Rules for Determining Geologic Sequence
advertisement

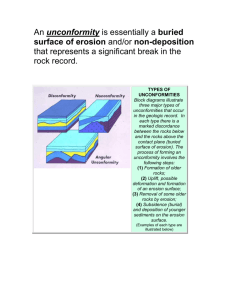
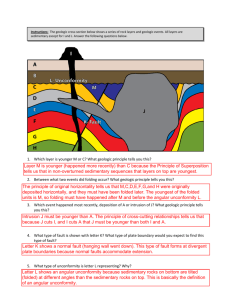
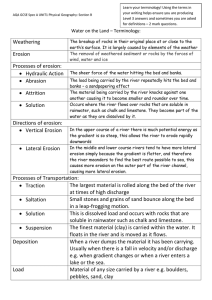
Lab 5-1: Sequence of Events Rules for determining the proper sequence of events for the reconstruction of a period of geologic history Relative age…. • Geologic event sequences are often ordered using relative time. • Relative time simply refers to whether some event is older or more recent than another event with little concern for the actual chronological age (actual age in years) Unconformity…. • An unconformity is a break in the sequence of the relative time scale… • Part of the record in the rock has been removed by erosion. 5 3 2 1 Erosion Surface... • The surface which is the boundary between 2 non-sequential layers where a layer is missing is most often an erosion surface. 5 3 2 1 Subsidence... • Refers to the sinking of land, often below sea level. Subsidence... • Refers to the sinking of land, often below sea level. Uplift... • Is the rising of the land above sea level Emergence and Submergence • Emergence refers to the land coming from below the sea to above sea level due to a lowering of sea level • Submergence refers to the sinking of the land below sea level due to a rise in sea level Uniformitarianism... • “The present is the key to the past” Superposition... Original Horizontality.. • When first deposited, rocks are laid down in flat horizontal layers. If they are tilted, folded, broken (faulted) or intruded into, those events took place after the rocks were laid down in their horizontal position.