Enzyme Activity Worksheet: Biochemistry Foldable
advertisement

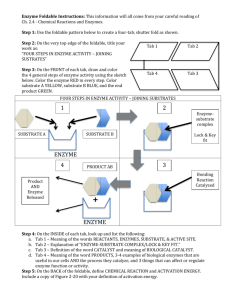
Biochemistry Name: ___________________________________ Period:_____ Enzyme Foldable Instructions Steps: 1. To create your foldable: Fold the paper in half with a hamburger fold and then a hot dog fold. Open the paper up. Fold the bottom edge of the paper to the center crease. Fold the top edge of the paper to the center crease. Cut the hot dog crease to create four flaps that open for your four-tab foldable! 2. On the FRONT of each tab, draw and color the 4 general steps of enzyme activity using the sketch below. Color the enzyme RED, substrate A – YELLOW, substrate B – BLUE, and the product GREEN. SUBSTRATES ENZYMESUBSTRATE COMPLEX 3 1 2 4 3. On the BACK of each tab, list the following: a. Tab 1 – Meaning of enzyme, substrate, & active site b. Tab 2 – Factors that affect enzyme action c. Tab 3 – Sketch the Energy Releasing Reaction (figure 2-20) graph on page 51 d. Tab 4 – Sketch the Energy Absorbing Reaction (figure 2-20) graph on page 51 4. On the CENTER FOLD, write ENZYME CHARACTERISTICS and then bullet each of these answers: a. Are enzymes reusable or NOT reusable? b. Are enzymes specific or NOT specific? c. What effect does an enzyme have on activation energy? What happens to the reaction as a result? d. What is meant by active site? e. What is the effect of an enzyme on activation energy? f. Explain induced fit (lock and key). g. Why are Enzymes important to living things? h. List 3 factors that can affect enzyme activity. i. What would adding a strong base or acid to do an enzyme catalyzed reaction? j. What is meant by the term substrate? Biochemistry Name: ___________________________________ ENZYME PRACTICE Period:_____ Word Bank: Active Site, Product, Enzyme, Substrate, Enzyme-Substrate Complex Label the diagram e The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions. Complete the chart by writing a strategy to help you remember the meaning of each term. One has been done for you. Term Definition How I’m Going to Remember the Meaning Activation energy Catalyst Chemical reaction Enzyme Product Reactant a) b) c) d) e) Are enzymes reusable or NOT reusable? Are enzymes specific or NOT specific? What effect does an enzyme have on activation energy? What happens to the reaction as a result? What would adding a strong base or acid to do an enzyme catalyzed reaction? The word act is found in the word reactant, and during a reaction, the reactants act together to form the products.