“Awakenings” Movie Guide
advertisement

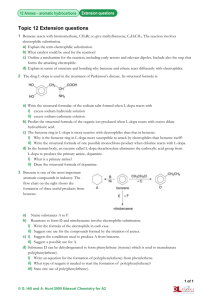
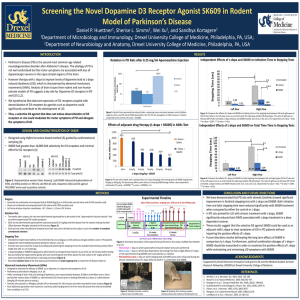
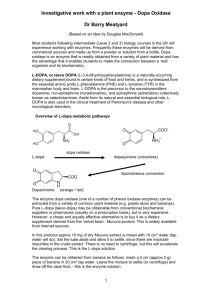
“Awakenings” Movie Guide Vocabulary Encephalitis lethargica- inflammation of the brain, sometimes caused by a virus and causing one to be sleepy Catatonic- a syndrome seen most frequently in schizophrenia, characterized by muscular rigidity and mental stupor, sometimes alternating with great excitement and confusion Dopamine- neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, retina, and sympathetic ganglia, acting within the brain to help regulate movement and emotion: its depletion may cause Parkinson's disease Parkinson’s Disease- disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination Tourette Syndrome- nervous system disorder which causes a person to make repeated and involuntary movements and sounds (vocalizations) called tics Epidemic– when a disease is in a large area with little cure stopping it Vicissitudes- a change of fate, normally in the negative direction Atypical- not normal, unseen before, unexplainable, not typical Autoimmune- a disease where your own immune system starts fighting your body instead of a virus or bacteria from the outside world. Background: Awakenings is a 2011 movie based on a 1973 non-fiction book by Oliver Sacks. It is a Hollywood version of real events that happened in New York and for science in the 1960’s. It recounts the life histories of those who had been victims of the 1920s encephalitis lethargica epidemic. Sacks recorded his efforts in the late 1960s to help these patients at the Beth Abraham Hospital (now Beth Abraham Health Services) in the Bronx, New York. The treatment used the then-new drug L-DOPA. In 1982, Dr. Sacks wrote: I have become much more optimistic than I was when I […] wrote Awakenings, for there has been a significant number of patients who, following the vicissitudes of their first years on L-DOPA, came to do – and still do – extremely well. Such patients have undergone an enduring awakening, and enjoy possibilities of life which had been impossible, unthinkable, before the coming of L-DOPA. Encephalitis lethargica, or the “sleepy sickness,” is a disease that attacks the brain, leaving some victims in a statue-like condition, speechless and motionless. It reached an epidemic state in the 1920’s. It still occurs today but in isolated cases. There is no known cause but it is thought to be some sort of autoimmune illness. There is currently no consistent treatment for the disease. Many drugs seem to work for a while but their effects run out after various amounts of time. Observation: 1. What observations did he make about Lucy? (He makes them more than once in the film… Continue listing them as they happen). 2. What observation did he make about the man watching TV? Question: 6. List the questions he asks Dr. Ingham. 13. What is his driving question? Hypothesis: 14. Come up with an “if…then…because…” hypothesis for his experiment with L-DOPA. Test: 7. He does a pre-experiment with Lucy. Describe his experimental procedure and results. 9. He did a pre-experiment with Lenard. Describe his experiment and results. 12. He ran a lot of tests on the group. List all the things he/the nurses tried. 15. He ran a trial run with Lenard. Describe it and the findings. 16. Describe his experimental set-up. a. What did he do to test his hypothesis about L-DOPA? b. What was his control group? c. What was his experimental group? d. What were his constants? e. What was the result? (Include the long term results). Analyze and Conclude: 8. What did he conclude from his pre-experiment? Discuss: 3. He discussed with two colleagues. Who were they? 4. What did he learn from Doctor Peter Ingham (the nice old man)? 5. How did he describe the patients? 10. He shared his results from Lenard with his colleagues. Why? 11. Did his colleague think his L-DOPA idea was a good one? Why or why not? Report: 17. How did he report his findings? 18. What was his overall conclusion?