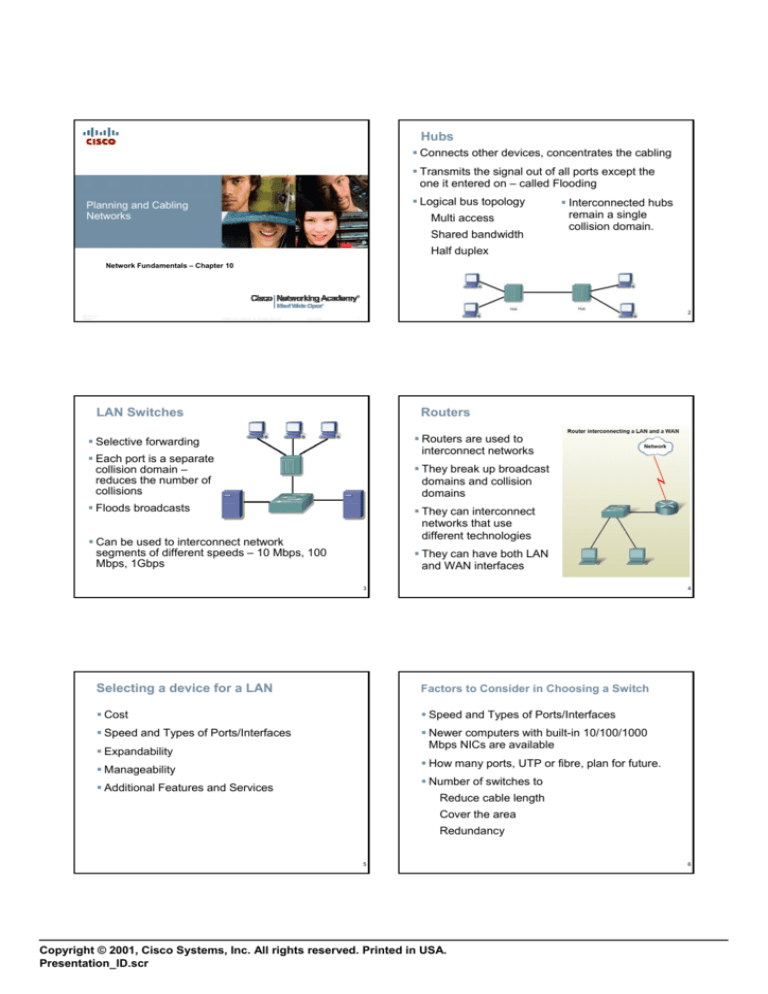
Hubs
Connects other devices, concentrates the cabling
Transmits the signal out of all ports except the
one it entered on – called Flooding
Logical bus topology
Planning and Cabling
Networks
Multi access
Shared bandwidth
Interconnected hubs
remain a single
collision domain.
Half duplex
Network Fundamentals – Chapter 10
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
2
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
1
LAN Switches
Routers
Routers are used to
interconnect networks
Selective forwarding
Each port is a separate
collision domain –
reduces the number of
collisions
They break up broadcast
domains and collision
domains
Floods broadcasts
They can interconnect
networks that use
different technologies
Can be used to interconnect network
segments of different speeds – 10 Mbps, 100
Mbps, 1Gbps
They can have both LAN
and WAN interfaces
3
4
Selecting a device for a LAN
Factors to Consider in Choosing a Switch
Cost
Speed and Types of Ports/Interfaces
Speed and Types of Ports/Interfaces
Newer computers with built-in 10/100/1000
Mbps NICs are available
Expandability
How many ports, UTP or fibre, plan for future.
Manageability
Number of switches to
Additional Features and Services
Reduce cable length
Cover the area
Redundancy
5
Copyright © 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
Presentation_ID.scr
6
Switch Redundancy
Factors to Consider in Choosing a Router
Cost and interface types.
Expandability
Media
Operating System features:
Security
Quality of Service (QoS)
Voice over IP (VoIP)
Routing multiple Layer 3 protocols
Special services, e.g. NAT and DHCP
7
8
9
10
11
12
LAN Cabling
Telecommunications room
Also known as the Distribution Facility
Contains racks and interconnection devices
May contain servers
Horizontal cabling
Also known as Distribution cabling
Connects work areas to distribution facility
Vertical cabling
Also known as Backbone cabling
Connects the distribution facilities
UTP – Basic Cabling Media
ANSI/TIA/EIA-568-B standard.
Maximum total cable length 100m.
5 meters max of patch cable for interconnecting
patch panels
5 meters max of cable from the cable termination
point on the wall to the telephone or computer
90 meters max horizontal cabling
Cross-connecting point or Patch Panel
Crossover or Straight-thru cables?
Copyright © 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
Presentation_ID.scr
Crossover UTP Cable
Pinouts: one end EIA/TIA T568A and the other
T568B
Use crossover when connecting the same type of
devices:
Switch to switch
Switch to hub
Hub to hub
Router to Router (via Ethernet port connection)
Computer to computer
Computer to a Router (Ethernet port)
13
14
LAN connectivity devices - hubs or switches - use
MDIX (media-dependent interface, crossover)
connections.
15
16
Straight-through UTP Cable
Pinouts: EIA/TIA T568A at both ends
Or EIA/TIA T568B at both ends
Use straight-thru when connecting devices via a
hub or switch
MDI (media-dependent interface) uses the normal
Ethernet pinout. Devices such as computers,
servers, or routers
WAN Connections
Serial DTE and DCE WAN Connections
WAN
Data Terminal Equipment:
V.35
Serial
cable
Also DB-60
connector
End-user’s device on the
WAN link
17
Copyright © 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
Presentation_ID.scr
Data Communications
Equipment:
End of the WAN
providers side of the
WAN link
Provides the clocking
signal
18
Network Design –
Developing an Addressing Scheme
Device Management Connection
Console port connection
Include future
requirements
Uses Rollover cable
19
Determine the optimum number of sub
networks in the larger internetwork
Count the segments between router interfaces.
20
Devise an Addressing Scheme
Why divide a network into subnets?
Manage broadcast domains
Different network requirements
Security
Addressing scheme
A unique subnet address and subnet mask for
each subnet
A range of usable host addresses for each subnet
21
10.4.1
The maximum number of hosts on one network or
subnet is calculated using the formula (2^n - 2)
where n is the number of host bits in the address
22
10.4.2
172.16.0.0 /22
23
Copyright © 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in USA.
Presentation_ID.scr
24