fungi & plant review2 answers
advertisement
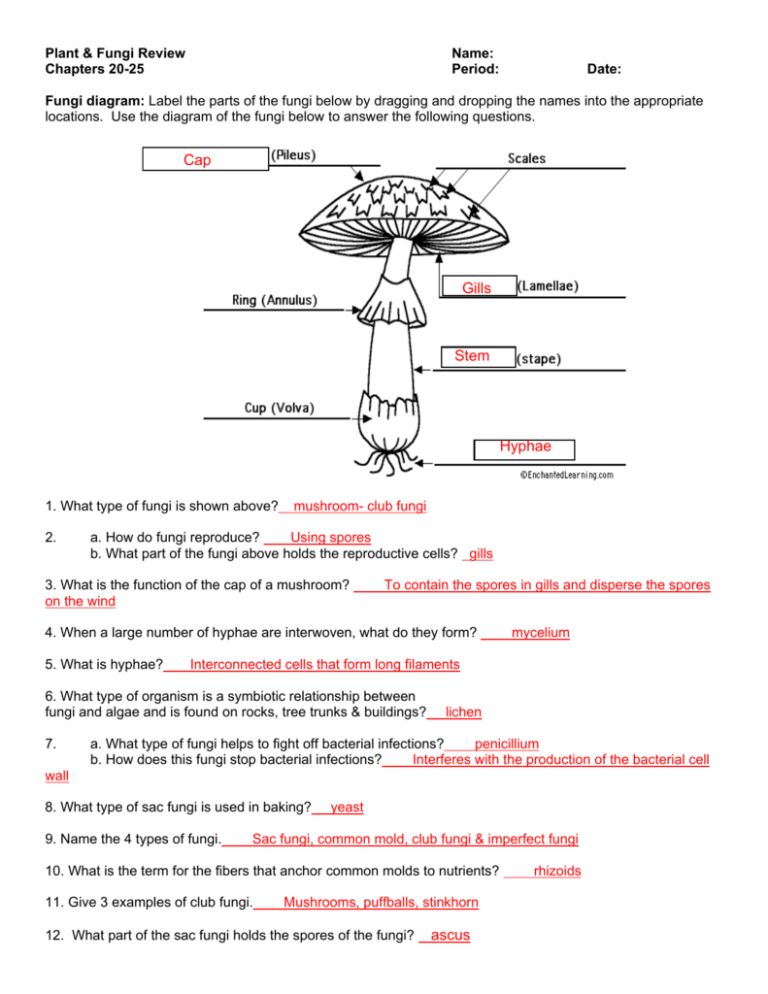
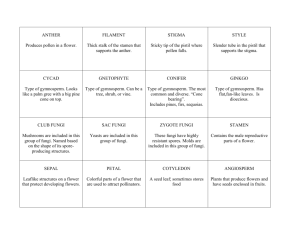
Plant & Fungi Review Chapters 20-25 Name: Period: Date: Fungi diagram: Label the parts of the fungi below by dragging and dropping the names into the appropriate locations. Use the diagram of the fungi below to answer the following questions. Cap Gills Stem Hyphae 1. What type of fungi is shown above? 2. mushroom- club fungi a. How do fungi reproduce? Using spores b. What part of the fungi above holds the reproductive cells? gills 3. What is the function of the cap of a mushroom? on the wind To contain the spores in gills and disperse the spores 4. When a large number of hyphae are interwoven, what do they form? 5. What is hyphae? Interconnected cells that form long filaments 6. What type of organism is a symbiotic relationship between fungi and algae and is found on rocks, tree trunks & buildings? 7. mycelium lichen a. What type of fungi helps to fight off bacterial infections? penicillium b. How does this fungi stop bacterial infections? Interferes with the production of the bacterial cell wall 8. What type of sac fungi is used in baking? 9. Name the 4 types of fungi. yeast Sac fungi, common mold, club fungi & imperfect fungi 10. What is the term for the fibers that anchor common molds to nutrients? 11. Give 3 examples of club fungi. Mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorn 12. What part of the sac fungi holds the spores of the fungi? ascus rhizoids Identify Fungi: Drag and drop the pictures of fungi in the appropriate categories below. Common Molds Club Fungi Sac Fungi Imperfect Fungi mildew bread mold athlete’s foot mushroom penicillium truffle yeast mushroom 1. How do yeast cells reproduce? budding 2. What category contains the human parasitic fungi? Imperfect fungi (athlete’s foot) 3. Fungi cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. What type of cell do they contain? eukaryotes 4. What is the main difference between plants and fungi? Fungi are heterotrophs with chitin in their cell walls and plants are autotrophs with cellulose in their cell walls 5. What type of carbohydrate is found in the cell walls of fungi? chitin Overview of Plants: Double click in the chart below and type: how the plant reproduces, if they are vascular or non vascular and examples of that type of plant. Drag and drop the pictures into the appropriate location. Category of Plant Bryophytes How do they reproduce? spores Vascular or Non-vascular? Examples non-vascular moss, hornworts & liverworts vascular ferns, horsetails vascular conifers, ginkgos, cycads vascular monocots & dicots Picture Seedless vascular Plants spores Gymnosperms seeds Angiosperms seeds 1. a. What is the difference between a bryophyte and seedless vascular plant? Bryophytes are non-vascular and seedless vascular are vascular b. What is similar between a bryophyte and seedless vascular plant? Both use spores for reproduction 2. a. What is the common ancestor to all plants? algae b. Name 2 pieces of evidence that support this organism as the common ancestor. Contain cell walls with cellulose, contian pigments similiar to chlorophyll, cell plate during cell division and extra glucose stored as starch 3. a. What is common between a gymnosperm and angiosperm? b. What is different between a gymnosperm and angiosperm? angiosperms have covered seeds in fruit Reproduce using seeds Gymnosperms have naked seeds in cones and Reproductive Methods of Plants: Match the pictures with the correct name of the plant below by dragging and dropping the words in the correct locations. 1. Ferns 2. Angiosperms 3. Gymnosperms 4. Bryophytes 5. a. What is the term for the round clusters found on the underside of the plant in picture #1? sorus b. What is inside these clusters? spores 6. a. The brown structures in picture #4 are the reproductive part of the plan, known as a capsule. What do you think the capsules contain? spores b. How are plants #1 and plants #4 different? Plant 1 is vascular and plant 4 in non-vascular 7. a. What is the term for the reproductive structure in picture #3? cones b. Is this structure male or female? female c. What is contained inside the structure in picture #3? seeds 8. a. What is the term for the reproductive structure in picture #2? b. Once this structure is fertilized, what will it become? fruit flower Plant Cells: In the chart below, type in the type of cell, its function in the plant and where it is found in the plant. Name of Cell: Parenchyma Name of Cell: Collenchyma Name of Cell: Sclerenchyma Function:perform photosynthesis Function:extra support to growing Function:extra support to non& store food parts of the plant growing parts of the plant Where found:leaves and all over Where found:where the plant the plant where photosynthesis grows- tips of roots and stems occurs Where found: where the plant does not grow- middles part of stems & roots Plant Structure: Label the parts of the plant below by dragging and dropping the parts of the plant in the appropriate locations. flower stem leaves roots storage Questions: Answer the following questions. 1. What type of plant is shown above? potato plant (dicot) 2. What type of tissue continually grows, such as the roots and top of the stem? meristematic 3. What type of tissue transports sugars and water through out the plant? Vascular (vein) 4. What is the term for the type of tissue that covers the outside surface of the plant? 5. If tissue is not dermal, meristematic or vascular, what type of tissue is it? dermal ground Functions: Double click ion the chart below and fill in the chart below by typing in the function of the following parts of the plant. Part of the Plant Stem Root Leaf Flower Function hold leaves up to the sun & transport water & sugars between roots & leaves absorb water & minerals and anchor plant to the ground perform photosynthesis to make glucose reproduction- to fertilize an egg (ovule) with sperm (pollen) to produce seeds Monocot or Dicot: For the following pictures, identify them as monocot or dicot by dragging and dropping the name in the correct location. 1. Monocot 2. Dicot 3. 4. Dicot 5. Dicot 6. Monocot 7. Monocot Dicot 8. Monocot 1. a. Give an example of a plant that is a monocot. Lily, grass b. How did monocots receive their name? they only have one cotyledon (part of the seed) 2. a. Give an example of a plant that is a dicot. Apple tree, rose b. How did dicots receive their name? they have 2 cotyledons (part of the seed) 3. a. What type of seedling is plant A? Has 1 leaf in seedling b. What type of angiosperm is plant A? monocot 4. a. What type of seedling is plant B? b. What type of angiosperm is plant B? Has 2 leaves in seedling dicot Plant A Plant B Flower Diagram: Label the parts of the flower below by dragging and dropping the labels in the appropriate location. petals anther stigma filament style ovary ovules sepals Anatomy of a flower: Identify the part of the flower that is being described in the chart below by double clicking in the chart and typing the answer. Anatomy sepals anther stigma filament ovules style ovary petals Function a sterile structure that is part of the leaves- protects the bud before it blooms into a flower part of the stamen that produces pollen that contain sperm part of the pistil that “catches” pollen with a sticky substance part of the stamen that connects the anther to the rest of the flower part of the pistil that contains the egg- once fertilized these become the seeds part of the pistil that connects the stigma to the ovary part of the pistil that contains ovules and become the fruit of the plant a sterile structure that uses its color to attract pollinators 1. What parts of the flower above make up the pistil? Stigma, style & ovary 2. What parts of the flower above make up the stamen? 3. Name 2 types of pollinators. Filament & anther Flies, bees, butterflies, animals 4. Name 3 methods of seed dispersal. Wind, water, sticky seed coats & fruit 5. a. What type of tissue transports water through out the plant? b. What direction does it flow? up c. How does the water move through the plant? transpiration 6. a. What tissue transports sugars through out the plant? b. What direction does it flow? Up & down xylem phloem