Imposter versus other types of unconformities. An unconformity
advertisement

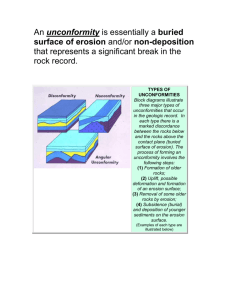
Imposter versus other types of unconformities. An unconformity surface is a contact between rocks of significantly different ages. An unconformity develops from either non-deposition or erosion of older rocks before the deposition of younger ones. An unconformity takes a long period of time for its development; but that time is commonly shorter than the time gap estimated from the ages of rocks bounding the unconformity surface. Yet, in the case of an unconformity which is developed by nondeposition the disconformity may have the same time for its development as the gap in time estimated from the rocks bounding the unconformity surface. One that takes short period of time for its development and which is limited to a sedimentary sequence is called a diastem or non-sequence. An imposter unconformity is not a diastem, for it requires uplift erosion and denudational faulting, but takes a shorter duration for its development than the conventional unconformity (e.g., angular unconformity or nonconformity) does. (continued in the next page) Imposter versus other types of unconformities (continued) 1). Suppose the ages of rocks A and B bounding an unconformity surface are 800 (A) and 200 (B) million years old. The gap in time between A and B represents 600 (800200) million years of missing record. However, the development of an unconformity (involving uplift, erosion and weathering followed by subsidence, or nondeposition) might have taken a 100 million years, which is much less than the 600 million years time gap suggested by the ages of rocks bounding the unconformity surface. 2) Suppose there is a fault contact between rock A and rock B, and the (denudational) faulting occurred 200 million years ago. Though there is a gap in age of 600 million years between the two rocks, the contact between A and B did not take 600 million years to develop. May be it lasted less than 10 million years. Such is the nature of faults that juxtapose rocks of different ages comparatively rapidly. (continued on the next page) 1 Imposter versus other types of unconformities (continued) 3) Suppose an unconformity surface is traceable to a fault, such as the surface of a rollover anticline on a listric (denudational) fault, the combined (fault plus surface on rollover anticline) surface is called an imposter unconformity. Sediments would lap on the fault surface (buttress unconformity). Sedimentary layer may lie nearly parallel to the rollover anticline surface (nonconformity or disconformity). Similar to an angular unconformity, the development of an imposter unconformity involves uplift, erosion and subsidence (by denudational faulting). Since the subsidence is by faulting, the development of an imposter unconformity takes much shorter time than and the geometry of rocks about the imposter unconformity is different from that of an angular unconformity. The significance of identifying an imposter unconformity is the recognition of the much shorter duration of time taken for the juxtaposing of rocks of different ages (e.g., rocks A and B). It follows that the geologic history of a region must be examined in detail before determining if nonconformities and disconformities might not be part of an imposter unconformity. Imposter versus other types of unconformities (continued) The subsequent pages develop the concept of missing record and unconformities by using yearbooks as examples 2 Menz High Yearbook: Missing & Incomplete Record Yearbook 1973 Menz High 1972 Menz High 1971 Menz High 1960 Menz High unconformity 1959 Menz High 1958 Menz High 1957 Menz High ß Each yearbook is an incomplete record, for it does not contain all school activities of a year. ß Yearbooks 1961 through 1970 are missing = Unconformity. Is the record for1961-1970 missing because yearbooks were not prepared for these years, or because they were destroyed? ß Is there necessary and sufficient data to make valid inferences. For example, can we determine the ratio of black/white soccer players, if that were what a study involved. 1990 McBride High at Gatwick 1989 McBride High at Gatwick 1988 McBride High at Gatwick Imposter Unconformity 1987 McBride High at Gatwick 1986 McBride High at Gatwick 1960 McBride High upon Perth 1959 McBride High upon Perth At Gatwick In 1985, pursuant to a decision to relocate McBride High, the mayor of McBride City lifted old yearbooks, threw away younger ones (1961 through1984) from McBride High upon Perth, and placed only the 1959 & 1960 yearbooks at Gatwick. In subsequent years, yearbooks from McBride at Gatwick were placed on top of those as they were published. 3 Summary 1) The process represented by an unconformity might be much shorter in duration than implied by the ages of rocks on either side of an unconformity as in the analogous case of McBride High. Such an unconformity is called an Imposter Unconformity 2) Discussion on imposter unconformity alerts us to pay attention to geologic processes at a locality, rather than to emphasize on the ages of rocks on either side of the unconformity. 3) Good examples, such as using yearbooks, enable the student to grasp the difficult idea of unconformity. 4) Incomplete or missing record when viewed globally may contain necessary and sufficient data for a particular study. Foreword to subsequent pages Photographs of the angular unconformity at Siccar Point, all kinds of unconformities at the Grand Canyon, and the nature of an imposter unconformity is provided with the aid of photos and sketches of Death Valley. 4 Angular Unconformity: Siccar Point, Scotland Devonian Old Red SS Silurian Turbidites Hutton’s impact: Shattered a belief that Earth was created 4004 BC. Unleashed human thought to ponder vast time with its immense possibilities. Grand Canyon. View from Tonto Plateau,Arizona across the Colorado to Utah. Mississippian Dis. Cambrian Non. Angular Grand canyon Supergroup. 715-1,250 MA Imposter Vishnu and Zoroaster. 1,400 to 2,000 MA Unconformities : Angular, Disconformity (Dis.), Nonconformity (Non.), and Imposter Unconformity 5 Death Valley, CA. View of Black Mountains from Panamint Range. Imposter Unconformity surface between Precambrian wall rock and Cenozoic sediment fill. Death Valley is a Pull-apart basin formed subsequent to uplift, erosion, and denudational faulting that propagated westward from Spring Mountains.. USGS Photo. Bahada on Panamint Range, western boundary of Death Valley. Contact between Precambrian and overlying young sediments is an imposter unconformity. Ocoee likely is submarine equivalent. 6 R S Q P R H G F E D C D B Q C B A a. Angular unconformity P A b. Disconformity T T S R S Q c. Nonconformity R Q P d. Imposter unconformity Conclusion 1) An imposter unconformity represents a missing record, which is much shorter in duration than the gap in age estimated from rock ages bounding the unconformity surface. 2) When a surface separates rock layers in obvious discordance (fault-like) on one side of an inferred depositional basin, and its continuation appears to be a nonconformity, that surface is an imposter unconformity. For further discussion go to the following URL http://www.utc.edu/Faculty/Habte-Churnet/ImposterU-Short.pdf 7