Mirabilis jalapa - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
advertisement
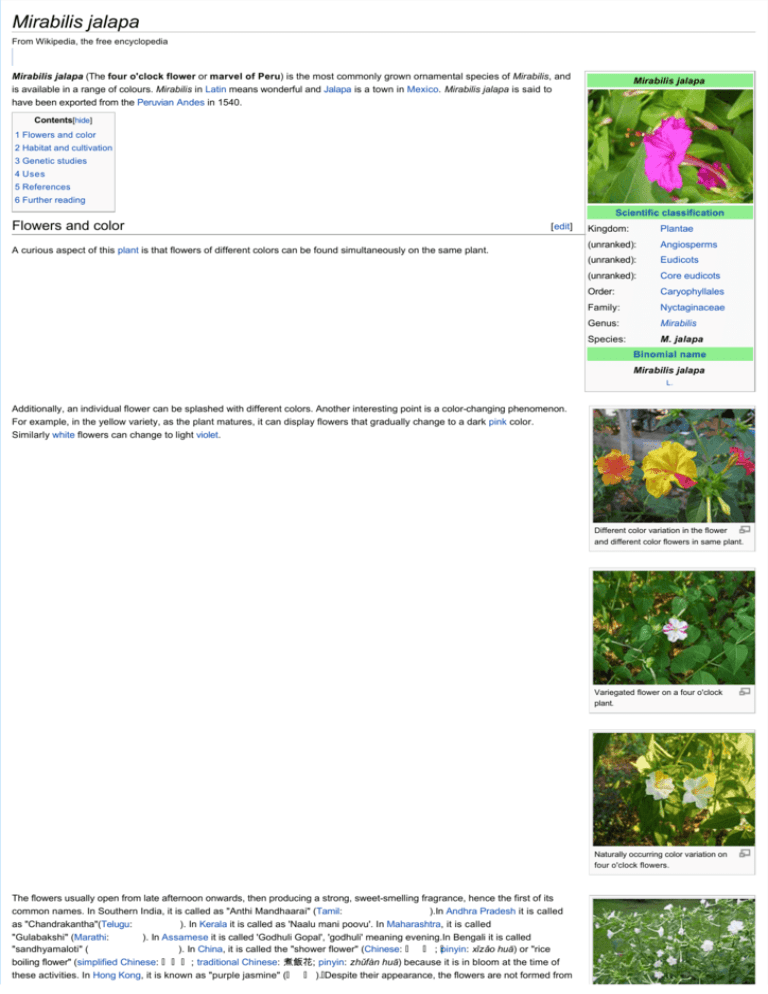
Mirabilis jalapa From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Mirabilis jalapa (The four o'clock flower or marvel of Peru) is the most commonly grown ornamental species of Mirabilis, and is available in a range of colours. Mirabilis in Latin means wonderful and Jalapa is a town in Mexico. Mirabilis jalapa is said to have been exported from the Peruvian Andes in 1540. Mirabilis jalapa Contents[hide] 1 Flowers and color 2 Habitat and cultivation 3 Genetic studies 4 Uses 5 References 6 Further reading Scientific classification Flowers and color [edit] A curious aspect of this plant is that flowers of different colors can be found simultaneously on the same plant. Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Eudicots (unranked): Core eudicots Order: Caryophyllales Family: Nyctaginaceae Genus: Mirabilis Species: M. jalapa Binomial name Mirabilis jalapa L. Additionally, an individual flower can be splashed with different colors. Another interesting point is a color­changing phenomenon. For example, in the yellow variety, as the plant matures, it can display flowers that gradually change to a dark pink color. Similarly white flowers can change to light violet. Different color variation in the flower and different color flowers in same plant. Variegated flower on a four o'clock plant. Naturally occurring color variation on four o'clock flowers. The flowers usually open from late afternoon onwards, then producing a strong, sweet­smelling fragrance, hence the first of its common names. In Southern India, it is called as "Anthi Mandhaarai" (Tamil: ).In Andhra Pradesh it is called as "Chandrakantha"(Telugu: ). In Kerala it is called as 'Naalu mani poovu'. In Maharashtra, it is called "Gulabakshi" (Marathi: ). In Assamese it is called 'Godhuli Gopal', 'godhuli' meaning evening.In Bengali it is called "sandhyamaloti" ( ). In China, it is called the "shower flower" (Chinese: ; pinyin: xǐzǎo huā) or "rice boiling flower" (simplified Chinese: ; traditional Chinese: 煮飯花; pinyin: zhǔfàn huā) because it is in bloom at the time of these activities. In Hong Kong, it is known as "purple jasmine" ( ). Despite their appearance, the flowers are not formed from petals – rather they are a pigmented modification of the calyx. The flowers are pollinated by long­tongued moths of the Sphingidae family, such as the sphinx moths or hawk moths and other nocturnal pollinators attracted by the fragrance.[1] Habitat and cultivation A four o'clock plant in full bloom. [edit] M. jalapa hails from tropical South America, but has become naturalised throughout tropical and warm temperate regions. In cooler temperate regions, it will die back with the first frosts, regrowing in the following spring from the tuberous roots. The plant does best in full sun. It grows to approximately 0.9 m in height. The single­seeded fruits are spherical, wrinkled and black upon maturity (see picture), having started out greenish­yellow. The plant will self­seed, often spreading rapidly if left unchecked in a garden. Some gardeners recommend that the seeds should be soaked before planting, but this is not totally necessary. In North America, the plant perennializes in warm, coastal environments, particularly in USDA Zones 9–10. Genetic studies [edit] Around 1900, Carl Correns used the four o'clock as a model organism for his studies on cytoplasmic inheritance. He used the plant's variegated leaves to prove that certain factors outside the nucleus affected phenotype in a way not explained by Mendel's theories.[2] Correns proposed that leaf color in Mirabilis was passed on via a uniparental mode of inheritance.[2] Also, when red­flowered plants are crossed with white­flowered plants, pink­flowered offspring, not red, are produced. This is an exception to Mendel's Law of Dominance, because in this case the red and white genes are of equal strength, so neither can dominate the other. Uses [edit] The flowers are used in food colouring. The leaves may be eaten cooked as well, but only as an emergency food.[3] An edible crimson dye is obtained from the flowers to colour cakes and jellies.[3] In herbal medicine, parts of the plant may be used as a diuretic, purgative, and for vulnerary (wound healing) purposes. The root is believed an aphrodisiac as well as diuretic and purgative. It is used in the treatment of dropsy. The leaves are used to reduce inflammation. A decoction of them (mashing and boiling) is used to treat abscesses. Leaf juice may be used to treat wounds. Powdered, the seed of some varieities is used as a cosmetic and a dye.[3] The seeds are considered poisonous.[4] References 1. 2. 3. 4. [edit] ^ http://www.botgard.ucla.edu/html/membgnewsletter/Volume4number2/Theplantsthatlovehawkmoths.html ^ a b Miko, I. Non­nuclear genes and their inheritance. Nature Education 1(1), (2008) ^ a b c http://www.pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Mirabilis%20jalapa ^ http://www.bbc.co.uk/dna/h2g2/A774704 Seed Further reading [edit] Correns, C. Vererbungsversuche mit blass (gelb) grünen und buntblättrigen Sippen bei Mirabilis, Urtica und Lunaria. ZIAV 1, 291–329 (1909) Pierce, B. Genetics: A Conceptual Approach, 2nd ed. (New York, Freeman, 2005) Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Mirabilis jalapa Plants portal Categories: Night­blooming plants | Mirabilis | Root vegetables | Garden plants