identification of unknowns
advertisement

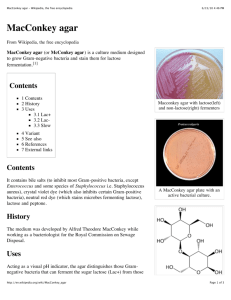
IDENTIFICATION OF UNKNOWNS Mon 11-3 IDENTIFICATION Over a four week period you will carry out a series of tests and experiments to identify an initially unknown Gram positive and Gram negative organism from a mixed broth culture By accumulating results from all the various tests you will identify each bacterium to a genus and species level. PHENOTYPIC IDENTIFICATION METHODS Morphological characteristics: Isolated colony-appearance and morphology from streak plates Cell morphology, arrangement and size by staining and microscopy Gaseous requirements: observe growth patterns in broth and deeps Differential staining: Gram-staining Spore-stain (only applies to Gm + bacilli) Biochemical tests: Differential and selective media: MacConkey, Mannitol Salt and Blood agar; Biochemical tests of carbohydrate and protein metabolism Tests of cell respiration such as: oxidase, catalase and nitrate tests REFERENCES Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology* Provides identification schemes for identifying bacteria and archaea Morphology, differential staining, biochemical tests Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Based on rRNA sequencing Bacteriology Provides phylogenetic information on bacteria and archaea We will use the Determinative manual. Copies available in the microbiology lab; biology resource center and on reserve at the CCSF library* On-line flow charts at: http://www.uiweb.uidaho.edu/micro_biology/250/IDFlowcharts.pdf Sample partial dichotomous key Possible Gram- bacteria Alcaligenes fecalis Citrobacter freundii Enterobacter aerogenes Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Morganella morganii Proteus mirabilis Proteus vulgaris Providencia stuartii Pseudomonas fluorescens Salmonella enterica Shigella flexneri Possible Gram+ bacteria Bacillus cereus Bacillus subtilis Corynebacterium xerosis Enterococcus fecalis Lactococcus lactis Micrococcus luteus Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epidermidis Week 1: Period 1 Begin with a mixed culture; record number Streak plates to obtain isolated colonies of gram negative and positive organisms on selective and differential media (MacConkey agar: Mannitol Salt agar) Streak on Trypticase soy (enrichment) agar Week 1: Period 2 Record growth characteristics (colony morphology, size, color, etc.) Transfer isolated colonies of two species onto 2 separate NA/TSA plates and keep them separate from now on Confirm separation of mixed culture by gram staining Transfer confirmed isolated bacteria to separate TSA slants to incubate Subculture on fresh TSA slants in subsequent weeks as needed Week 2: Period 1 Perform biochemical tests of carbohydrate metabolism and respiration on unknowns Inoculate and incubate media Each bench include an uninoculated control for comparison Week 2: Period 2 Get results and interpret all biochemical tests (do not simply record color changes) Make note of any reagents needed to perform tests Fresh subcultures Week 3: Period 1 Perform tests of protein metabolism on each unknown Inoculate and incubate media Each bench include an uninoculated control for comparison Week 3: Period 2 Get results and interpret all biochemical tests (do not simply record color changes) Make note of any reagents needed to perform tests Fresh subcultures Week 4 Perform any additional NECESSARY biochemical tests (eg. spore stain). These will vary per student Compile your unknown report per lab manual guidelines Presentation, organization, and completeness count! No late reports accepted (Due 12/10/14) Note: if you lose your unknowns or do not keep them growing you will only be reassigned organisms once Guideline for unknown ID Follow aseptic techniques at all times Label all cultures (date, name, section, organism) and keep track of subcultures. Do not discard a culture until you have new growth. Cultures < 2 days put at 37 C unless otherwise advised Cultures > 2 days put in RT incubator Draw, label and color and/or photograph observations as you go Guideline for unknown ID Keep organized and detailed records of all materials, methods, results and interpretations in a chronological order Work independently & be responsible for your work Do NOT touch other students work and make sure it is left in appropriate shelf for your lab section in the incubator and the refrigerator Lab report Research paper format Title: Should be descriptive and relevant to the project. Do not use the word “unknown” in the title. Abstract: Should state the topic of study and its significance, describe general methods, highlight major findings, and have concluding sentence on what you learnt from your study. Lab report Introduction: Describe the main purpose and goals of this project. Materials and Methods: Briefly outline the types of media and methods used. Results: Include drawings of ALL your results and include controls. Use a template for a petri plate or test tube. Include a brief interpretation of the results next to or below the figures. Do not just state positive or negative outcomes. Lab report Discussion: Show your dichotomous keys to show how you concluded the identity of each organism. Once identified research each organism and discuss any related diseases and symptoms (if any) and any relevant prevention and treatment. If they have been involved in a disease outbreak you can discuss that information. Write about half a page for each organism. Bibliography: Include a current bibliography and at least 3 references in addition to your text and Lab Manual Lab report Throughout the paper keep to the facts and avoid repetition. Use the third person (passive voice) in reports and avoid the use of “I” or “me”. Use the same tense (usually past) to be consistent. Check your spelling and grammar before submitting your report CHECKLIST OF RESULTS TO RECORD FOR BOTH ORGANISMS Isolated colony characteristics (enlarge image) Gram stain and cell morphology (enlarge image) and document cell size Appearance on MAC/MSA/TSA media Biochemical tests of respiration, carbohydrate & protein metabolism with controls Other: motility if present, gaseous requirements, hemolytic outcome on blood agar, spore stain if needed Mixed culture vs. pure culture • Mixed culture: a microbial culture consisting of two or more species • Pure culture: a culture that contains only one species of microorganisms • Methods of isolation: achieve pure culture from a mixed culture Methods of isolation • Isolation is a prerequisite to microbial ID • Quadrant streak: during streaking, the cell density decreases, eventually leading to individual cells being deposited separately on the agar surface • Each colony comes from one individual cell, so is a pure population (colony-forming units / CFU) Selective media • Nutritional components: • Selected to obtain optimal growth for certain bacteria • Inhibitors: • Inhibit growth of some bacteria • Differentiating substrates: • Substrates that only one group of organisms can utilize • Indicators: • Make reactions visible Mannitol Salt Agar • Selective: for Staphylococcus, against all other bacteria • Differentiating substrate: Mannitol • S. aureus ferments mannitol and forms bright yellow colonies • Other Staphylococcus bacteria don’t ferment mannitol and form pink-red colonies • Inhibitor: NaCl (7.5%) • High salt kills most bacteria • Indicator: phenol red • Bright yellow at low pH (<6.8) • Red or pink at high pH (>7.4) Mannitol Salt Agar S. aureus S. epidermidis Not Staphylococcus https://c2.staticflickr.com/4/3470/3396459999_7d79cd3f62.jpg MacConkey Agar • Selective: for Gm- bacteria (enteric bacteria), against Gm+ bacteria • Differentiating substrate: lactose • Coliforms: lactose fermentors • Inhibitor: Bile salts and crystal violet • Inhibit Gm+ bacteria • Indicator: neutral red • Red at low pH (<6.8) • Colorless at high pH (>6.8) MacConkey Agar Gram+ Gramcoliform Gram- coliform (bile precipitate) Gramnonfermenter http://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/843/flashcards /663843/jpg/picture31318207525204.jpg Lab Report Grading Rubrics • Download from Dr. Toebe’s website • • • • • Total points: 75 Summary charts: 15 X 2 Actual results chart: 15 Dichotomous keys (flow chart): 15 Research of identified bacteria and bibliography: 15 Lab Report Grading Rubrics • Summary chart 1: due 11/17/14 • Should include all the carbohydrate metabolism and respiration tests we will do on 11/17 • Show protocols and expected results • Summary chart 2: due 11/24/14 • Should include the protein metabolism tests we will do on 11/24 • Show protocols and expected results