Define Key Points SIPOC Measure Key Points Patient Value Stream
advertisement
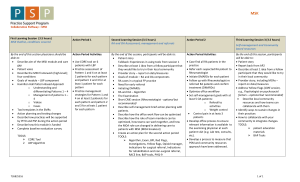
Team Leader: Eric Goodman Team Sponsor: Jason Spaulding Team Coach: Yvonne Cheung Team Members: Heather LaPorte, Nanci Adams, Paula Hebert Douglas Goodwin J. Allen Graham Project Information and Background Fluoroscopic-guided MSK (Musculoskeletal) procedure are procedures in which patients are imaged using a fluoroscopic system while a needle is used to access the joint space either for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. We perform these procedures in Diagnostic Radiology daily, and felt that we could improve the efficiency of our workflow. The number of MSK Procedures is currently high and growing and it is important to be able to provide service to patients in a timely manner Key Project Goals• Timely appointments without a long wait time • Shorter duration of individual exam time • Decrease the Physician time per procedure to allow for reading more examinations • Standardizing workflow and supplies to optimize technologist time, and simplify examination procedure By using the DMAIC process, we identified some root causes to prolonged total procedure time. We streamlined workflows by: • Implementing standardized trays • Standardized documents • Limiting parallel scheduling conflicts by assigning a dedicated room for MSK procedures DMAIC Define Key Points SIPOC • Project purpose and scope • Obtain Info about process and customers • Statement of the problem Fluoroscopic-Guided MSK procedures were felt to take too long. Suppliers • Patient • Secretary • Schedulers • Radiology Technologist • Radiology Resident • Radiology Attending • Orthopedics By reducing cycle time, it was hoped to lessen patient’s time in the department. This in turn will create increased access, and improved ability for the department to accommodate add-on requests Measure Key Points Situation Determine process performance vs. requirements Summarize data regarding current process The average patient spends: 63 minutes in 3T 21 minutes in the waiting room 38 minutes in the procedure room 10 minutes with the physician 6 minutes having the MSK procedure Analyze Key Points Determine potential root causes Confirm root causes with data Provide focused problem statement 4 key root causes: • Patient Communication • Procedural Issues • Clinic Communication • Space Inputs Process • Order • Demographic Info • Medications • Physician availability • Register at Front Desk • Prepare Room for patient • Patient Brought to Room • Consent Patient • Position Patient • Perform Procedure • Give After Care instructions Outputs Customers • Treated Patient • Fluid for lab study • Patient • Orthopedics Patient Value Stream Map Check In Waiting Room Tech Pre-Procedure Work Rad Consent Tech Post-Procedure Work Patient Positioning Procedure Cycle Time 0:03:18 0:20:30 0:03:00 0:04:18 0:04:36 0:05:42 0:00:54 Process Time 0:04:24 0:20:30 0:07:24 0:04:18 0:04:36 0:14:30 0:07:18 Fishbone Diagram PATIENT COMMUNICATION PROCEDURAL ISSUES No standard positioning guide for techs Lacking commonly requested supplies in room Patient Mobility Issues Proper supplies not put on trays Radiologist and Tech having duplicate conversations Incorrect forms given to patients by reception (e.g. contrast sheets) Lack of standardized consent Various attending preferences Patient does not understand changing instructions, and is not properly undressed for the procedure Referring Provider orders incorrect examination or wrong side Referring Provider does not order labs (for aspirations) Prolonged Patient Time in Fluoroscopy No dedicated MSK room/ no “overflow” space to accommodate addon cases. CLINIC COMMUNICATION GI/GU Procedures run long Slow room turn-over SPACE Improve Key Ideas Control Key Ideas • Standardized work & documents • Education of support staff • Dedicated MSK procedure room • New C-arm to allow for “overflow” into a non-fluoro room • Switch to “OR-style” clean-up process • Standardized pre-made procedure trays Maintain gains by standardizing process Create feedback systems Monitor control plan • Monitor system with repeat observation • Allow the technologists, schedulers, and secretaries to become owners of the improvement process. • Use PDSA cycles to target areas of continued concern or weakness in the process Develop potential solutions Test solutions Develop future state Actions eliminate or reduce impact of the identified root cause