SCH4C Activity Series Metals and Halogens
advertisement

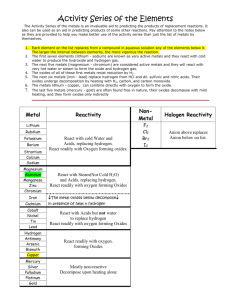
Activity Series of Metals Metal Lithium Potassium Strontium Calcium Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Zinc Chromium Iron Cadmium Cobalt Nickel Tin Lead Symbol Li K Sr Ca Na Mg Al Zn Cr Fe Cd Co Ni Sn Pb Hydrogen gas H2 Antimony Arsenic Bismuth Copper Mercury Silver Paladium Platinum Gold Sb As Bi Cu Hg Ag Pd Pt Au Reactivity MOST Reactive displaces H2 gas from water, steam and acids and forms hydroxides displaces H2 gas from steam and acids and forms hydroxides displaces H2 gas from acids only and forms hydroxides included for comparison combines with O2 to form oxides and cannot displace H2 found free in nature, oxides decompose with heating LEAST Reactive Activity Series of Halogens Halogen Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine Symbol F Cl Br I Reactivity MOST Reactive LEAST Reactive The Activity Series of the metals is an invaluable aid to predicting the products of replacement reactions. It also can be used as an aid in predicting products of some other reactions. Pay attention to the notes below as they are provided to help you make better use of the activity series than just the list of metals by themselves. 1. Each element on the list replaces from a compound any of the elements below it. The larger the interval between elements, the more vigorous the reaction. 2. The first five elements (lithium - sodium) are known as very active metals and they react with cold water to produce the hydroxide and hydrogen gas. 3. The next four metals (magnesium - chromium) are considered active metals and they will react with very hot water or steam to form the oxide and hydrogen gas. 4. The oxides of all of these first metals resist reduction by H2. 5. The next six metals (iron - lead) replace hydrogen from HCl and dil. sulfuric and nitric acids. Their oxides undergo reduction by heating with H2, carbon, and carbon monoxide. 6. The metals lithium - copper, can combine directly with oxygen to form the oxide. 7. The last five metals (mercury - gold) are often found free in nature, their oxides decompose with mild heating, and they form oxides only indirectly.