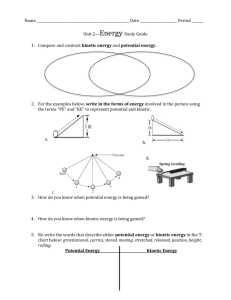
Potential and Kinetic Energy

Potential and Kinetic Energy
What is Energy?
• The ability to cause change
Energy notes entry # 4 11/5
Potential
Energy
Kinetic
Energy
Definitions
Dependent on…
Examples
Forms of
Potential Energy
Definition
• Potential Energy is stored energy. It is not energy in motion.
• Potential energy is dependent on its position
(location) and its condition
(new battery vs. used battery.)
Examples
• Batteries
• Gasoline
• Food
• Plant on a windowsill
• Acorn hanging on a tree
POTENTIAL ENERGY
• Things have energy depending on where they are
(position/ location).
The penny has LOTS of potential energy; the rock doesn’t. penny flowers rock
Empire State
Building
Common Uses
• Potential energy is stored energy so it is used to “run” many things for example
– Gasoline “runs” cars
– Batteries “run” our
toys
Common Uses
• Food is our potential energy and it helps us survive and do activities.
FORMS OF POTENTIAL ENERGY
• Chemical (food, gasoline)
• Nuclear (fusion & fission)
• Gravitational (position or place)
• Stored Mechanical (stretched rubber band)
Understanding Check
• Tell the person next to you: Why do these people have potential energy?
Choose one of the following sentence frames. Using your science journal, fill in the blanks using what you know about potential energy.
• ___________ can be described as
________________.
• Characteristics (components) of
_____________include _______________ and
__________________.
• __________ is widely acknowledged as
___________ and exhibits
_______________________.
Please grab your science journals!
Kinetic Energy
Definition
• Energy in the form of motion
• Kinetic energy is dependent on mass and speed. The greater the mass and speed the more kinetic energy the object has
Examples
• Person running
• Bicycle wheel spinning
• Frisbee flying in the air
KINETIC ENERGY
Things have energy depending on how fast they move .
Which has more kinetic energy?
FORMS OF KINETIC ENERGY
• Sound
– Travels in waves, JUST LIKE IN THE OCEAN
– Has to have something to travel through.
Energy traveling through AIR
FORMS OF KINETIC ENERGY
• Radiant
– Also travels in waves
– DOESN’T need anything to travel through
Sun
Energy traveling through SPACE
Earth
FORMS OF KINETIC ENERGY
• Electrical
– When electrons move.
– lightning and electricity are kinetic
energy.
EXAMPLES OF KINETIC ENERGY
Sound
Light
Dancing
Electricity
Understanding Check
• Tell the person next to you: How do you know he has kinetic energy?
Choose one of the following sentence frames. Using your science journal, fill in the blanks using what you know about kinetic energy.
• One example of ____________ is
______________.
• Characteristics (components) of
_____________include _______________ and __________________.
• Frequently associated with _________,
___________ is understood as
____________.
Comparing and Contrasting Potential and Kinetic Energy
• There are many different types of energy. The two main types of energy are potential and kinetic energy.
• How are these two types of energy alike
(compare) and how are they different
(contrast) ?
Use one of the following types of graphic organizers to compare and contrast Potential energy and Kinetic energy
Kinetic
Alike
Potential
Alike
Different
Different
Potential Kinetic
When you are done with your graphic organizer, answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper to be turned into me as your ticket out the door
1. Use and example (not given in the
PowerPoint presentation) to explain how potential energy can transform into kinetic energy.
2. Why is understanding potential energy and kinetic energy important to understanding motion (movement)?
ENERGY DAY 2
Warm up
• Today we are going to warm up with a few science demonstrations (and short play time)
• Please set up your science journals with the following data table (using a ruler is optional)
Activity When does it have potential energy?
When does it have kinetic energy?
Poppers
Ping Pong poppers
Rattle backs
Gyro rings
Astroblaster
Button Whizzer lab
• Learning target: to observe how potential and kinetic energy can be transferred, stored and released
ENERGY DAY 3
Warm up
Law of conservation of energy
• Energy is neither created nor destroyed. It just changes from one form to another. You always have the same amount of energy in a system. No more no less!
What does this really mean?
• New concept: Law of Conservation of energy
• Example Sentence:
Definitions:
.
.
.
Essential characteristics
.
.
.
.
Examples:
.
.
.
. diagrams
.
Conservation of Energy
• This means that kinetic energy can turn into potential energy which can turn into kinetic energy which can turn into potential energy which can turn into kinetic energy which can turn into potential energy which can turn into kinetic energy which can turn into potential energy
……..
Kinetic Potential
CONVERSION
From http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/science/formsofenergy.html
LAVA LAMP
KE: Motion
LAVA LAMP
Kinetic: Electricity, Light, Heat, Motion
Potential: stored energy in the wax, which
KE: Heat isn’t transformed.
KE: Electricity
Energy Flow
1. Kinetic energy in the form of electricity enters the lamp through the outlet and cord.
2. A bulb turns this electricity into another form of kinetic energy: light. The light flows into the room.
3. This light also creates heat, yet another form of kinetic energy.
4. The heat flows into the room, and also melts the wax inside the lamp, making it move.
5. The same amount of energy that went into the lamp comes out of the lamp in 3 different forms: light, heat, and motion.
Energy Flow
Electricity
Light
Heat
THE
ROOM
Motion
KE: Motion
LAVA LAMP
KE: Heat
Energy Flow
Electricity
Light
Heat
Motion
KE: Electricity
THE
ROOM
The yo-yo.
Consider:
PE: height, string
The Yo-Yo
PE: height, string
PE: height, string
PE: height, string
KE: motion
KE: motion
KE: motion
Potential: height, wound string
Kinetic: yo-yo falling & rising
Energy Flow
Height Wound String
Motion
Energy Flow
1. The Yo-Yo has only potential energy at the beginning.
There are two kinds: potential energy because of height, and the wound string.
2. As the yo-yo drops, the potential energy is transformed into the kinetic energy of the yo-yo moving.
3. When it is halfway down, the yo-yo has the same amount of potential and kinetic energy.
4. When the yo-yo gets to the bottom all the potential energy has turned into kinetic energy.
5. As the yo-yo comes back up the string the process is reversed. Kinetic energy is transformed back into potential energy (the wound string, and height).
Let’s practice together
1. What types of energy?
2. How does energy flow?
3. Concept map of energy flow.
4. Describe the flow of energy.
1. Kinetic energy, Chemical Potential energy, thermal energy, light (radiant) energy, electrical energy
2. Kinetic (motion), chemical potential (batteries), electrical (wires connecting to light) thermal(from light and wires), light (given off into the room)
3. KE CPE electrical thermal light
The Room
Can we fill more of this in?
• New concept: Law of Conservation of energy
Definitions:
.
.
.
Examples:
.
.
.
.
Essential characteristics
.
.
.
.
Diagrams
.
Energy Flow
1. Pick an object and sketch it
2. Identify the types of energy that your object uses.
3. Draw arrows on your object to show the flow of energy.
4. Make a chart/concept map of the energy flow.
5. Write a SHORT paragraph describing the energy flow. How does this show that energy isn’t created or destroyed, it just changes?
ENERGY DAY 4
Thermal Energy
• We call this heat.
• Actually the internal energy in substances .
• As molecules and atoms within substances move around this is what causes thermal energy.
• The faster the movement, the greater the amount of thermal energy.
Hard to understand?
• Think about when you are running, what happens the more you move?
• Muscles move
• Start to sweat
• Temperature increases
• Basically you are converting kinetic energy (motion) into thermal energy (heat) by moving the molecules that make up your body
Other Examples of Thermal Energy (Heat)
• Geothermal energy
• Friction
• Stoves/ ovens
• Fire
Quick Demonstration
• Rub your hands together
– What do you notice?
• Move faster and then slow down
– Do you notice a difference?
Choose one of the following sentence frames. Using your science journal, fill in the blanks using what you know about thermal energy.
• When ___________ is added,
___________increases.
• ________ has been caused by _______, thus
__________.
• _______ has/have caused _______. Which, in turn, results/resulted in____________.
How does Heat Travel
• Heat always transferred from hot items to cold items.
• Hot soup refrigerator
• Hot spoon
• Warm soda ice cream
Ice cubes
Remember the hotter something is, the faster the molecules and atoms are moving which means more energy. This energy overcomes the cooler things that have less energy. It transfers energy into them which heats them up.
Demonstrations
• Place one hand on the table- what do you feel?
– Your hand is transferring heat from your hand to the table.
• Ring and ball (demo)
• Hand boilers
• Fortune fish
• Thermo boards