Product Mix Strategies
advertisement

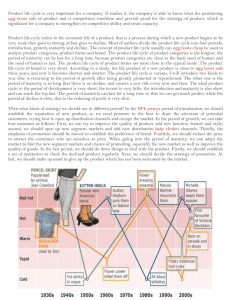
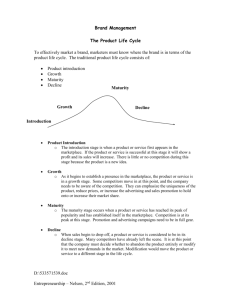
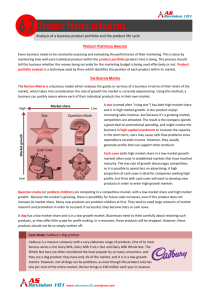
Product Mix Strategies Project #3 :: She Sells Cell Phones at the Cell Store Product Mix and Product Line § The product mix is the set of all products offered for sale by a company. § A product mix has two dimensions: § Width Width - the number of product lines carried. § Depth - the variety of sizes, colors, and models offered within each product line.. § § A product line is a broad group of products, intended for similar uses and having similar characteristics. Expanding the Product Mix MixMix-extension strategies include: § Same brand, related product (Tim Horton coffeemaker) § Same brand, unrelated product (Swiss Army watch) § Different brand, unrelated product (Pepsi & KFC) § Different brand, related product (P&G adds Luvs diapers; already makes Pampers) Trading Up and Trading Down § Trading up: Adding a higher-priced product to a line to attract a higher-income market and improve the sales of existing lower-priced products. § Trading down: Adding a lower-priced item to a line of prestige products to encourage purchases from people who cannot afford the higher-priced product, but want the status. Other Product Mix Strategies § Alteration of Existing Products: § Improve an established product with new design, new package, new uses. § ProductProduct-Mix Contraction: Contraction: o Eliminate an entire line or reduce assortment within it. o Pruning to reduce similar brands. o Dump unprofitable or indistinct brands. The Product Life Cycle § the concept of the product life cycle applies to product categories, not to brands; it is related to the concept of diffusion of innovation § different products will have differently-shaped life cycle curves; will diffuse at different rates § a product is normally perceived to pass through four stages over its life cycle; introduction, growth, maturity, and decline § each stage requires different marketing strategies Product Life Cycle Stages § Introduction—most risky and expensive. Introduction § Growth—both sales and profits rise, often rapidly. Growth § Maturity—sales increase at a decreasing rate and profits decline. Maturity § Decline Decline—demand drops, often because of another product development. Strategic Implications of the Stages § introductory stage: developing the market, creating awareness, reaching the innovators § growth stage: competition begins, sales grow quickly, profits peak, market penetration § maturity stage: competition is intense, sales slow down, differentiated product offerings, customers are brand loyal, few new entrants § decline stage: customers move to other options, competitors leave, profits are low, consider exit Characteristics of Life Cycles § § § § § length of the life cycle will vary across markets; some are quite short and may be getting shorter some fads have very short life cycles, while other products stay at maturity for years in high-tech markets, life cycles are very short some products do not make it through all four stages; they may fail in introduction the life cycle must be considered in relation to a specific market; stage may vary across markets Managing the Life Cycle Successful life-cycle management requires predicting the shape of the curve and then successfully adapting strategies at each stage. § when to consider entering the market § how to manage to capitalize on growth § it is possible to develop strategies that will extend the maturity stage; modify the product, devise new uses, or design new appeals § greatest challenge comes at the decline stage which may result in product abandonment Planned Obsolescence Fashion and Style Planned Obsolescence: § Technological or functional obsolescence; other things do it better now. § Style obsolescence: Still serviceable, but looks out of date now. Style: § A distinctive manner of construction or presentation in any art, product or endeavor. Fashion: § Any style that is accepted and purchased by successive groups of people over a long period of time. Fashion-Adoption Process § Series of buying waves as a given style is popularly accepted by one group after another. § Three theories of fashion adoption: § Tricklegiven fashion flows down through several socioeconomic levels. Trickle-down—a down § Trickle -across—the fashion moves horizontally and simultaneously within several Trickleacross socioeconomic levels. § Tricklestyle first becomes popular at lower levels and then flows upward. Trickle-up—a up