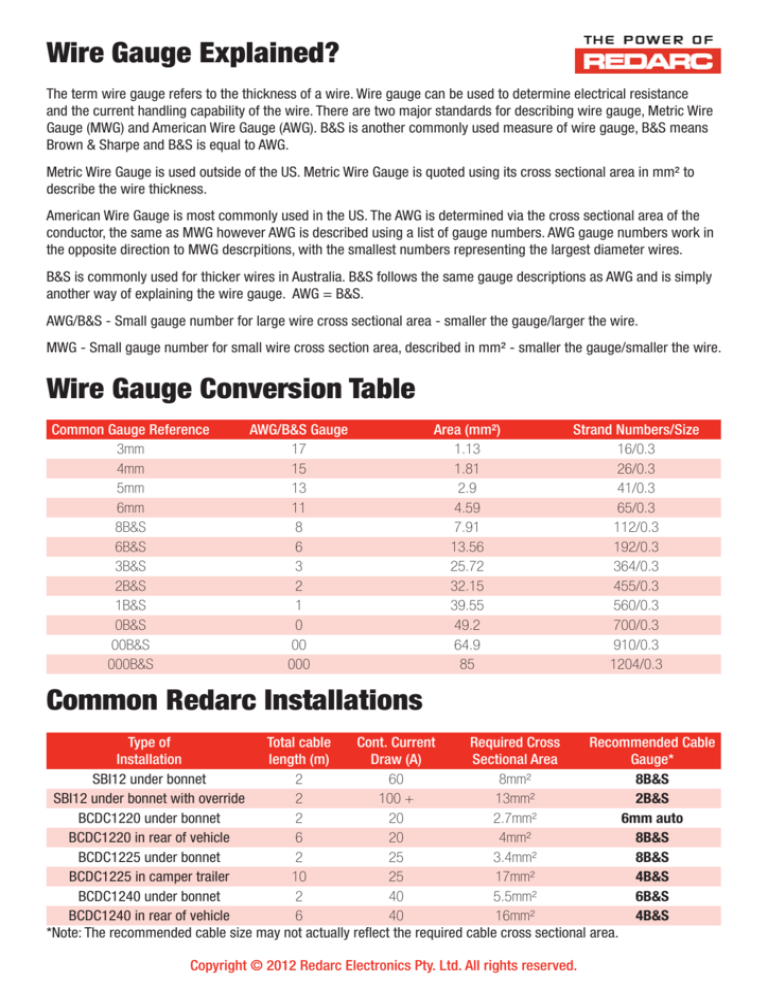
Wire Gauge Explained?
The term wire gauge refers to the thickness of a wire. Wire gauge can be used to determine electrical resistance
and the current handling capability of the wire. There are two major standards for describing wire gauge, Metric Wire
Gauge (MWG) and American Wire Gauge (AWG). B&S is another commonly used measure of wire gauge, B&S means
Brown & Sharpe and B&S is equal to AWG.
Metric Wire Gauge is used outside of the US. Metric Wire Gauge is quoted using its cross sectional area in mm² to
describe the wire thickness.
American Wire Gauge is most commonly used in the US. The AWG is determined via the cross sectional area of the
conductor, the same as MWG however AWG is described using a list of gauge numbers. AWG gauge numbers work in
the opposite direction to MWG descrpitions, with the smallest numbers representing the largest diameter wires.
B&S is commonly used for thicker wires in Australia. B&S follows the same gauge descriptions as AWG and is simply
another way of explaining the wire gauge. AWG = B&S.
AWG/B&S - Small gauge number for large wire cross sectional area - smaller the gauge/larger the wire.
MWG - Small gauge number for small wire cross section area, described in mm² - smaller the gauge/smaller the wire.
Wire Gauge Conversion Table
Common Gauge Reference
3mm
4mm
5mm
6mm
8B&S
6B&S
3B&S
2B&S
1B&S
0B&S
00B&S
000B&S
AWG/B&S Gauge
17
15
13
11
8
6
3
2
1
0
00
000
Area (mm²)
1.13
1.81
2.9
4.59
7.91
13.56
25.72
32.15
39.55
49.2
64.9
85
Strand Numbers/Size
16/0.3
26/0.3
41/0.3
65/0.3
112/0.3
192/0.3
364/0.3
455/0.3
560/0.3
700/0.3
910/0.3
1204/0.3
Common Redarc Installations
Type of
Total cable
Cont. Current
Required Cross
Recommended Cable
Installation
length (m)
Draw (A)
Sectional Area
Gauge*
SBI12 under bonnet
2
60
8mm²
8B&S
SBI12 under bonnet with override
2
100 +
13mm²
2B&S
BCDC1220 under bonnet
2
20
2.7mm²
6mm auto
BCDC1220 in rear of vehicle
6
20
4mm²
8B&S
BCDC1225 under bonnet
2
25
3.4mm²
8B&S
BCDC1225 in camper trailer
10
25
17mm²
4B&S
BCDC1240 under bonnet
2
40
5.5mm²
6B&S
BCDC1240 in rear of vehicle
6
40
16mm²
4B&S
*Note: The recommended cable size may not actually reflect the required cable cross sectional area.
Copyright © 2012 Redarc Electronics Pty. Ltd. All rights reserved.
Required Wire Gauge Chart
The below diagram will advise the minimum required wire gauge for a given cable length and the current draw or
wattage. Simply draw a line from the required cable length (meters or feet), to the required current draw or wattage
figure. Where the line passes through the gauge column will indicate the required wire gauge.
Watts
Amps
AWG/B&S
mm2
Ft
m
Amps
Watts
24V
AWG/B&S
mm2
Ft
m
12V
100
100
25
20
The example shows
a BCDC1220 install
with a total cable
length of 3 metres.
The chart suggests
a 4mm² cross
sectional area to
handle the 20A
maximum current
draw.
15
80
70
50
35
60
50
25
40
10
8
6
5
4
3
30
1
0.8
10
6
20
15
10
4
2.5
1.5
1
0.75
2
1.5
16
2/0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
50
40
30
0.5
20
25
20
400
15
300
10
20
15
200
8
150
6
5
10
8
6
5
4
5
100
700
600
500
3
100
4
80
3
60
50
80
60
50
40
50
35
30
25
16
20
1.5
1
2
20
0.8
6
4
10
2.5
1.5
1
5
30
3
10
15
2
40
120
95
70
0.75
0.5
5/0
150
4/0
3/0
2/0 100
0
80
2
60
4
50
6
40
4000
8
800
10
12
14
16
18
20
3
30
3000
2000
1500
1000
600
20
15
500
400
300
10
8
200
6
150
5
Gauge chart supplied by Ashdown-Ingram
How to Calculate Voltage Drop or Cable Size
Cable Cross Section
T = Temperature of
l = Total
cable
Length of
wire (not shroud)
n = Number of
individual strands
of wire
A
I
d = Diameter
= Cross Sectional
Area
of wire
strands
= Current Draw
Vd= Voltage Drop
Cross Sectional Area (cable size)
A=
pd2 Gn
4
Voltage drop (at 25°C)
Vd = l G I G 0.017
A
Cross Sectional Area (cable size)
A = l G I G 0.017
Vd
Voltage drop (other temperatures)
Vd = lGIG0.017 G(1+0.004G(T-25))
A
Want an easier way to work out Voltage Drop or required Cable Size?
www.redarc.com.au/handy-hints/calculator/