Chapter 1: Digital Data Representation and Communication
advertisement
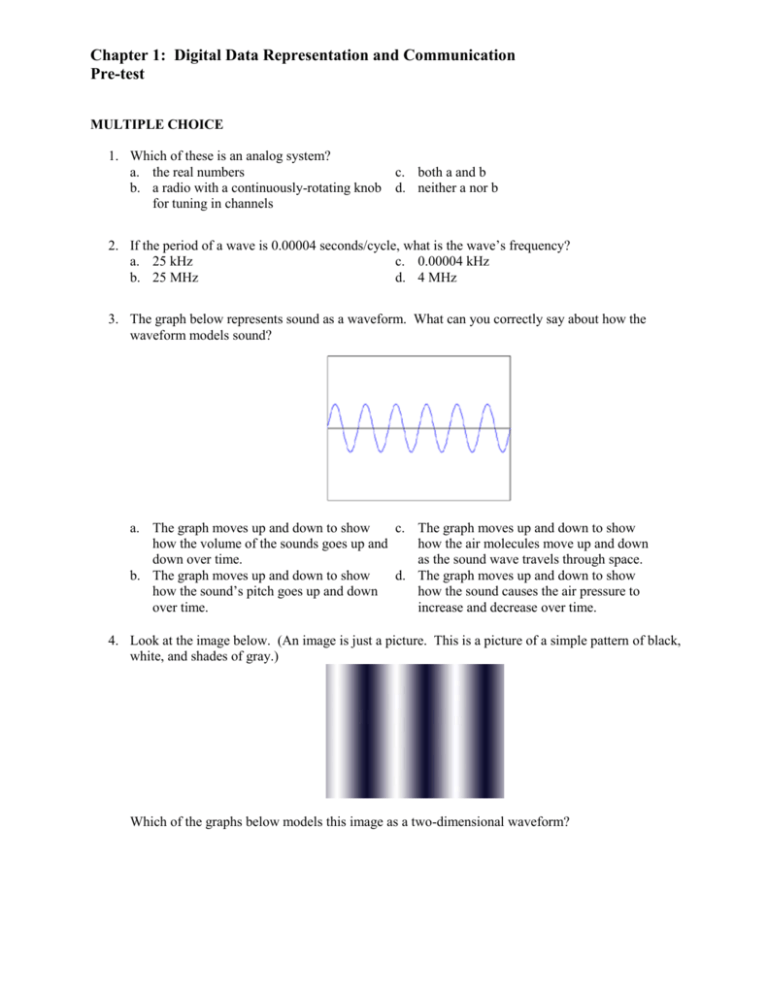
Chapter 1: Digital Data Representation and Communication Pre-test MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of these is an analog system? a. the real numbers b. a radio with a continuously-rotating knob for tuning in channels c. both a and b d. neither a nor b 2. If the period of a wave is 0.00004 seconds/cycle, what is the wave’s frequency? a. 25 kHz c. 0.00004 kHz b. 25 MHz d. 4 MHz 3. The graph below represents sound as a waveform. What can you correctly say about how the waveform models sound? a. The graph moves up and down to show c. The graph moves up and down to show how the volume of the sounds goes up and how the air molecules move up and down down over time. as the sound wave travels through space. b. The graph moves up and down to show d. The graph moves up and down to show how the sound’s pitch goes up and down how the sound causes the air pressure to over time. increase and decrease over time. 4. Look at the image below. (An image is just a picture. This is a picture of a simple pattern of black, white, and shades of gray.) Which of the graphs below models this image as a two-dimensional waveform? a. c. 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 -0.2 -0.4 -0.6 -0.8 -1 b. d. 5. What can you correctly say about the following waveforms? a. A, B, and C are the frequency components c. A, B, and C are the phases of D. of D. b. A, B, and C are the cycles of D. d. None of the above. 6. What is the cause of aliasing in digital media? a. a bit depth that is too small c. a sampling rate that is too low b. applying the Fourier transform too d. a wavelength that is too long frequently 7. Say that you want to digitally record a sound that has a highest frequency component of 800 Hz. According to the Nyquist theorem, what minimum sampling rate do you have to use to be sure that you don’t get sound aliasing? a. 800 Hz c. 400 Hz b. 1600 Hz d. 6400 Hz 8. If 10 bits are used to encode image samples, how many different sample values are possible? a. 1010 c. 102 10 b. 2 d. 10 9. What can you correctly say about a digital audio clip that has a wide dynamic range? a. it sounds very lively c. there’s a big difference between the loudest and the softest part of the clip b. the difference between high pitched and d. there’s a big difference between the low pitched sounds varies frequently highest note and the lowest note in the clip 10. What is the signal-to-quantization-noise ratio of a digital audio file quantized with 16 bits? a. about 16 decibels c. about 50 decibels b. about 32 decibels d. about 96 decibels 11. How many bits of data are generated for one minute of uncompressed audio file with a sampling rate of 44.1 kHz and 16 bits per sample for each of two stereo channels? a. about 81 Mb c. about 10,000,000 bits b. about 2.5 MB d. about 85,000 bytes 12. If a data signal has frequency components that range from 400 kHz to 1400 kHz, what is the width of the signal? a. It is impossible to tell from the c. 1000 kHz information given. b. 1400 kHz d. 2 * 1400 kHz 13. The definition of data rate is D = 2B; that is, the data rate equals twice the bandwidth of a signal (assuming that the signal has only two possible levels). Which of the statements below is (or are) true with regard to this formula? a. It is impossible to achieve this theoretical c. If more than two bits are communicated data rate because there is always noise per cycle, the data rate is actually larger introduced in the signal. than what is computed by the above equation. b. Bandwidth is measured in Hertz and data rate is measured in bits per second. d. All of the above are true. 14. If a data signal has a bandwidth of 20 MHz, how many bits can it send per second, assuming that there are 16 signal levels? a. 20,000,000 c. 320,000,000 b. 80,000,000 d. 160,000,000 15. If eight different signal levels can be communicated in a data signal, how many bits can be communicated in each individual signal? a. 2 c. 4 b. 3 d. 8 TRUE/FALSE 1. Both analog and digital data can be communicated by copper wire, coaxial cable, optical fiber, or airwaves. 2. Both analog and digital data can be modulated onto a carrier signal wave. 3. Bit rate and bandwidth are synonymous. 4. The bit rate of digital audio is a function of the speed of sound. 5. Decibels are measured in Watts.