The Bill of Rights (Amendments 1 – 10) http://bensguide.gpo.gov/m
advertisement
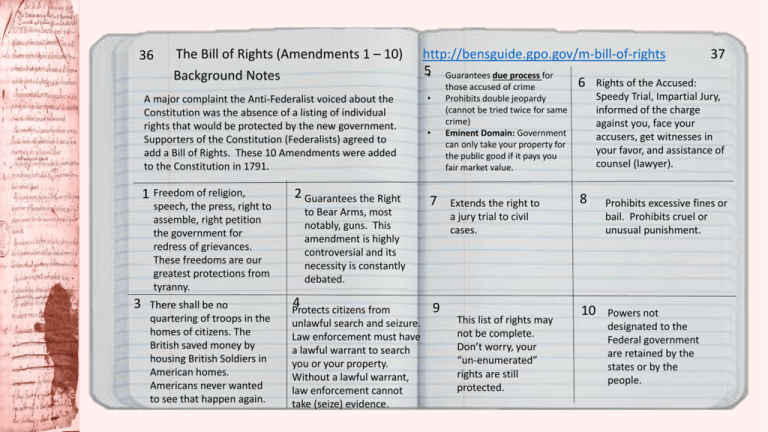
36 The Bill of Rights (Amendments 1 – 10) Background Notes A major complaint the Anti-Federalist voiced about the Constitution was the absence of a listing of individual rights that would be protected by the new government. Supporters of the Constitution (Federalists) agreed to add a Bill of Rights. These 10 Amendments were added to the Constitution in 1791. 1 Freedom of religion, speech, the press, right to assemble, right petition the government for redress of grievances. These freedoms are our greatest protections from tyranny. 3 There shall be no quartering of troops in the homes of citizens. The British saved money by housing British Soldiers in American homes. Americans never wanted to see that happen again. 2 Guarantees the Right to Bear Arms, most notably, guns. This amendment is highly controversial and its necessity is constantly debated. 4 Protects citizens from unlawful search and seizure. Law enforcement must have a lawful warrant to search you or your property. Without a lawful warrant, law enforcement cannot take (seize) evidence. http://bensguide.gpo.gov/m-bill-of-rights 37 5• Guarantees due process for 6 Rights of the Accused: those accused of crime • Speedy Trial, Impartial Jury, informed of the charge against you, face your accusers, get witnesses in your favor, and assistance of counsel (lawyer). Prohibits double jeopardy (cannot be tried twice for same crime) Eminent Domain: Government can only take your property for the public good if it pays you fair market value. • 7 9 Extends the right to a jury trial to civil cases. This list of rights may not be complete. Don’t worry, your “un-enumerated” rights are still protected. 8 10 Prohibits excessive fines or bail. Prohibits cruel or unusual punishment. Powers not designated to the Federal government are retained by the states or by the people.