Homework Review Pg. 190 #1-8 , 4 ways to determine absolute age
advertisement

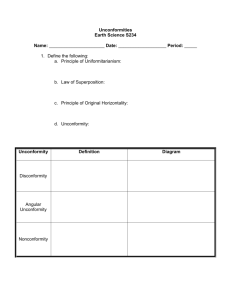
Homework Review Pg. 190 #1-8 , 4 ways to determine absolute age HW pg. 190 #1-8 1. Why is it important for scientists to be able to determine the relative age of rocks? So that they can understand the age and history of the Earth. What events came before and after one another. 2. State the principle of uniformitariansm in your own words. The same processes and events have occurred throughout time in the same way. HW pg. 190 #1-8 3. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of sedimentary rocks. HW pg. 190 #1-8 4. Explain the difference between an unconformity and a nonconformity. -An unconformity is any break in the geological record -A nonconformity is a type of unconformity where Metamorphic or igneous rock layers are covered with layers of sedimentary rock Nonconformity: part of the geological record are missing HW pg. 190 #1-8 5. Compare an angular unconformity with a disconformity. HW pg. 190 #1-8 6. Describe how the law of crosscutting relationships helps scientists determine the relative ages of rocks. HW pg. 190 #1-8 7. Which would be more difficult to recognize: a nonconformity or a disconformity? Explain your answer. A disconformity would be harder because it has horizontal layers of sedimentary rock on both sides of the boundary. A nonconformity can be identified by the presence of metamorphic or igneous rock below the unconformity HW pg. 190 #1-8 8. Crosscutting relationships. HW. 4 ways to determine absolute age of rock formations Rates of erosion • study erosion rates today (principle of uniformitarianism), should be similar to past rates •for newer formations (past 10,000-20,000 years) Rates of deposition •average about 30 cm of sedimentary rock deposited over 1,000 years • not all sediments deposited at an average rate (e.g. storms) HW. 4 ways to determine absolute age of rock formations Varve count: annual layers can be counted Usually form in glacial lakes Coarse summer layer covered by fine winter layer HW. 4 ways to determine absolute age of rock formations Radiometric dating. Use the known rate of radioactive decay to estimate age of rocks by their composition • decomposition of isotopes of an element