AP Biology Enzyme Catalysis Inquiry Lab Backgro
advertisement

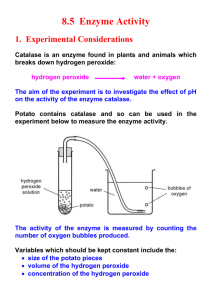
Name: ________________________________________________ Date: ___________________ AP Biology Enzyme Catalysis Inquiry Lab Background: In general, enzymes are proteins produced by living cells; they act as catalysts in biochemical reactions. A catalyst affects the rate of a chemical reaction. One consequence of enzyme activity is that cells can carry out complex chemical activities at relatively low temperatures. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substance to be acted upon (the substrate = S) binds reversibly to the active site of the enzyme (E). One result of this temporary union is a reduction in the energy required to activate the reaction of the substrate molecule so that the products (P) of the reaction are formed. E + S ES E + P Note that the enzyme is not changed in the reaction and can be recycled to break down additional substrate molecules. Each enzyme is specific for a particular reaction because its amino acid sequence is unique and causes it to have a unique three-dimensional structure. The active site is the portion of the enzyme that interacts with the substrate, so that any substance that blocks or changes the shape of the active site affects the activity of the enzyme. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a common but poisonous by-product of cellular metabolism, but H2O2 does not accumulate in cells because it is decomposed to water and oxygen gas. The decomposition of the hydrogen peroxide is mediated by catalase, an enzyme present in most cells. The balanced equation for the reaction is 2H2O2 -----> 2H2O + O2. One molecule of catalase can catalyze the decomposition of approximately 4 x 107 molecules H2O2 per second! The enzyme used in this lab – catalase – has four polypeptide chains, each composed of more than 500 amino acids. This enzyme is found throughout aerobic organisms. One function of catalase within cells is to prevent the accumulation of toxic levels of hydrogen peroxide (formed as a byproduct of metabolic processes). Catalase may also take part in some of the many oxidation reactions that occur in all cells. The primary reaction catalyzed by catalase is the decomposition of H2O2 to form water and oxygen: 2H2O2 2H2O + O2 (gas) In the absence of catalase, this reaction occurs spontaneously, but very slowly. Catalase speeds up the reaction considerably. In this experiment, the rate of reaction will be indirectly measured. The assay system used in this lab consists of a filter paper disk that is coated with the enzyme and then dropped into a cup of substrate (hydrogen peroxide). As the catalyst breaks down the hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas, the bubbles of oxygen collect underneath the filter paper disk and make it rise to the surface of the hydrogen peroxide. The time it takes for the filter paper disk to rise (from the bottom of the cup) is an indication of the rate of enzyme activity. 1|Page RATE ENZYME ACTIVITY = DISTANCE DEPTH OF HYDROGEN PEROXIDE IN MM/TIME IN SEC We will assume that each filter disk is coated with the same amount of catalase (except in the investigation of the effect of enzyme concentration of enzyme activity). Safety: You will be using glass, hot water, acids, and bases. Use caution and wear goggles. Directions: You will be working with your lab partner to design an experiment to test the activity of the enzyme catalase. At this point, you should be well-versed in the following: The general functions and activities of enzymes The relationship between the structure and function of enzymes The concept of initial reaction rates of enzymes In general, how environmental changes (changes in temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, salt concentration, and substrate concentration) might affect the reaction rates and efficiency of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Basic Catalase Assay Procedure: (use this as a reference for how to set up your basic protocol): 1. Prepare catalase using mortar and pestle, strainer and distilled water 2. Pour 20 mL H2O2 into a 25 mL graduated cylinder (or a tall cup with mm markings) 3. Pick up 1 filter paper disc with forceps 4. Soak the filter paper disc in catalase solution for 5 seconds and then air dry 5. Drop disc into graduated cylinder and start stopwatch as soon as the disc hits the surface of the H2O2 6. Stop the stop watch when the disc reaches the top of the liquid in the graduated cylinder 7. Measure the total distance in mm the disc travels Note: use the mL markings as if they were mm Note: for some of the trials, the disc may not reach the bottom of the cylinder! Note: total distance is distance the disc travels down and back up! 8. Record the time in seconds 9. Calculate rate as mm/s (Note: the disc traveled 20 mL down and then 20 mL back up to the surface!) 10. Repeat 3—5 times and calculate average rate You will need to work with your partner to prepare and run a detailed experiment testing the effect of something on enzyme activity. You will need to decide what variable you will be manipulating (such as temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, substrate concentration, salinity, or another that requires prior teacher approval). 2|Page Basic Lab Report Format: Problem (in the form of a question) Hypothesis (in the form of a statement) Dependent variable (the data you will collect) Independent variable (what you will be manipulating) Standardized variables (list at least 4 factors that must be kept equal in all treatments) Levels of treatment (values set for the independent variable) Control treatment (independent variable either eliminated or set to standard value) Materials list Protocol (be extremely specific, so another could read your report and completely replicate the experiment) Observations, Data Table(s), & Graphs Analysis Conclusion Questions to ponder o Construct 5 questions that you would ask someone who repeated your lab protocol to see if they understand what the lab tested and the results that were achieved. Then prepare answers to those questions. Experimental Research Proposal Form attached (each person needs their own) The final lab report must be typed. Laptops will be available in the classroom for this purpose. The lab groups are partner teams. You may not perform the same experiment as the other team at your table. Anticipated Plan for Completion of Lab: Day One (two periods) Brainstorm ideas for lab Complete Experimental Research Proposal Form Specifically outline protocol 3|Page Day Two (one period) Collect data Day Three (one period) Analyze data Prepare lab report EXPERIMENT RESEARCH PROPOSAL FORM Teacher Approval ________________________________________________ 1. Title ______________________________________________________________________ 2. Team Members _____________________________________________________________ 3. Research Relationship (What is affecting what?) ___________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 4. Research Predication (What results do you expect?) ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 5. Hypothesis (Be specific. Include your variable, using an ”if…then…”format) _____________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 6. Experimental Design (Briefly describe the protocol) ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 7. Independent variable ________________________________________________________ 8. Dependent variable __________________________________________________________ 9. Standardized variables _______________________________________________________ 4|Page 10. Levels of treatment (how will you vary the variable?) _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 11. Title of Data Table & Graph ____________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 12. Proposed Plan to Analyze Data (In what way will you compare these numbers after you collect them?) _____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 13. Explain what results you would expect to see to support your hypothesis __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 5|Page 6|Page 7|Page