Flower Anatomy - The Fightin' Gnomes
advertisement
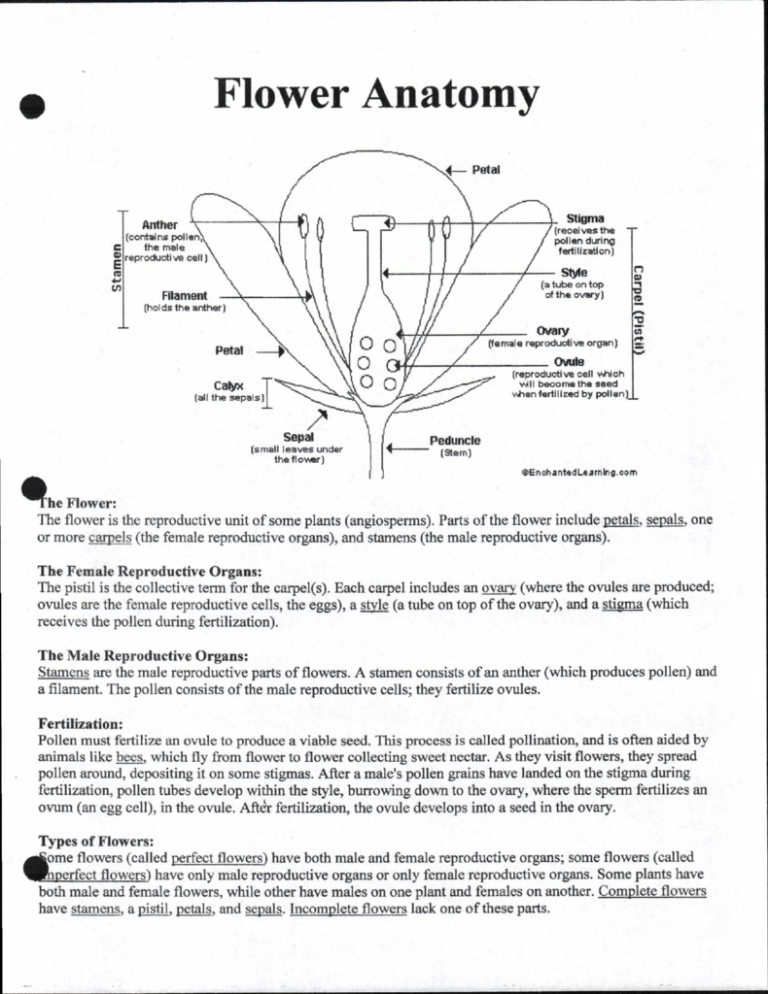
Flower Anatomy • 1— Petal Stigma Anther (receives the pollen during fertilization) (contains pollen, the male reproductive cell) Stile (a tube on top of the ovary) Filament 03 eD (holds the anther) Ovary (female reproductive organ) Petal rr Ovule (reproductive cell which will become the seed when fertilized by pollen) Calyx (all the sepals) Sepal (small leaves under the flower) Peduncle (Stem) @En chantedLearning.corn he Flower: The flower is the reproductive unit of some plants (angiosperms). Parts of the flower include petals, sepals, one or more carpels (the female reproductive organs), and stamens (the male reproductive organs). The Female Reproductive Organs: The pistil is the collective term for the carpel(s). Each carpel includes an ovary (where the ovules are produced; ovules are the female reproductive cells, the eggs), a style (a tube on top of the ovary), and a stigma (which receives the pollen during fertilization). The Male Reproductive Organs: Stamens are the male reproductive parts of flowers. A stamen consists of an anther (which produces pollen) and a filament. The pollen consists of the male reproductive cells; they fertilize ovules. Fertilization: Pollen must fertilize an ovule to produce a viable seed. This process is called pollination, and is often aided by animals like bees, which fly from flower to flower collecting sweet nectar. As they visit flowers, they spread pollen around, depositing it on some stigmas. After a male's pollen grains have landed on the stigma during fertilization, pollen tubes develop within the style, burrowing down to the ovary, where the sperm fertilizes an ovum (an egg cell), in the ovule. After fertilization, the ovule develops into a seed in the ovary. Types of Flowers: oime flowers (called perfect flowers) have both male and female reproductive organs; some flowers (called flowers) have only male reproductive organs or only female reproductive organs. Some plants have ilkbothperfect male and female flowers, while other have males on one plant and females on another. Complete flowers have stamens, a pistil, petals, and sepals. Incomplete flowers lack one of these parts. Flower Basics Name 1. Label the parts of the flower shown in the diagram below. 2. Identify each part of the flower described below using the words in the word list. - The female part of a flower - A small plant that is just starting to grow - The place where pollen develops and is stored - The female sex cell in a plant - Occurs when the sperm and egg cells unite - A sugary substance that attracts insects - The male sex cell in a plant - The male part of a flower - The stalk that supports the anther - The part of the pistil that receives the pollen - Part that connects the stigma and ovary Word List: Anther Fertilization Filament Fruit Imperfect Nectar Ovary Perfect Petals Pistil Pollen Seedling Sepals Stamen Stigma Style - Protective leaf-like enclosure for the flower bud - The ripened ovary of a plant that contains seeds - Flower that contains both male and female parts - Flower that lacks either male or female parts - The structures that make up the outside of the flower and may be colored or contain nectar or perfume glands Image: http://www.smithlifescience.com/SciFlowerDiagramBlank.jpg T. Trimpe 2010 Worksheet developed for use with the "Our Flowering World" video from United Streaming.








