aeronautical sector in 2012 Total DGAC workforce at 1st janvier 2013 10,963 staff, including 4,083 air traffic control officers. La navigation aérienne number of flights controlled in 2012: 2,809,461 domestic flights: 457,016 international flights: 1,077,681 overflights: 1,274,764 Economic impact (revenue in billions of euros) air transport: 24.4 (CA groupe AF-KLM 2011) airports: 3.3 (2011) (ADP + the first nine airports) industry: 38.5 (2011) up 3.3% on 2010 French airport sector number of aerodromes: 500 number of passengers: 166.91 millions (among wich 10 millions french overseas) Top 5 French airports in 2012 (in millions of local passengers) Paris-CDG : 61.38 Roissy-CDG is the first european airport in terms of movements and the second in passenger terms. Paris-Orly: 27.19 Nice: 11.78 Lyon: 8.36 Marseille: 8.17 Follow us on Twitter : @DGACfr French airlines number of licensed air carriers: 124 number of registered aircraft: 16,403 Air France-KLM is in 2012, the leading European group in terms of passenger-kilometres performed (PKP) and the world’s secondranking group in total tonne-kilometres performed (TKP). French airlines account for 3.5% of global traffic in terms of passenger-kilometres performed (PKP). Top 7 French airlines (in millions of passengers) Air France Group: 46.24 Régional CAE: 2.45 Aigle Azur: 1.85 Brit Air: 1.5 Transavia: 1.65 Air Corsica: 1.62 Air Méditerrannée: 1.34 A major source of employment (in millions of employment in 2011) airlines (85 % of these jobs are with Air France): 63,500 jobs airports managers (77 % of these are with the Aéroports de Paris Group): 10,700 jobs ground handling companies: 12,000 (excluding ADP) aerospace manufacturing sector: 162,000 jobs Directorate general for civil aviation 50 rue Henry Farman - 75720 Paris cedex 15 - France - tel.: +33 (0)1 58 09 43 21 DGAC publication / Design and realization SG-com / © S. Soriano/Air-France / DGAC duplicates may 2013 Directorate for civil aviation safety