NERVOUS SYSTEM: NEURAL TISSUE
advertisement

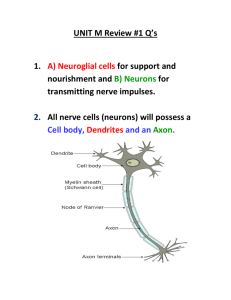
Human Anatomy Unit 4 NERVOUS SYSTEM: NEURAL TISSUE Overview • Includes all neural 8ssue in the body • 2 divisions 1. Central (CNS) 2. Peripheral (PNS) – Afferent • Sensory • Info to CNS • Receptors – Efferent • Motor • Info from CNS • Effectors PNS Organiza8on • Soma8c – Skeletal muscle – Soma8c motor • CNS controls skeletal muscle – Soma8c sensory • Sensory info from muscles to CNS • Autonomic (Visceral) – Gut structures – Visceral motor • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Sympathe8c division • Parasympathe8c division – Visceral sensory Nervous System Organiza8on Cellular Organiza8on • 2 dis8nct types of cells 1. Neurons • Transfer and processing informa8on in the nervous system 2. Neuroglia • Cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Anatomy Soma Dendrites Axon (telodendria) Synap8c bulb Axon hillock Myelin Neuroglia CNS Glial Cells • Astrocytes – Inters88al environment – Blood‐brain barrier – Structural support – Repairing damaged nervous 8ssue – Neuron development • Oligodendrocytes – Not all nerves in the CNS are myelinated – myelin • Microglia – macrophage • Ependymal cells – Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) CNS Glial Cells PNS Glial Cells • Schwann cells – Myelin • All peripheral nerves are myelinated – Nodes of Ranvier • Axolemma – Neuron plasma membrane • Neurilemma – Superficial cytoplasmic covering • Satellite cells Schwann Cells Neurons Neural Development and Growth • Stem cells differen8ate into neurons or glia (before birth) • Each neuronal daughter cell differen8ates and sends out processes that will be axons and dendrites • Growth cone – – – – Forms a 8p at the end of an axon Directs the route and final target for the axon Guided along glial cells Synapses become ac8ve before matura8on • Determines final func8on • Apoptosis – Programmed cell death – 50‐70% of neurons and synapses in developing CNS Neural Regenera8on • Severed neurons can be repaired as long as the damage – Occurs outside of the CNS – Does not damage the soma • Slow process – 1mm/day Types of Synapses Structural Classifica8on of Neurons • Anaxonic neuron – CNS – Special sense organs • Bipolar neuron • Pseudounipolar neuron – Con8nuous axon‐dendrite processes – Soma is off to the side – Visceral sensory neurons – Axons may be myelinated Single dendrite Centrally located soma Between axon and dendrite • Mul?polar neuron – Mul8ple dendrites Special senses (vision, – Single axon smell, hearing) – Not myelinated – Most common in CNS – – – – • Soma8c motor neurons • All axons are myleninated Structural Classifica8on of Neurons Func8onal Classifica8on of Neurons • Sensory neurons – Afferent division of PNS – Deliver info to CNS – Pseudounipolar neurons • Afferent fibers • From sensory receptors to spinal cord or brain • Motor neurons • Interneurons Func8onal Classifica8on of Neurons Sensory Neurons • Afferent division of PNS • Soma?c sensory neurons – Deliver info to CNS • Outside world • Our posi8on in it – Receptors located in the belly of muscles • Monitor tension • Monitor stretch – Pseudounipolar neurons • Afferent fibers • From sensory receptors to spinal cord or brain • Visceral sensory neurons – Transmit info on internal condi8ons – Status of organ systems Func8onal Classifica8on of Neurons Sensory Neuron Receptors • Types – Exteroreceptor (soma8c sensory receptors) • • • • • External environment Touch Temperature Pressure Special senses (vision, hearing, olfac8on) – Proprioceptor (soma8c sensory neurons) • Posi8on and movement of skeletal muscles and joints – Interoreceptor (visceral sensory neurons) • • • • Diges8ve, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, reproduc8ve systems Sensa8ons of deep pressure Pain Taste Func8onal Classifica8on of Neurons Motor Neurons • Efferent division of PNS • Mul8polar neurons • S8mulates or modifies the ac8vity of – Peripheral 8ssue – Organ – Organ system • Soma8c nervous system • Visceral nervous system (Autonomic nervous system) Func8onal Classifica8on of Neurons Soma8c Nervous System • • • • • Soma8c motor neurons Innervate skeletal muscles Cell bodies within CNS Axons extend to neuromuscular synapses Most ac8vi8es are consciously controlled Func8onal Classifica8on of Neurons Autonomic Nervous System • Visceral motor neurons • 2 neuron system – Preganglionic fiber • Soma in the brain or spinal cord • Control neurons in peripheral ganglia – Postganglionic fiber • Soma in a peripheral ganglia • Control the peripheral effectors – 2 divisions of the ANS • Sympathe8c – “Fight or Flight” • Parasypathe8c – “Rest and Repose” Peripheral Effectors: Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Glands Func8onal Classifica8on of Neurons Interneurons • Connect neurons within the CNS – Sensory ‐ ‐> Sensory – Motor ‐ ‐ > Motor – Sensory ‐ ‐ > Motor • Analysis of sensory inputs • Coordina8on of motor outputs • May be excitatory or inhibitory based on the effect on the postsynap8c membrane of other neurons The Synapse • Communica8on from a neuron to an effector • A nerve impulse triggers events that transfers informa8on • Chemical – Vesicular synapse – Neurotransmiber released from presynap8c membrane – Binds to receptors on postsynap8c membrane • Electrical – Gap junc8ons The Structure of a Synapse Anatomical Organiza8on of the Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System • Center • Nucleus • Ganglia – Collec8on of nerve cell bodies • Neural cortex – Superficial gray maber • Tracts – White maber • Columns • Pathways – Ascending (sensory) – Descending (motor) – Collec8on of nerve cell bodies – Gray maber • Spinal nerves – White maber – Emerge from the spinal cord – All mixed nerves • Cranial nerves – – – – – White maber Emerge from the brain Sensory Motor mixed Anatomical Organiza8on of the Nervous System