Planned Shortages with Back
advertisement
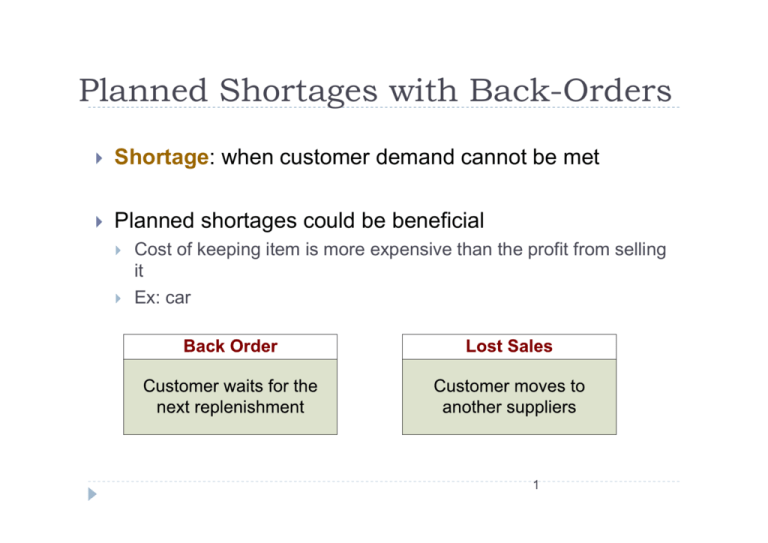
Planned Shortages with Back-Orders ` Shortage: when customer demand cannot be met ` Planned shortages could be beneficial ` ` Cost of keeping item is more expensive than the profit from selling it Ex: car 1 Customer Demands an item Alternatives for customers when their demand cannot be met from stock Customer demands an item The item is out of stock Back Order Lost Sales Customer waits for the next replenishment Customer moves to another suppliers Customer keeps all future businesses 2 Customer transfers some future business to another supplier Customer transfers some future business to another supplier Customer transfers all future business to another supplier Planned Shortages with Back-Orders Optimal order size Optimal amount to be backordered Qo = 2 × RC × D × (HC + SC ) HC × SC So = 2 × RC × HC × D SC × ( HC + SC ) Time during which demand is met T1 = (Qo − S o ) / D Time during which demand is back-ordered T2 = S o / D Cycle time T = T1 + T2 3 Ex 4: Back order Demand for an item is constant at 100 units a month. ` Unit cost is $50 ` Reorder cost is $50 ` Holding cost is 25% of value a year ` Shortage cost for back order is 40% of value a year Find an optimal inventory policy for the item 4 IM 322 Inventory Management Chapter 5 Models for Uncertain Demand -5- Textbook: Donald Waters, Inventory Control and Management, 2nd ed Chapter Outline ` ` ` ` ` ` Uncertainty in inventory management Variables that take uncertain value Probabilistic models for inventory model Uncertain demand Uncertain lead time Service level / safety stock 6 Areas of Uncertainty For example ` Changes in customer demand during leadtime ` Price uncertainty ` Operations change ` New products ` Disrupted supply chain ` Trading conditions ` etc 7 Uncertain Demand Inventory level Q Reorder point, R 0 LT LT Time 8 Lead time demand ` ` ` ` Inventory level Uncertain Demand – Safety Stock Buffer added to on hand inventory during lead time Extra reserved stock To prevent stockout under Q Reorder uncertain demand point, R Safety stock will not normally be used, but it is available under uncertain demand 0 How much safety stock should we hold? Judgment on service level 9 Safety Stock LT Time LT Service Level 10 Service Level Several ways of measuring the service level ` Percentage of order completely satisfied from stock ` Percentage of units demanded that are delivered from stock ` Percentage of units demanded that are delivered on time ` Percentage of time there is stock available ` Percentage of stock cycles without shortages ` Percentages of item-months there is stock available 11 Reorder Level Inventory level Reorder Reorder Level Level (ROL) (ROL) Reorder Reorder Level Level (ROL) (ROL) == == LT LT xx D D (LT (LT xx D) D) ++ Safety Safety Stock Stock Q Reorder point, R Safety Stock 0 12 LT Time LT Reorder Point for a Service Level Probability of meeting demand during lead time = service level Average demand during lead time Probability of a stockout Safety stock zσ LT Demand 13 R Reorder Point with Uncertain Demand ` Reorder point with safety stock ` Service level = probability of NO stockout σL ROL = (LT × D ) + zσ LT d = average demand L = lead time σ t = standard deviation of demand Standard deviation during leadtime Safety Stock z = number of standard deviations correspond ing to the service level probabilit y zσ t 14 L = safety stock Ex 1: Uncertain Demand PM Computers assembles microcomputers from generic components. It purchases its color monitors from a manufacturer in Taiwan. There is a long lead time of 25 days. Daily demand is normally distributed with a mean of 2.5 monitors and a standard deviation of 1.2 monitors. Determine the safety stock and reorder point corresponding to a 90% service level 15 Ex 2 Uncertain Demand ` ` ` ` ABC company finds that demand for an item is normally distributed with a mean of 2,000 units a year and standard deviation of 400 units. Unit cost is $100, reorder cost is $200, holding cost is 20% of value a year and lead time is fixed at 3 weeks. Describe an ordering policy that gives a 95% service level. What is the cost of safety stock? 16








