AP Biology - Evolution Review Key Terms
advertisement

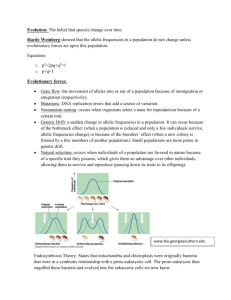
AP Biology - Evolution Review Key Terms Adaptation Adaptive Radiation Allopatric Speciation Analogous Structure Apomorphic character Artifical Selection Assortative Mating Balanced Polymorphism Biogeography Bottleneck Effect Catastrophism Comparative Morphology Convergent Evolution Descent with Modification Directional Selection Divergent Evolution Diversifying Selection Endemic Species Evolution Fitness Fossil Founder Effect Gene Flow gene pool Genetic Drift Geologic Time Scale Gradualism Heterozygote Advantage Homologous Structure Industrial Melanism Macroevolution Morphological Convergence Morphological Divergence Natural Selection Phylogeny Plate Tectonics Pleisomorphic character Polyploidy population Postzygotic Barrier Prezygotic Barrier Punctuated Equilibrium Radiometric Dating Reproductive Isolation Sexual Selection Speciation Species Stabilizing Selection Sympatric Speciation Theory of Uniformity Transient Polymorphism Vestigial Structure Enduring Understanding 1A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution Essential Knowledge 1.A.1: Natural Selection is a major mechanism of evolution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is the difference between evolution and natural selection? What is the smallest unit that can evolve? What is a species? How do you know? In your own words describe Darwin’s theory of natural selection as the mechanism of evolution. Explain how antibiotic resistance is an example of natural selection. What ideas/ people influenced Darwin in the development of his theory? Essential Knowledge 1.A.2: Natural selection acts on phenotypic variations in populations 1. 2. 3. 4. How is variation in a population created? Explain the classic example of peppered moth (Biston betularia) evolution. Why is sexual reproduction the preferred method for most organisms on earth? How does artificial selection show human impact on variation in a population? Essential Knowledge 1.A.3: Evolutionary change is also driven by random processes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. How are gene flow and genetic drift different? What is a defining characteristic of the bottleneck effect? How does a population’s genetic diversity become reduced? Give an example of how genetic variation decreases in a population? Why does gene flow typically occur more in motile organisms? Essential Knowledge 1.A.4: Biological evolution is supported by scientific evidence from many disciplines, including mathematics. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What are 3 pieces of evidence scientists use to support the theory of evolution? How do you know when a population is evolving? What is DNA and how is it related to evolution? What are the 5 assumptions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? In a theoretical population in H-W equilibrium, 150/1000 have aa. For this population, what is p? what is q? Explain how fossils can be used to show the history of life on earth. Explain HOX genes and how they relate to evolution. Adapted by Matt Rice from Campbell Biology 9th ed & AP Teacher Guide – Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life, Silber, Wade, Fedas, Whitis Enduring Understanding 1.B: Organisms are linked by lines of descent from common ancestry Essential Knowledge 1.B.1: Organisms share many conserved core processes and features that evolved and are widely distributed among organisms today. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Name a feature humans share with a common ancestor. Why is this true? How do we know all organisms evolved from a common ancestor? Bird wings and bat wings are an example of what idea? Bird wings and dragonfly wings are an example of what idea? If species 1 and 2 have similar appearances but different DNA sequences while species 3 and 4 have different appearances but very similar DNA, which pair of species is more likely to be closely related? How can this be explained? Based on your knowledge, describe 4 features of a common ancestor for all living organisms. How can it be explained that snakes and lizards are both reptiles but have different features? Enduring Understanding 1.C: Life continues to evolve within a changing environment Essential Knowledge 1.C.1: Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Why do some species go extinct and others don’t? Why did the dinosaurs go extinct 65 million years ago? Where did life first evolve? Give an example of 2 mass extinctions and how they changed the evolutionary history of life on earth. Are we currently living through a mass extinction event? Why or why not? Explain the basic progression of life on earth from bacteria to humans. Essential Knowledge 1.C.2: Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Explain the evolution of many different species of finches on the Galapagos Islands in your own words. What is a gamete and a zygote? How do you get a mule? A liger? A tigon? Are all hybrids sterile? Graphically represent allopatric and sympatric speciation. Give an example of each. Name 4 prezygotic barriers and how each works. Explain sexual selection and give an example. Essential Knowledge 1.C.3: Populations of organisms continue to evolve. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Do all traits in a population change over time? Why or why not? Does evolution have a goal? Why or why not? Give an example of evolution happening today. How does evolution explain both unity and diversity of life? Give an example of how humans continue to evolve. What happens to a species that can no longer evolve? Why might this occur? Enduring Understanding 1.D : The origin of living systems is explained by natural processes Essential Knowledge 1.D.1: There are several hypotheses about the natural origin of life on Earth, each with supporting evidence. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What molecules were present on early earth? What molecule was noticeably absent from early earth? What is the difference between monomers and polymers? Explain the steps outlined by Oparin and Haldane for the origin of life. Explain the Miller and Urey experiment. Why were the first cells on early Earth anaerobic prokaryotes? How did aerobic cells evolve? Essential Knowledge 1.D.2: Scientific evidence from many different disciplines supports models of the origin of life. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is the big bang theory and what does it explain? What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? What is the function of the plasma membrane and why do cells need them? Graphically represent the theory of endosymbiosis. Explain the theory and give 3 pieces of evidence that support the theory. What are the similarities and differences between archae and bacteria? What are cyanobacteria and why were they important to the formation of life as we know it today? Adapted by Matt Rice from Campbell Biology 9th ed & AP Teacher Guide – Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life, Silber, Wade, Fedas, Whitis