the marketing mix
advertisement

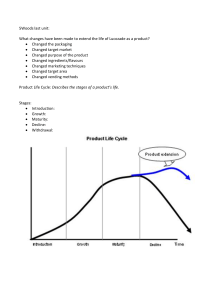
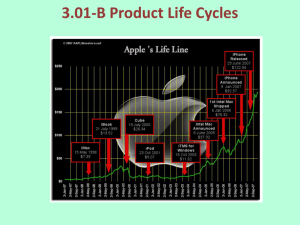
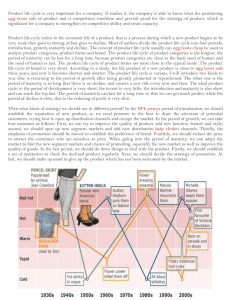
THE MARKETING MIX HIGHER BUSINESS MANAGEMENT • This is often referred to as the 4 Ps! 1. 2. 3. 4. Product Price Place Promotion • Each of these factors will influence the customer buying a product. PRODUCT • This is the good or service that the customer will buy. • It must meet the needs of the customer, both actual and potential. • A PRODUCT MUST BENEFIT THE CUSTOMER. CORE PRODUCT • The basic benefit of the product. PRODUCT Shampoo Trainers Video Recorder BASIC FUNCTION To clean hair To protect feet To record TV programmes ACTUAL PRODUCT • Most products are not bought to meet just a single need. • There are a number of factors which make up a product concept. • Will have characteristics such as brand name, design and packaging. AUGMENTED PRODUCT • Producers often add an element of attraction to their product to gain a competitive edge. • Additional features include: – – – – – – High after sales service 0% credit terms Style Colour Quality Brand name PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE • Markets are constantly changing due to – – – – Technology Fashion Politics Economics • Because of this products become obsolete eventually. • Every product will go through a number of stages over a period of time. • From the birth of the product until the end of it’s life. • Some products will have a short life cycle e.g. Pop Record • Others will have a very long life e.g. Mars Bars, Coca Cola. Sales DECLINE SATURATION MATURITY GROWTH INTRODUCTION R&D Time RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT • At this stage of it’s life the product is not yet on the market. • There are no sales and the product is probably making a loss for the firm. INTRODUCTION • This is when the product is first put onto the market. • Sales are low because there is limited customer awareness and brand loyalty for other products. • Cost are also high at this stage due to heavy advertising and holding stocks. GROWTH • Sales at this stage are increasing quickly. • There is heightened awareness of the product. • At this stage the product is making it’s highest amount of profits due to little competition. MATURITY • More and more competition is coming on to the market. • Sales begin to slow down. Price is likely to be cut to attract customers. SATURATION • Here there is lots of competition that the market is flooded with similar products. • Sales will begin to dip. • Supply will outstrip demand. DECLINE • At this stage the product the product is not fashionable, becoming obsolete. • Everyone has one and there are new and better products on the market. • Sales fall away as does profits. PRODUCTS AT DIFFERENT STAGES R&D Introduction Maturity Saturation PS3 Games PS3, Iphones, Blue Ray DVDs Video Mobiles, Recordable DVDs MP3 Players, IPODS DVD Players Decline Video Recorders Growth EXTENDING THE LIFE CYCLE • Not all products will go into decline. • Some companies will alter elements of the marketing mix in order to inject new life into a old product. STRATEGIES • Changing the product – shape, size, colour e.g. diet drinks • New variants – fun size • Altering the package to appeal to a different segment of the market. E.g. Pepsi cans to blue • Altering where the product is sold, e.g. selling online • Changing the price • Altering the advertising or promotions e.g. special offers, free gifts. • Changing the use of the product e.g. Luzocade • Change the name of the product. Extension Strategies Sales Time PRODUCT MIX/PRODUCT PORTFOLIO • This is a range of products that a firm may have. • E.g. – Cadbury – chocolate sweet range – Virgin – records, banking, insurance, flights. • By having a range of products you can spread the risk. • If they had only one product and that failed, the firm would be in trouble. • Wide range means that you can target different market segments, which can also increase profits. • A firm may introduce a new product just as an older product is going into decline. • This way they will always have products at the various stages of the Product Life Cycle. Sales Product 3 Product 2 Product 1 Time BOSTON MATRIX • This is used by some firms to look at their product mix. • It places products into one of four categories. • These categories are based on: • The market share each product has – ie the percentage of the market they hold. • and • Market Growth – the potential for the product to experience growth in it’s market. MARKET SHARE MARKET GROWTH HIGH LOW HIGH STAR PROBLEM CHILD LOW CASH COW DOG • Firms want to have a few problem children. These are products that have a low market share but there is potential for growth. • Firms want a lot of stars, products with both high market share and high market growth. • They want a few cash cows, where the market share is high but there is not a lot of potential for growth. MILK THE CASH COW. • And no or very few dogs, these products do not make a lot of money. PUT DOWN DOGS. PRODUCT INNOVATION • Coming up with new products is extremely important for businesses, to replace those going into decline. STAGES • • • • • • Generation of the idea Analyse the idea (will customer buy?) Produce a prototype and test it Test market Adapt and review Launch • There is a high failure rate with product innovation. • Only 1 in 50 are successful! • A lot of time and money is spent on producing new products. BENEFITS TO R&D • New products developed give a competitive edge. • Can develop new production techniques • Improve efficiency and productivity which reduces costs • May gain a patent which gives you a competitive advantage • Staff are highly motivated as they are allowed to be creative.