Reading CRCT Study Guide
advertisement
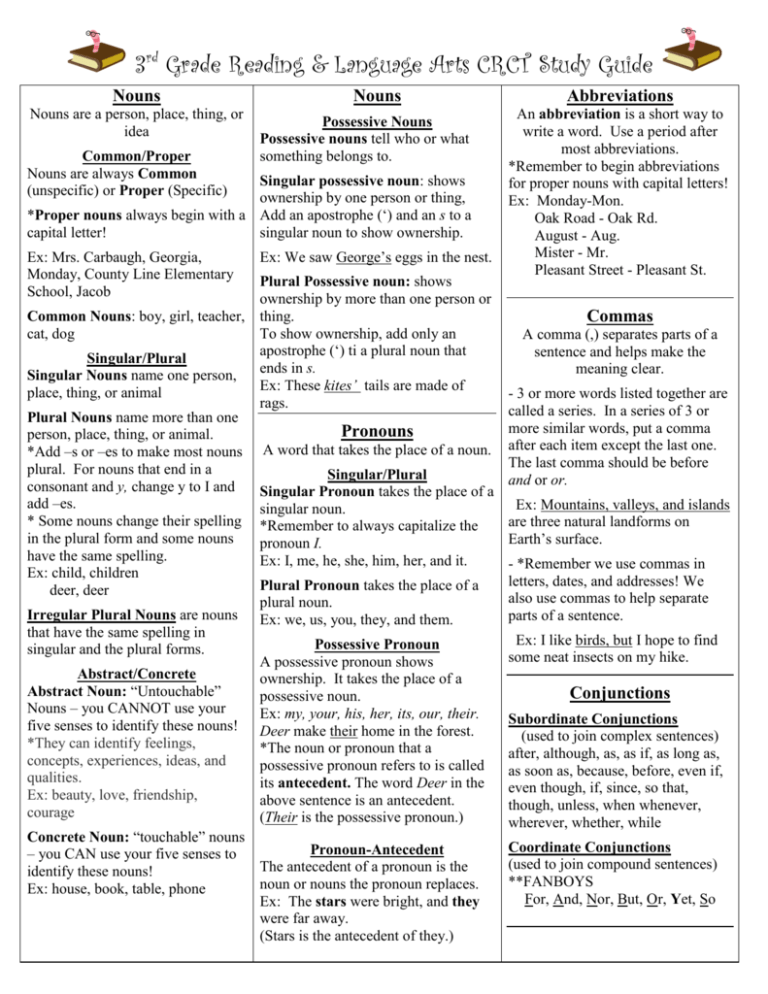
3rd Grade Reading & Language Arts CRCT Study Guide Nouns Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea Common/Proper Nouns are always Common (unspecific) or Proper (Specific) Nouns Possessive Nouns Possessive nouns tell who or what something belongs to. Singular possessive noun: shows ownership by one person or thing, *Proper nouns always begin with a Add an apostrophe (‘) and an s to a capital letter! singular noun to show ownership. Ex: Mrs. Carbaugh, Georgia, Monday, County Line Elementary School, Jacob Ex: We saw George’s eggs in the nest. Plural Possessive noun: shows ownership by more than one person or Common Nouns: boy, girl, teacher, thing. cat, dog To show ownership, add only an apostrophe (‘) ti a plural noun that Singular/Plural ends in s. Singular Nouns name one person, Ex: These kites’ tails are made of place, thing, or animal rags. Plural Nouns name more than one Pronouns person, place, thing, or animal. A word that takes the place of a noun. *Add –s or –es to make most nouns plural. For nouns that end in a Singular/Plural consonant and y, change y to I and Singular Pronoun takes the place of a add –es. singular noun. * Some nouns change their spelling *Remember to always capitalize the in the plural form and some nouns pronoun I. have the same spelling. Ex: I, me, he, she, him, her, and it. Ex: child, children Plural Pronoun takes the place of a deer, deer plural noun. Irregular Plural Nouns are nouns Ex: we, us, you, they, and them. that have the same spelling in Possessive Pronoun singular and the plural forms. A possessive pronoun shows Abstract/Concrete ownership. It takes the place of a Abstract Noun: “Untouchable” possessive noun. Nouns – you CANNOT use your Ex: my, your, his, her, its, our, their. five senses to identify these nouns! Deer make their home in the forest. *They can identify feelings, *The noun or pronoun that a concepts, experiences, ideas, and possessive pronoun refers to is called qualities. its antecedent. The word Deer in the Ex: beauty, love, friendship, above sentence is an antecedent. courage (Their is the possessive pronoun.) Concrete Noun: “touchable” nouns Pronoun-Antecedent – you CAN use your five senses to The antecedent of a pronoun is the identify these nouns! noun or nouns the pronoun replaces. Ex: house, book, table, phone Ex: The stars were bright, and they were far away. (Stars is the antecedent of they.) Abbreviations An abbreviation is a short way to write a word. Use a period after most abbreviations. *Remember to begin abbreviations for proper nouns with capital letters! Ex: Monday-Mon. Oak Road - Oak Rd. August - Aug. Mister - Mr. Pleasant Street - Pleasant St. Commas A comma (,) separates parts of a sentence and helps make the meaning clear. - 3 or more words listed together are called a series. In a series of 3 or more similar words, put a comma after each item except the last one. The last comma should be before and or or. Ex: Mountains, valleys, and islands are three natural landforms on Earth’s surface. - *Remember we use commas in letters, dates, and addresses! We also use commas to help separate parts of a sentence. Ex: I like birds, but I hope to find some neat insects on my hike. Conjunctions Subordinate Conjunctions (used to join complex sentences) after, although, as, as if, as long as, as soon as, because, before, even if, even though, if, since, so that, though, unless, when whenever, wherever, whether, while Coordinate Conjunctions (used to join compound sentences) **FANBOYS For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So Quotation Marks Verbs Adjectives Direct Quotation: Someone’s exact words are called a direct quotation. We use quotation marks (“ “) to show the exact words of a speaker. Ex: “It’s hot in here,” said Marsha. A verb is the main word in the predicate of a sentence. An adjective is a word that describes a noun. *Modifies the Nouns and Pronouns and Answers: What Kind? How Many? Which Ones? *Remember to use a comma to separate a speaker’s words from the other words in a sentence. Capitalize the first word of a quotation. Titles *Remember to underline the titles of books, magazines, and newspapers. *Place quotation marks around the titles of stories, poems, magazine articles, newspaper articles, and songs! *Capitalize the first word, last word, and every important word in a title. Adverbs An adverb is a word that describes, or tells about, a verb. (Some adverbs tell how something happens.) *Modifies Adjectives, Verbs, & Adverbs and Answers: How? When? Where? To What Extent? **Usually ends in (-ly) Ex: really, extremely, quietly, carefully, nervously, quite, too, well. Ex: The gym teacher said I ran fast. Firefighters and police officers work hard for you. The storyteller closed the book gently. *Remember, a subject and its verb must always agree in number. Action Verb: A word that tells what the subject of a sentence does. Ex: Joel enjoys his bath. The Verb Be: Forms of the verb be link the subject to a word or words in the predicate. Ex: Julia is strong. Singular: I am, you are, he is, she is, it is Plural: we are, you are, they are Main Verbs and Helping Verbs A main verb is the most important verb in the predicate. A helping verb can work with the main verb to tell about the action. Ex: They are teaching Kimi Japanese ways. (are is the helping verb teaching is the main verb) Ex: beautiful, glossy, unpredictable, nervous, lovely, rough, star-like, green, seven, several Sentence Types Simple Sentence One independent thought or idea. Compound Sentence 2 independent sentences joined by a semi-colon or a comma AND coordinate conjunction Complex Sentence One independent clause and one dependent clause. The subordinate conjunction always begins the dependent clause. Past, Present, and Future Tense 4 Kinds of Sentences Past-Tense Verbs: shows that an action happened earlier. (voted, helped, played) Declarative-Makes a statement Ex: The musical begins at 9:00. Present-Tense Verbs: show action that is happening now. (finds, asks, plays) Future –Tense Verbs: shows that an action will happen later. (will vote, will play, will ask) Sentences Interrogative-Asks a question Ex: Does the musical begin at 9:00? Imperative-Gives a command Ex: Start the musical at 9:00. Exclamatory-Shows EXPRESSION! Ex: Wow! That was the best musical! Articles A sentence is a group of words that tells a complete thought. One part of a The words a, an, and the are sentence tells who or what the articles. sentence is about. This is the subject. Articles are a special group of The other part of the sentence tells adjectives. Use a before singular what the subject is or does. This part nouns and adjectives that begin with is called the predicate. a consonant sound. Simple Sentence a sentence with one Ex: A farmer, An orchard, The town complete thought. Compound Sentences are two or more simple sentences combined to make a complete thought. Subject/Predicate Subject: Tells Who/What the sentence is about - (Contains the main noun) Predicate: Tells what happened (Contains the Verb) *95% of the time, the predicate will begin with the verb! Ex: Tom studied diligently for his test. Complete Subject/Complete Predicate The complete subject of a sentence includes the simple subject and all the other words in the subject that describes it. Ex: My friend Jared loves music. The complete predicate of a sentence is all the words that tell what the subject of the sentence is or does. Ex: A building has many parts. * Don’t Forget* Antonym A word that means the opposite. Ex: good, bad Synonym A word that means the same. Ex: good, excellent Homograph Two words that are spelled the same but have different meanings. Ex: Bat(baseball bat, bat-animal) Homophones Homophones are words that sound the same, but have different meanings. Usually they are spelled differently, but they can also be spelled the same. An easy way to remember this is to remember that you listen and speak when you are on a “phone”. Combining Sentences Poetry Compound Subjects Sentences with compound subjects have two or more subjects that share the same predicate. The words and and or are usually used to join the subjects. Use commas to separate two or more subjects. Literature written in verse. Ex: A banjo has strings. A cello has strings. A banjo and a cello have strings. Poem: A written composition, often using rhythm, rhyme, metaphor, and other artistic techniques to express an idea, feelings, or a story. Poet: a person who writes poems. Main Idea/Details Main Idea: The most important idea or thought of a story or paragraph. Common Prefixes/Suffixes Common Prefixes Dis-: the opposite of, not (disagree) In-: not, into (incorrect) Mis-: badly, wrong, not (misprint, misjudge) Non-: the opposite of, not (nonsense, nonrefundable) Pre-: in front of, before (preheat) Un-: the opposite of, not (unlikely, unheard) Supporting Details: Facts that support the main idea of a topic or text Common Suffixes -able: able to be or to become something (loveable) -ful: having a lot of (beautiful) -less: without something (odorless) -ly: in such a manner, like or suited to, occurring every so often (quickly, weekly) -ness: the state of being something (goodness) -ous: full of or having something (adventurous, famous) Conclusion or Resolution (how the story ends)- The main conflict is resolved or the story simply ends. Parts of a Book Table of Contents: a list of the titles with the page numbers, located near the front of the book. Heading: title of a section in a nonfiction book Glossary: Dictionary of terms used in the book, usually located in the back of the book Index: alphabetical list of topics and page numbers in the back of the book. Plot The plot is sequence of events in a story where each event causes the next event to happen. Climax-“Turning Point” or highest interest point of a story Theme What the story is about in one word. *To find the theme of a story, ask yourself, “In one word, what important part of life is this story about?” Six common themes in Children’s Literature: Growing up, courage, family/friendship, perseverance, acceptance, and compassion! Context Clues Types of Fiction (Genres) Literary Terms The different ways authors help readers figure out unfamiliar words (The clues are usually found around the word.) 1.A definition 2.An explanation 3.An example 4.A synonym (word that means the same) 5.An antonym (word that means the opposite) *Realistic Fiction: stories with situations that can happen in real life *Historical Fiction: stories that take place during past historical times (world wars, the titanic) *Mystery :stories involving suspense, danger, and intrigue *Adventure: relatively realistic, character have many exciting experiences *Fantasy: imaginative stories, characters and settings are different from real world, often dealing with magic, battles of good and evil *Science Fiction: a type of fantasy, stories generally set in a future time or world in which scientific advances have changed society in important ways *Folktales: traditional stories that real the values and beliefs of a culture *Myth: a traditional story, usually of unknown authorship, that answers basic questions about the world. Myths attempt to explain such things as human nature, the origin of the world, mysteries of nature, and social customs. *Fable: a brief tale that teaches a lesson about human nature. Many fables feature animals. *Legend: a story handed down from the past about a specific personusually someone of heroic achievement *Poetry: Literature written in verse. Theme: Life lesson learned; The main idea of a story. Main Idea: the central focus Setting: Where and when the story occurs. Characters: the people in the story Summarize: A short version of something with main points Chronological Order (Sequencing): When a story is told in the order that the events actually happened. (First, next, finally) Compare and Contrast: Shows how two or more things (subjects) are alike and different. Cause and Effect: describes an event or condition that causes other things to happen. A fact states something that happens, has happened or is certain to be true, or is real or exists. An opinion states something believed to have occurred, believed to exist, or believed to be true. Narrator: a person who tells the story or events. Moral: having to do with what is right and what is wrong in how a person acts. Dialogue: a conversation between characters. I had a dismal attitude because I failed my test, but my best friend was very pleased about her A. (Context Clue=Antonym) Dismalbad Author’s Purpose (P. I. E.) The author’s intent or reason for producing a piece of writing. Persuade: to use convincing strategies or facts to get someone to agree or see that your view is worth considering. (editorials, advertisements, letters) Inform: to give information or news (Newspaper, Informational texts) Entertain: to humor or to enlighten. (books, comics) Informational Genre Common Text Features Title: the name, or heading of the article Headings: Same as titles Subheadings: identifies the main idea of the section of text that follows Topic Sentences: Tells what the entire paragraph is discussing. Words in italics or boldface type Side bars: brief text written on the outside of the actual text. Captions: brief text that provides information about the subject of photograph or an illustration Headline: a short title Graphic Features Bar graphs: compare amounts of similar kinds of information Diagrams: show how things work. Timelines: shows you what happened and when Reference Resources When searching for information, you can use the following sources: Almanac – gives facts about populations, current events, ancient history, famous people, sports, elections, and many other things. New editions come out every year. Atlas – a book of maps Dictionary – find the definition of a word. Encyclopedia – find detailed information about a topic Glossary – a mini-dictionary at the end of a book Newspaper/Magazine – has news on things that are happening right now Table of Contents – a list of chapters or topics found near the beginning of the book. Thesaurus – find synonyms & antonyms; make better word choices Index – a list of topics & page numbers found at the end of a book Internet – quickly find anything & everything! Phonebook – find a person’s or business’ address & phone number. Thank you so much for purchasing my product! Please let me know if you see any errors or mistakes that need to be fixed. I would love any feedback! A special “thank you” to my wonderful editors! You guys rock! Thank you! Julie Carbaugh © 2014, Julie Carbaugh for distribution on www.TeachersPayTeachers.com








