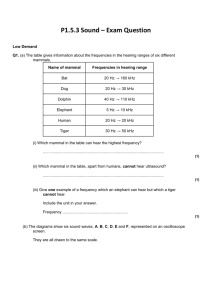
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
advertisement

Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering FIFTH SEMESTER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM TELECOMMUNICATION LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Prepared By: Checked By: Approved By: Engr. Yousaf Hameed Engr. M.Nasim Khan Dr.Noman Jafri Lecturer (Lab) Electrical, FUUAST-Islamabad Senior Lab Engineer Electrical, FUUAST-Islamabad Dean, FUUAST-Islamabad ____________________________________________________________________________ 1 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Name: ____________________________________________ Registration No: ____________________________________ Roll No: ___________________________________________ Semester: _________________________________________ Batch: ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 2 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering C CO ON NT TE EN NT TSS Exp No List of Experiments Page 1 Study Of Colpitts Oscillator 4 2 Study of Hartley Oscillator 6 3 Design an Amplitude Modulator Using Mc1496 8 4 Implementing an Amplitude Demodulator with Diode 16 5 Study of Double-Side Band Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC) Modulator 20 6 Study of Single-Sideband (SSB) Balanced Modulator 29 7 Demodulating DSB-SC Signals Using Product Detector 35 8 Demodulating SSB Signals using Product Detector 9 Implementing a Frequency Modulator with Voltage-Controlled Oscillator by using LM566 10 Demodulating FM Signal by using FM to AM Conversion Discriminator 41 47 50 11 Implementing a Pulse Width Modulator with LM555 52 12 Implementing a Pulse- Width Demodulator by using a Product Detector 55 13 Implementing an FSK Modulator with LM566 59 14 Performing a Frequency-Shift Keying Detector using Phase Locked Loop (FSK Demodulator) 61 15 16 17 18 19 To Implement an Amplitude-Shift Keying (ASK) Modulator To Implement Non-coherent ASK Demodulator To Implement Coherent ASK Demodulator To Implement PSK/QPSK Modulator To Implement PSK/QPSK Demodulator 63 65 67 70 77 ____________________________________________________________________________ 3 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment -1 Title: Study Of Colpitts Oscillator Equipment Required 1. Module KL-92001 2. Module KL-93001 3. Oscilloscope 4. LCR Meter Procedure Colpitts Oscillator Circuit 1. Locate Colpitts Oscillator circuit on Module KL-93001.lnsert connect plugs in J1 and J3 to set C3= 0.001µF, C4 = 0.015 µF and L1 = 27 µH. 2. Set the vertical input of oscilloscope to AC position and connect to output terminals (O/P). Observe and record the waveform and frequency in Table. If the circuit operates improperly, recheck the dc bias of transistor. 3. Remove the connect plugs from J1 and J3. Using the LCR meter, measure the values of C3, C4 and L1 and record the results in Table, and then calculate the output frequency 4. Insert connect plugs in J2 and J4 to change C3 to C5 (100 pF), C4 to C6 (1000 pF), and L1 to L2 (2.7 µH). Repeat steps 2 and 3. ____________________________________________________________________________ 4 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table: Nominal Value C3 C4 L1 0.001µF 0.015µF 27µH Measured Value Output waveform Calculated f = 0 Measured f = 0 Nominal Value Measured Value 100pF 1000pF 2.7µH Calculated f = 0 Measured f = 0 ____________________________________________________________________________ 5 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment-2 Title: Study of Hartley Oscillator Equipment Required 1. Module KL-92001 2. Module KL-93001 3. Oscilloscope 4. LCR Meter Procedure Hartley Oscillator Circuit 1. Locate Hartley Oscillator circuit on Module KL-93001. Insert connect plugs in J1 and J3 to set L1 = 68 µH, L2 = 2.7 µH, and C3 = 100 pF. 2. Set the vertical input of oscilloscope to AC position and connect to output terminals (OlP). Observe and record the waveform and frequency in Table. If the circuit operates improperly, recheck the dc bias of transistor. 3. Remove the connect plugs from J 1 and J3. Using the LCR meter, measure the values of C3, C4 and L1 and record the results in Table 1-2, and then calculate the output frequency. 4. Insert connect plugs in J2 and J4 to change C3 to C4(150 pF), L1 to L3(47µH), ____________________________________________________________________________ 6 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering and L2 to L4(470 µH). Repeat steps 2 and 3. Table: Nominal Value L1 L2 C3 68µH 2.7µH 100pF Measured Value Output waveform Calculated f = 0 Measured f = 0 Nominal Value Measured Value 470µH 47µH 150pF Calculated f = 0 Measured f = 0 ____________________________________________________________________________ 7 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment-3 Title: Design an Amplitude Modulator Using Mc1496 Equipment Required 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-93002 3 - Oscilloscope 4 - Spectrum Analyzer 5 - RF Generator Procedure Amplitude Modulator Using MC1496 Amplitude Modulation Waveforms ____________________________________________________________________________ 8 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Spectrum of AM Signal 1. Locate AM modulator circuit on Module KL-93002. Insert connect plugs in J1 and J3 to set R8=1 kΩ and R9=6.8kΩ 2. Connect a 250mVp-p, 1 kHz sine wave to the audio input (1/P2), and a 250mVpp, 100 kHz sine wave to the carrier input (1/P1). 3. Connect the vertical input of the oscilloscope to the AM output (O/P). Observe the output waveform and adjust the VR1 for the modulation index of 50%. Record the result in Table -1 4. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table -1 5. Using the results above and Equation calculate and record the percentage modulation of output signal in Table -1 6. Using the oscilloscope, observe the output signals for the audio amplitudes of 200 mVp-p and 150 mVp-p and record the results in Table -1 7. Repeat steps 4 and 5 8. Connect a 150mVp-p, 1 kHz sine wave to the input (1/P2), and a 100mVp-p, 100 kHz sine wave to the carrier input (1/P1). ____________________________________________________________________________ 9 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering 9. Using the oscilloscope, observe the AM signal at output terminal (O/P) and record the result in Table -2 10. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record output spectrum in Table -2 11. Using the results above and Equation, calculate the percentage modulation of output signal and record the results in Table -2 12. Repeat steps 9 to 11 for carrier amplitudes of 200mVp-p and 300mVp-p. 13. Connect a 150mVp-p, 3kHz sine wave to the audio input (1/P2), and a 250mVp-p, 100kHz sine wave to the carrier input (I/P1). 14. Using the oscilloscope, observe the modulated signal at output terminal (DIP) and record the result in Table -3 15. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table -3 16. Using the results above and Equation, calculate and record the percentage modulation of output signal in Table -3 17. Repeat steps 14 to 16 for the audio frequencies of 2 kHz and 1 kHz. 18. Connect a 150mVp-p, 2 kHz sine wave to the audio input (1/P2), and a 250mVp-p, 500 kHz sine wave to the carrier input (1/P1). 19. Using the oscilloscope, observe the modulated signal at output terminal (O/P) and record the result in Table-4 20. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record the output spectrum in Table -4 21. Using the results above and Equation. calculate and record the percentage ____________________________________________________________________________ 10 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering modulation of output signal in Table -4 22. Repeat steps 19 to 21 for the carrier frequencies of 1 MHz and2MHz. Equation m= Where And E E max E max E min max − E min × 100 % + E min = A c = A c + A m − A m ____________________________________________________________________________ 11 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 (Vc=250mVp-p, fc=100 kHz,fm=1 kHz) Audio Output Waveform Amplitude Output Signal Spectrum Percentage Modulation 250mVp-p E E max min = = 200mVp-p E E min max = = E E max = = 150mVp-p min ____________________________________________________________________________ 12 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-2 (Vc=150mVp-p, fc=100 kHz,fm=1 kHz) Audio Output Waveform Amplitude Output Signal Spectrum Percentage Modulation 100mVp-p E E max min = = 200mVp-p E E min = = E E min = = max 300mVp-p max ____________________________________________________________________________ 13 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-3 (Vc=250mVp-p, Vm=150mVp-p,fc=100 kHz) Audio Output Waveform Frequency Output Signal Spectrum Percentage Modulation 3 kHz E E max min = = 2 kHz E E min max = = E E max = = 1 kHz min ____________________________________________________________________________ 14 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-4 (Vc=250mVp-p, Vm=150mVp-p,fc=2 kHz) Audio Output Waveform Frequency Output Signal Spectrum Percentage Modulation 500kHz E E max min = = 1MHz E E min max = = E E max = = 2MHz min ____________________________________________________________________________ 15 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment - 4 Title: Implementing an Amplitude Demodulator with Diode Equipment Required 1. Module KL-92001 2. Module KL-93002 3. Oscilloscope 4. RF Generator Fig-1: Block diagram of a rectified demodulator Fig-2: Amplitude Modulator Using MC1496 Fig-3: Diode Detector Circuit ____________________________________________________________________________ 16 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Procedure 1. The AM signal source in this experiment is from the AM modulator output (the circuit of Fig-2). 2. Set the input signals of AM modulator for the carrier of 250mVp-p, 200kHz sine wave, and the audio signal of 150mVp-p, 3kHz sine wave 3. Adjust the VR 1 of AM modulator to get maximum amplitude of AM signal output. 4. Connect the AM signal output to the input (l/P) of diode detector. 5. Switch the vertical input of scope to DC coupling and observe the output waveforms of the amplifier and the diode detector, and record the results in Table -1 6. Change the audio frequencies for 2 kHz and 1 kHz, and repeat step 5. 7. Adjust the carrier to a 250mVp-p, 300 kHz sine wave, and the audio to a 250mVpp, 3 kHz sine wave. 8. Adjust the VR1 of AM modulator to get maximum amplitude of AM signal output. 9. Set the vertical input of scope to DC coupling and observe the output waveforms of the amplifier and the diode detector, and record the results in Table-2. 10. Change the audio frequencies for 2 kHz and 1 kHz, and repeat step 9. ____________________________________________________________________________ 17 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 (Vc=250mVp-p, Vm=150mVp-p, fc=200 kHz) Audio Input Waveform Frequency Detector Output Waveform 3kHz 2 kHz 1kHz ____________________________________________________________________________ 18 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-2 (Vc=250mVp-p, Vm=250mVp-p, fc=300 kHz) Audio Input Waveform Frequency Detector Output Waveform 3kHz 2 kHz 1kHz ____________________________________________________________________________ 19 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment-5 Title: Study of Double-Side Band Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC) Modulator Equipment required 1. Module KL-92001 2. Module KL-93003 3. Oscilloscope 4. Spectrum Analyzer 5. RF Generator DSB-SC Modulator Circuit Procedure 1. Locate DSB-SC Modulator circuit on Module KL-93003. Insert connect plugs in J1 and J3 to set R11 = 270Ω and R12 = 6.8kΩ 2. Check each of source follower circuits for a proper bias. Set the vertical input of oscilloscope to AC and observe the source output and the input signals. Ensure that these two signals are the same but the output amplitude is slightly smaller than the input amplitude. If done, insert connect plugs in J5 and J6. 3. Turn the VR1 to its mid-position 4. Connect the audio input (1/P2) to ground and connect a 500mVp-p, 500 kHz sine wave to the carrier input (1/P1). Carefully adjust the VR1 to get the output signal of ____________________________________________________________________________ 20 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering zero or minimum. 5. Connect a 300mVp-p, 1 kHz sine wave to the audio input and change the carrier amplitude to 300mVp-p. 6. Using the oscilloscope, measure and record the waveforms listed in Table -1. 7. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table -1. 8. Change the audio amplitude to 600mVp-p. Measure and record the waveforms listed in Table -2 using the oscilloscope. 9. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table -2. 10. Change the carrier amplitude to 600mVp-p. Measure and record the waveforms listed in Table -3 using the oscilloscope. 11. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table -3. 12. Change the audio amplitude to 300 mVp-p and frequency to 2kHz, and the carrier amplitude to 300mVp-p and frequency to 1 MHz. Using the oscilloscope, measure and record the waveforms listed in Table -4. 13. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table -4. 14. Remove the connect plug from J1 and insert it in J2 to change R11 (270Ω) to R15 (330Ω). Change the audio amplitude to 600mVp-p and frequency to 1 kHz, and the carrier amplitude to 600mVp-p and frequency to 500 kHz. Hold VR1 position. Using the oscilloscope, measure and record the waveforms listed in Table -5. 15. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table -5. 16. Remove the connect plug from J3 and then insert it in J4 to change R12 (6.8 kΩ) to R16 (10kΩ). Using the oscilloscope, measure and record the waveforms listed in Table -6. 17. Using the spectrum analyzer, observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table -6. ____________________________________________________________________________ 21 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering ____________________________________________________________________________ 22 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 (R11=270Ω, R12=6.8kΩ, Vc=300mVp-p, Vm=300mVp-p, fc=500kHz, fm=1kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 23 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-2 (R11=270Ω, R12=6.8kΩ, Vc=300mVp-p, Vm=600mVp-p, fc=500kHz, fm=1kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 24 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-3 (R11=270Ω, R12=6.8kΩ, Vc=600mVp-p, Vm=600mVp-p, fc=500kHz, fm=1kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 25 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-4 (R11=270Ω, R12=6.8kΩ, Vc=300mVp-p, Vm=300mVp-p, fc=1MHz, fm=2kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 26 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-5 (R11=330Ω, R12=6.8kΩ, Vc=600mVp-p, Vm=600mVp-p, fc=500kHz, fm=1kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 27 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-6 (R11=330Ω, R12=10kΩ, Vc=600mVp-p, Vm=600mVp-p, fc=500kHz, fm=1kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 28 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment-6 Title: Study of Single-Sideband (SSB) Balanced Modulator Equipment required 1. Module KL-92001 2. Module KL-93003 3. Oscilloscope 4. Spectrum Analyzer 5. RF Generator SSB Modulator Circuit Procedure 1. Locate SSB Modulator circuit on Module KL-93003. Insert the connect plug in J2 to bypass ceramic filters. 2. Check each of source follower circuits for a proper bias. Set the vertical input of oscilloscope to AC and observe the source output signal and the input signal. Ensure that these two signals are the same but the output amplitude is slightly smaller than the input amplitude. If done, insert connect plugs in J3 and J4. 3. Turn the VR1 to its mid-position. 4. Connect the audio input (1/P2) to ground and connect a 500mVp-p, 457 kHz sine wave to the carrier input (1/P1). Carefully adjust VR1 to get a minimum output or zero. Then remove the connect plug from J2 and insert it in J1. ____________________________________________________________________________ 29 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering 5. Connect a 300mVp-p, 2 kHz sine wave to the audio input and change the carrier amplitude to 300mVp-p. 6. Using the oscilloscope, measure and record the waveforms listed in Table -1. 7. Using the spectrum analyzer observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table-1. 8. Change the audio amplitude to 600mVp-p. Measure and record the waveforms listed in Table -2 using the oscilloscope. 9. Using the spectrum analyzer observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table-2. 10. Change the carrier amplitude to 600mVp-p. Measure and record the waveforms listed in Table-3 using the oscilloscope. 11. Using the spectrum analyzer observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table-3. 12. Change the audio amplitude to 300mVp-p and frequency to 1 kHz, and the carrier amplitude to 300mVp-p. Using the oscilloscope, measure and record the waveforms listed in Table -4. 13. Using the spectrum analyzer observe and record the output signal spectrum in Table-4. ____________________________________________________________________________ 30 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 (R11=270Ω, R12=6.8kΩ, Vc=300mVp-p, Vm=300mVp-p, fc=457kHz, fm=2kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 31 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-2 (R11=270Ω, R12=6.8kΩ, Vc=300mVp-p, Vm=600mVp-p, fc=457kHz, fm=2kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 32 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-3 (R11=270Ω, R12=6.8kΩ, Vc=600mVp-p, Vm=600mVp-p, fc=457kHz, fm=2kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 33 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-4 (R11=270Ω, R12=6.8kΩ, Vc=300mVp-p, Vm=300mVp-p, fc=457kHz, fm=1kHz) Carrier Waveform Audio Waveform Output Waveform Output Spectrum ____________________________________________________________________________ 34 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment -7 Title: Demodulating DSB-SC Signals Using Product Detector Equipment Required: 1. Module KL-92001 2. Module KL-93003 3. Oscilloscope 4. RF Generator Procedure: DSB-SC modulator circuit Product Detector DSB-SC & SSB signal ____________________________________________________________________________ 35 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering 1. This experiment uses the modulated DSB-SC output of DSB-SC Modulator circuit as the DSB-SC input of product detector circuit. First, complete the DSB-SC modulator circuit. 2. Connect a 500mVp-p, 500 kHz sine wave to the carrier input and a 500mVp-p, 1 kHz sine wave to the audio input of DSB-SC modulator. (Carry and audio signals should be adjusted alone before connecting to circuits, because if you adjust them during circuit testing, there'll be loading errors) 3. Turn the VR1 of DSB-SC modulator to get a DSB-SC modulated signal output. 4. Locate the DSB-SC and SSB Product Detector circuit on Module KL-93003. Insert connect plugs in J1 and J3 to set R5=270Ω and R6=10kΩ 5. Connect the carrier signal used in step 2 to the carrier input of product detector. Connect the modulated output of DSB-SC modulator to the DSB-SC input of product detector. 6. Using the oscilloscope, observe the output signal and turn the VR1 of product detector circuit to get minimum distortion, and record the result in Table -1. 7. Change the carrier to a 500mVp-p, 500 kHz sine wave and the audio to a 500mVp-p, 3 kHz sine wave. Carefully turn the VR1 to get a DSB-SC modulated output signal. 8. Repeat step 6 and record the result in Table -2. 9. Remove the connect plug from J1 and then insert it in J2 to change R5 (270Ω) to R10 (330Ω). Repeat step 6 and record the result in Table -3. 10. Remove the connect plug from J3 and then insert it in J4 to change R6 (10kΩ) to R11 (30kΩ). Repeat step 6 and record the result in Table -4. ____________________________________________________________________________ 36 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 (R5=270Ω, R6=10kΩ, Vc=500mVp-p, Vm=500mVp-p, fc=500kHz,fm=1kHz) Input Waveform Output Waveform ____________________________________________________________________________ 37 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-2 (R5=270Ω, R6=10kΩ, Vc=500mVp-p, Vm=500mVp-p, fc=500kHz, fm=3kHz) Input Waveform Output Waveform ____________________________________________________________________________ 38 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-3 (R5=330Ω, R6=10kΩ, Vc=500mVp-p, Vm=500mVp-p, fc=500kHz,fm=1kHz) Input Waveform Output Waveform ____________________________________________________________________________ 39 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-4 (R5=330Ω, R6=30kΩ, Vc=500mVp-p, Vm=500mVp-p, fc=500kHz,fm=1kHz) Input Waveform Output Waveform ____________________________________________________________________________ 40 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment-8 Title: Demodulating SSB Signals using Product Detector Equipment Required 1. Module KL-92001 2. Module KL-93003 3. Oscilloscope 4. RF Generator Procedure SSB Product Detector Product Detector DSB-SC & SSB signal ____________________________________________________________________________ 41 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering 1. This experiment uses the modulated SSB output of SSB Modulator circuit as the SSB input of product detector circuit. First, complete the SSB modulator circuit. 2. Insert connect plug in J2 to bypass ceramic filters. Connect a 500mVp-p, 457 kHz sine wave to the carrier input (I/P1) and a 500mVp-p, 2 kHz sine wave to the audio input (I/P2). (Carry and audio signals should be adjusted alone before connecting to circuits, because if you adjust them during circuit testing, there'll be loading errors) 3. Turn the VR1 to get a DSB-SC modulated output (O/P). Remove the connect plug from J2 and then insert it in J1 to recover the ceramic filters. The output signal will be the SSB modulated signal. 4. Insert connect plugs in J1 and J2 of product detector circuit to set R5 =270Ω and R6 = 10 kΩ 5. Connect the carrier signal used in step 2 to the carrier input (I/P1) of product detector, and connect the SSB modulated output to the SSB input (I/P2). 6. Using the oscilloscope, observe the demodulated output waveform (O/P) and carefully turn the VR1 to get minimum distortion. Record the result in Table-1. 7. Remove the connect plug from J 1 and insert it in J2 to bypass the ceramic filters of SSB modulator. Change the carrier to a 700mVp-p, 457 kHz sine wave and the audio to a 700mVp-p, 2 kHz sine wave. Turn the VR1 to get a DSB-SC modulated signal, and then remove the connect plug from J2 and inset it in J 1 to recover the ceramic filters. Then the output signal will be the SSB modulated signal. 8. Repeat step 6 and record the result in Table-2. 9. Remove the connect plug from J1 and then insert it in J2 to change R5 (270 Ω) to R10 (330 Ω). Repeat step 6 and record the result in Table -3. 10. Remove the connect plug from J3 and then insert it in J4 to change R6 (10 kΩ) to R11 (30 kΩ). Repeat step 6 and record the result in Table -4. ____________________________________________________________________________ 42 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 (R5=270Ω, R6=10kΩ, Vc=500mVp-p, Vm=500mVp-p, fc=457kHz,fm=2kHz) Input Waveform Output Waveform ____________________________________________________________________________ 43 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-2 (R5=270Ω, R6=10kΩ, Vc=700mVp-p, Vm=700mVp-p, fc=457kHz,fm=2kHz) Input Waveform Output Waveform ____________________________________________________________________________ 44 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-3 (R5=330Ω, R6=10kΩ, Vc=500mVp-p, Vm=500mVp-p, fc=457kHz,fm=2kHz) Input Waveform Output Waveform ____________________________________________________________________________ 45 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-4 (R5=330Ω, R6=30kΩ, Vc=500mVp-p, Vm=500mVp-p, fc=457kHz,fm=2kHz) Input Waveform Output Waveform ____________________________________________________________________________ 46 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment - 9 Title: Implementing a Frequency Modulator with Voltage-Controlled Oscillator by using LM566 Equipment Required: 1. Module KL-92001 2. Module KL-93004 3. Oscilloscope 4. Spectrum Analyzer Procedure: LM566 Frequency Modulator Circuit 1. Locate the LM566 FM Modulator circuit on Module KL-93004. Insert connect plugs in J1 and J3 to set the capacitor to C4 (0.01 µF). Turn the VR1 to get the output frequency of 20kHz. 2. Connect a 500mVp-p, 1 kHz sine wave to the audio input (I/P1). Using the oscilloscope, observe the output waveform (O/P) and record the result in Table -1. 3. Change the audio frequencies to 3kHz and 5kHz sequentially. Observe the output waveforms corresponding to the audio inputs and record the results in Table -1. 4. Change the audio input to a 1Vp-p, 1kHz sine wave. Observe the output waveform and record the result in Table -2. 5. Change the audio frequencies to 3kHz and 5kHz sequentially. Observe the output waveforms corresponding to the audio inputs and record the results in Table -2. ____________________________________________________________________________ 47 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 (Vm=50mVp-p,C3=0.01µF, f = 20kHz ) 0 Input Input Waveform Frequency Output Waveform 1 kHz 3 kHz 5 kHz ____________________________________________________________________________ 48 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-2 (Vm=1Vp-p,C3=0.01µF, f = 20kHz ) 0 Input Input Waveform Frequency Output Waveform 1 kHz 3 kHz 5 kHz ____________________________________________________________________________ 49 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment-10 Title: Demodulating FM Signal by using FM to AM Conversion Discriminator Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-93004 3 - Oscilloscope Procedure: FM to AM Frequency Discriminator Circuit 1. Locate MC1648 FM Modulator circuit on Module KL-93004. Insert connect plugs in J1 and J3 to set the inductor to L1 (220µH) and the 1SV55 varactor operating at 5V. 2. Connect a 2Vp-p, 1 kHz sine wave to the input (I/P1). Turn the VR1 to get the output amplitude of 600mVp-p. 3. Connect the output of MC1648 FM Modulator to the input of FM to AM Discriminator Circuit on the lower of Module KL-93004. 4. Using the oscilloscope, observe and record the input and output waveforms of frequency demodulator in Table-1. 5. Repeat steps 2 to 4 for audio frequencies of 2 KHz and 3 KHz, respectively. ____________________________________________________________________________ 50 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 (Vm=2Vp-p) Audio Frequency Input Waveform output Waveform 1 kHz 2 kHz 3 kHz ____________________________________________________________________________ 51 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment - 11 Title: Implementing a Pulse Width Modulator with LM555 ~ Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-94002 3 - Oscilloscope Procedure: ~ Pulse Width Modulator using LM555 1. Locate the PWM Modulator circuit on Module KL-94002. 2. Connect a 5Vp-p, 1 kHz square wave to the audio signal input. 3. Using the oscilloscope, observe the n test point and the output waveforms and adjust the VR1 to get a rectangular wave (duty cycle is not equal to 50%) at n. 4. Switch the coupling mode of oscilloscope to DC position. Observe and record the output waveform in Table -3. 5. Change the input signal to triangle wave and repeat step 4. 6. Change the input signal to sine wave and repeat step 4. Record the results in Table -4. 7. Change the input amplitude to 3Vp-p and repeat steps 4 to 6 and record the results in Table -4. ____________________________________________________________________________ 52 Communication System ~ Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-3 (Vm=5Vp-p, fm= 1 kHz) Input Signal Input Waveform output Waveform Square Wave Triangle Wave Sine Wave ____________________________________________________________________________ 53 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-4 (Vm=3Vp-p, fm= 1 kHz) Input Signal Input Waveform output Waveform Square Wave Triangle Wave Sine Wave ~ ____________________________________________________________________________ 54 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment 12 Title: Implementing a Pulse- Width Demodulator by using a Product Detector Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-94002 3 - Oscilloscope Procedure: Fig-1 PWM Modulator Circuit Pulse Width Demodulator Circuit 1. Locate the PWM Demodulator circuit on Module KL-94002. 2. Complete the PWM Modulator circuit in Fig-1. Connect a 3Vp-p, 700Hz sine wave ____________________________________________________________________________ 55 Communication System ~ Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering to the audio input. 3. Connect the test point T1 of the PWM Modulator circuit to the carrier input (1/P1) of the PWM Demodulator circuit. 4. Connect the PWM modulated output of the PWM Modulator circuit to the PWM input (l/P2) of the PWM Demodulator circuit. 5. Vary the VR1 to get an output signal with minimum distortion at U1 µA 7 41 output. 6. Carefully adjust VR2 and VR3 until getting a proper demodulated signal. 7. Using the oscilloscope, observe the signals of PWM input signal, carrier signal, U1 output signal, U2 output signal, MC1496 output signal (pin 12), and PWM demodulated signal. Record the results in Table -1. 8. Repeat steps 5 to 7 and record the results in Table -2. ____________________________________________________________________________ 56 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 (Vm=3Vp-p,fm=700Hz) Test point Output Waveform Carrier Input Terminal PWM Input Terminal U1 Output Terminal U2 Output Terminal MC1496 (pin 12) Output Terminal PWM Demodulated Signal Output ____________________________________________________________________________ 57 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-2 (Vm=3Vp-p,fm=500Hz) Test point Output Waveform Carrier Input Terminal PWM Input Terminal U1 Output Terminal U2 Output Terminal MC1496 (pin 12) Output Terminal PWM Demodulated Signal Output ____________________________________________________________________________ 58 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment -13 Title: Implementing an FSK Modulator with LM566 Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-94003 3 - Oscilloscope Procedure: FSK Modulator Circuit 1. Locate the FSK modulator circuit on Module KL-94003. 2. Connect 5Vdc to digital signal input (l/P). Using the oscilloscope, observe the LM566 output frequency (pin 3) and adjust VR2 to obtain the frequency of 1070Hz, and then record the result in Table -1. 3. Using the oscilloscope, observe and record the FSK output signal in Table -1. 4. Connect digital signal input (l/P) to ground (0V). Using the oscilloscope, observe the LM566 output frequency (pin 3) and adjust VR1 to obtain the frequency of 1270Hz, and record the result in Table -1. 5. Using the oscilloscope, observe and record the FSK output signal in Table -1. 6. Set the output of signal generator to TTL level and the frequency of 200 Hz and ____________________________________________________________________________ 59 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering then connect the output to the digital signal input (l/P). Using the oscilloscope, observe and record the input, LM566 output (pin 3), and FSK output signals in Table -2. 7. Change the output frequency of signal generator to 5 kHz and repeat step 6. Table-1 Input LM566(pin 3) Output Waveform FSK Output Waveform Signal 0V 5V Table-2 Input Ferquency 200Hz 5kHz 0V 5V ____________________________________________________________________________ 60 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment -14 Title: Performing a Frequency-Shift Keying Detector using Phase Locked Loop (FSK Demodulator) Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-94003 3 - Oscilloscope Procedure: FSK Demodulator Circuit 1. Locate the FSK Demodulator circuit on Module KL-94003. Connect the vertical input of oscilloscope to VCO output (T1). Observe the free-running frequency of LM 565 and Adjust VR1 to obtain a frequency of 1170 Hz. 2. Connect a 1070Hz, 2Vp-p sine wave to the input terminal (l/P). Set oscilloscope vertical input to DC range and observe the output waveform and record the result in Table-1. 3. Change the input frequency to 1270Hz and repeat step 2. 4. Complete the FSK Modulator circuit on Module KL-94003. Apply a 150Hz TTL square wave to the input of FSK modulator. 5. Connect the output of FSK modulator to the input of FSK demodulator. Using the oscilloscope, observe and record the demodulated output waveform in Table-2. If the demodulated signal is not obtained, check the input FSK frequencies 1070 Hz and 1270Hz. 6. Change the input frequency of FSK modulator to 200Hz. Set oscilloscope vertical input to DC range and observe the output waveform and record the result in Table-2. ____________________________________________________________________________ 61 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table -1 (Vm =2Vp-p) Input Input Waveform Output Waveform FSK Modulator FSK Demodulator FSK Demodulator Input Frequency Input Waveform Output Waveform Frequency 1070 Hz 1270 Hz Table -2 150 Hz 200 Hz ____________________________________________________________________________ 62 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment-15 Title: To Implement an Amplitude-Shift Keying (ASK) Modulator Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-94005 3 - Oscilloscope Procedure: Fig-1 ASK Modulator 1. Locate the ASK modulator circuit shown in Fig-1 on the KL-94005 module. 2. Connect a 500 KHz, 4Vp-p sine wave to the VC Carrier in terminal. 3. Connect a 20 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to the VD Signal in terminal. 4. Turn the VR1 fully CW to obtain a maximum amplitude of ASK modulated signal on VT out. Measure and record the ASK signal waveform in Table-1. 5. Turn the VR1 fully CCW to obtain a minimum amplitude of ASK modulated signal on the VT out. Measure and record the ASK signal waveform in Table-1. 6. Connect a 1 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to the VD Signal in terminal. 7. Repeat steps 4 and 5. 8. Connect a 10 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to the VD Signal in terminal 9. Repeat steps 4 and 5. 10. Connect a 50 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to the VD Signal in terminal. 11. Repeat steps 4 and 5. ____________________________________________________________________________ 63 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 ASK modulator (VC Carrier in = 500 kHz, 4V p-p) VD Signal (TTL level) VT out Waveform (VR1 fully CW) VT out Waveform (VR1 fully CCW) 20kHz 1kHz 10kHz 50Khz ____________________________________________________________________________ 64 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment 16 Title: To Implement Non-coherent ASK Demodulator Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-94005 3 - Oscilloscope Procedure: Fig-1 Noncoherent ASK Demodulator Circuit 1. Complete the noncoherent ASK demodulator shown in Figure-1 by placing the jumpers in positions 2, 6, and 8. 2. Connect a 500 KHz, 4Vpp sine wave to VC Carrier in terminal. 3. Connect a 20 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to VD Signal in terminal. 4. Turn VR1 fully CW to set maximum amplitude on VT out terminal. Measure and record the waveforms on terminals VT out, VE out, VLP out, and Vo out in Table1. 5. Connect a 1 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to VD Signal in terminal. ____________________________________________________________________________ 65 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering 6. Repeat step 4. 7. Connect a 10 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to VD Signal in terminal. 8. Repeat step 4. 9. Connect a 50 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to VD Signal in terminal. 10. Repeat step 4. 11. Compare the waveforms on VD Signal in and Vo out terminals and write down your comment. Table-1 Non-coherent ASK demodulator (VC Carrier in = 500 kHz, 4V p-p) VD Signal in VT out VE out VLP out (TTL level) Waveform Waveform Waveform Vo out Waveform 20kHz 1kHz 10kHz 50Khz ____________________________________________________________________________ 66 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment -17 Title: To Implement Coherent ASK Demodulator Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-94004 3 - Module KL-94005 4 - Oscilloscope Procedure: Fig-1 Coherent ASK Demodulator Circuit 1. Complete the coherent ASK demodulator shown in Figure -1 by placing the jumpers in positions 1, 3, 4,7,8,9, 10, and 11. 2. Connect a 500 KHz, 4Vpp sine wave to VC Carrier in terminal. 3. Connect a 20 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to VD Signal in terminal. 4. Turn VR 1 fully CW to obtain the maximum amplitude on VT out terminal. The VT ____________________________________________________________________________ 67 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering out waveform is an ASK modulated wave. 5. Turn VR4 to make the VCO OUT signal frequency equal to the carrier frequency 500 KHz. 6. Turn VR5 to make the signals on VLO out and VT out in phase. 7. Turn VR2 to obtain maximum signal amplitude on Vx out. 8. Turn VR3 to obtain a 5Vpp signal on VLP out. 9. Measure and record the signal waveforms on terminals VT out, Vx out, VSO in, VLP out, and Vo out in Table 18-4. 10. Connect a 1 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to VD Signal in terminal. 11. Repeat steps 6 through 9. 12. Connect a 10 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to VD Signal in terminal. 13. Repeat steps 6 through 9. 14. Connect a 50 KHz, TTL-Level square wave from Function Generator TTL/CMOS out to VD Signal in terminal. 15. Repeat steps 6 through 9. 16. Compare the waveforms on Vo out and VD Signal in terminals and write down your comment. ____________________________________________________________________________ 68 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 Coherent ASK Modulator (VC Carrier in = 500 kHz, 4V p-p) VD Signal in (TTL Level) VT out Waveform Vx out Waveform VSO out Waveform VLP out Waveform Vo out Waveform 20kHz 1kHz 10KHz 50Khz ____________________________________________________________________________ 69 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment -18 Title: To Implement PSK/QPSK Modulator Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-94006 3 – Oscilloscope Procedure: A. 2fc Measurement (KL-94006) ____________________________________________________________________________ 70 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Fig-6 KL-94006 Module 1. Connect a 500Hz, TTL-Level digital signal to Digital DATA IN. 2. Connect scope CH1 IN to TP12 and CH2 IN to TP13. Measure and record the waveforms and frequencies in Table-1. Compare the phase difference between these two waveforms. 3. Connect scope CH1 IN to TP15. Measure and record the waveform and frequency ____________________________________________________________________________ 71 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering in Table-1. The frequency should be twice the carrier frequency, 2fc. B. Sync Cycle Measurement 4. Measure and record the waveforms and frequencies on the test points listed in Table-2. C. Control Shift Register Measurement 5. Connect scope CH1 IN to TP10 and CH2 IN to TP11. Measure and record the waveforms and frequencies in Table-3. 6. Repeat step 5 for digital signal frequencies 100Hz and 1 KHz to Digital DATA IN. 7. Recover the digital signal frequency to 500Hz. D. PSKlQPSK modulated Signal Measurement 8. Connect scope CH1 IN to PSK/QPSK OUT. Measure and record the waveform with the various TIME/DIV settings in Table -4. ____________________________________________________________________________ 72 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 2fc Measurement (KL-94006) Test Point Waveform & Frequency TP12 (CH1) TP13 (CH2) TP15 ____________________________________________________________________________ 73 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-2 Sync cycle Measurement Test Point Waveform & Frequency TP15 TP16 TP8 TP17 ____________________________________________________________________________ 74 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Table-3 Shift Register Measurement Digital DATA IN Frequency CH1 = TP10 Electrical Engineering Test Point CH2 = TP11 500Hz 100Hz 1kHz ____________________________________________________________________________ 75 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-4 PSK/QPSK modulated signal measurement Test Point PSK/QPSK OUT 2.5ms 1ms 500µs 250µs 100µs ____________________________________________________________________________ 76 Communication System Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Experiment -19 Title: To Implement PSK/QPSK Demodulator Equipment Required: 1 - Module KL-92001 2 - Module KL-94007 3 – Oscilloscope Procedure: A. Sync Cycle Detector Measurement (KL-94007 module) 1. Connect a 500Hz, TTL-Level square wave to the Digital DATA IN terminal. 2. Set DC voltage on TP4 to the values listed in Table -1. Using the scope, measure and record the waveforms and frequencies on TP5, TP6, TP7, and TP13 for each de setting value in Table -1. 3. Set DC voltage on TP4 to -5V. B. Full-wave Rectifier Measurement 4. Connect TTL-level square wave with the frequencies, listed in Table -2, to Digital DATA IN terminal. Using the scope, measure and record the waveforms and frequencies on TP2, TP3, and TP9 for each input frequency in Table -2. 5. Connect a 500Hz, TTL-level square wave to the Digital DATA IN terminal. C. 32fc, 4fc and 2fc Measurement 6. Measure the frequency on TP11 to obtain a frequency equal to 32fc by adjusting the VR3. Measure and record the waveforms and frequencies on TP11, TP8, and TP12 in Table -3. D. Shift Register Measurement 7. Measure and record the waveforms and frequencies on TP7, TP12, TP14, U7 Q2, and U7 Q3 in Table-4. E. Demodulator Output Measurement 8. Measure and record the waveforms and frequencies on DATA OUT and RX ClK OUT in Table -5. 9. Repeat step 8 for the Digital DATA IN frequencies of 100Hz and 1KHz. __________________________________________________________________________________ Communication System 77 Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Fig- KL-94007 Module __________________________________________________________________________________ Communication System 78 Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-1 Sync cycle detector measurement (KL-94007) TP4 DC Voltage Test Point TP5 TP6 TP7 TP13 -5Vdc -3Vdc -1Vdc 0Vdc +3Vdc Table-2 Full Wave rectifier measurement __________________________________________________________________________________ Communication System 79 Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad DC DATA IN Frequency (KL-94006) Electrical Engineering Test Point TP2 TP3 TP9 500Hz 100Hz 1Khz __________________________________________________________________________________ Communication System 80 Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-3 3fc, 4fc and 2fc measurement Test Point Waveform & Frequency TP11 (32fc) TP8 (2fc) TP12 (4fc) __________________________________________________________________________________ Communication System 81 Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Electrical Engineering Table-4 Shift register measurement Test Point Waveform & Frequency TP12 TP7 TP14 U7 Q2 U7 Q3 Table-5 Demodulator Output Measurement __________________________________________________________________________________ Communication System 82 Federal Urdu University of Arts Science & Technology Islamabad Digital DATA IN Frequency (KL-94006) Electrical Engineering Test Point DATA OUT RX CLK OUT 500Hz 100Hz 1kHZ __________________________________________________________________________________ Communication System 83