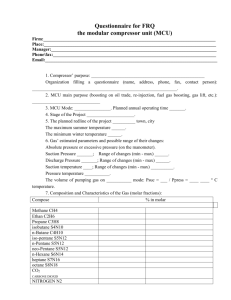
Q1. What do you understand by refrigeration? Define the terms, Unit
advertisement

Q1. What do you understand by refrigeration? Define the terms, Unit of refrigeration and Enumerate refrigeration system. Q2.Method of refrigeration in details. Q3 Define the open and closed air refrigeration and reversed Carnot cycle. Q4. What do you understand by aircraft refrigeration system? And classification of Q5.What do you mean by dry air rated temperature? Q5.Limitation of Carnot cycle with Air or Gas as Refrigerant. Q6.A Carnot refrigerator has working temperature of -30°C and 35°C.If it operates withR-12 as a working fluid, calculate:1.Isentropic compression work 2. Refrigeration effect 3.Heat rejected per unit mass of the refrigerant 4. COP of the cycle If an actual refrigerator has a COP which is 75% of that of the ideal Carnot cycle, calculate the power consumption and heat rejected to the surrounding per ton of refrigeration. Q7..20 tons of "Fish" are required to be stored in a cold storage plant at a temperature of -10°C. The specific heat of fish above freezing point is 2.94KJ/kg°C and below freezing point of fish is 1.25KJ/kg°C. The freezing point of the fish is -3°C and its latent heat is 233KJ/kg. if the cooling is achieved in 10 hours . Calculate the capacity of the refrigerating plant and the Carnot cycle COP between the temperature range. Q8. a closed cycle air refrigeration system, air is drawn from at -5°C and 1bar and compressed to 6 bar. The air is cooled to 20°C and then expanded to 1bar. To produce 10 TR, Find the mass flow rate of air, COP and Power required running the compressor. Q9.An air refrigeration system operating on bell-Coleman cycle draws air from a cold chamber at pressure of 1bar and temperature 1 0°C.it is then compressed in compressor up to a pressure of 5bar and after being cooled at constant pressure up to a temperature of 40°C,it enter the expander. Assuming both compression and expansion processes to be isentropic, calculate the COP of the system. Take Cp =1 .005KJ/kgK and γ =1.4 Q10.In the air cooling system of a jet aircraft, air is bled from the engine compressor at 3bar and it is cooled in a heat exchanger to 105°C. it is expanded to .69bar in air turbine, Isentropic efficiency of the process being 85%. The air is then delivered to cockpit and leaves the aircraft at 27°C. Calculate the temperature at which the air enters the cockpit and mass flow of air required for refrigerating effect of 4KW. If the air turbine is used to help to drive the auxiliaries, calculate its contribution in power. Q11.Bootstrap air refrigeration system is used for an aero plane to take 10TR of refrigeration load. The ambient air condition is 15°C and 0.9bar. This air is rammed isentropic ally to pressure of 1.1bar.The pressure of air bled off the main compressor is 3.5bar and this is further compressed in secondary compressor to a pressure of 4.5bar. The isentropic efficiency of both the compressor is 90% and that of cooling turbine is 85%. The effectiveness of both the heat exchanger is 0.6. If the cabin is to be maintained at 25°C and the pressure in the cabin is 1 bar, Find: a. Mass of air passing through the cabin.B.Power used for refrigeration system C.COP of the system Draw the schematic and t-s diagram for the system take, γ=1 .4,CP=1KJ/kgK, Q12.Th e reduced ambient air cooling system is used for an aircraft speed of 1200km/h. It uses two cooling turbines, a heat exchanger and a cooling air fan which is driven by the power output of both the cooling turbine. Following data is available: a. Ambient pressure and temperature is 0.5bar, -23°C b. Ram efficiency is 100% c. Main compressor pressure having isentropic efficiency of 85% and pressure is4 bar. d. Temperature of the cabin air cooled in heat exchanger is 60°C e. Pressure of ram air after expansion in cooling turbine having isentropic efficiency of 80% is 0.9bar. f. Pressure of cabin expanded in cooling turbine having isentropic efficiency is 80% and pressure is 1bar g. Cabin temperature is 25°C Determine 1 .Mass flow rate of air supplied t o cabin for a refrigeration load of 30TR 2. Mass flow rate of ram air into heat exchanger if its temperature rise is Limited to 16°C. 3. Combined output of cooling turbines. 4. COP of system Take Cp=1KJ/kgK Q14.A regenerative air cooling system is employed for a supersonic aircraft which require 2.5 TR. The ambient conditions are at 0.6bar and -3°C.The diffuser raise the pressure to 1. 1bar with 100% diffuser efficiency. The ram air is compressed in the main compressor up to 4.4 bar pressure. The ram air is bled off to a heat exchanger of 65% effectiveness and then passed to cooling air fan from where it is discharged to waste. While, air bled from main compressor passes to the ram air heat exchanger where it is cooled by ram air .This cooled air from heat ex changer passes to cooling by the air bled from cooling turbine after expansion up to a temperature of 57°C in the regenerative heat exchanger and the bled air is heated up to 97°C before discharge to atmosphere. The isentropic efficiency of the compressor and cooling turbine are 90% and 82% respectively. If the cabin pressure is to be maintained at bar and, 25°CFind:a. Aircraft velocity in kmph. b. mass of air bled for regeneration. Mass flow rate of air from compressor in kg/min d.COP of the system Take γ=1 .4, Cp=1 .0 KJ/kgK Q. 15. A plane moving with a speed of M/3 uses simple air refrigeration system with ambient conditions of 0.5 bars and -5°C. The pressure ratio in the main compressor is 0.85. The compressed air is cooled to a temperature which is 5°C above the rammed air temperature. The air is expended to cabin pressure of 1bar in the turbine having isentropic efficiency 0f 0.9. If the air leaves cabin at 25C, find 1) COP (2)Mass flow rate of air for a system of 50TR capacity Take γ=1.4Cp=1.0 KJ/kgK Q.16.A refrigeration system working on reversed Brayton cycle operates 1 bar and 5 bar .the temperature at the inlet to the compressor and expander are 30°C and 40°C, respectively. Isentropic efficiency for the compressor is 0.8 and the same for the expansion is 0.9. If the capacity of the system is 5 tons of refrigeration, determine:(1) Mass flow rate of refrigerant (air) (b) Power input to the compressor Take γ=1 .4, Cp=1 .004 KJ/kgK Q.1 6.Discuss the effect of the variation of evaporator and condenser temperature on the COP of the Carnot cycle. Q.1 7. In a Bootstrap air refrigeration system of an air craft, the ram air temperature and pressure are 17°C and 1.05 bars, respectively. Air leaving the main compressor at 4 bars is cooled to 27°C using rammed air. This air is then compressed in the auxiliary compressor (driven by the cooling turbine) and again cooled to 27°C in auxiliary heat exchanger using rammed air. Finally expansion takes place to cabin pressure of 1.01 bars and air leaves the cabin at 25°C. Determine the maximum pressure and COP of the system. Take γ=1 .4, Cp=1 .004 KJ/kgK Q.1 8. A Bell Coleman refrigerator operates between pressure limits of 1.1 bar and 5 bar. The temperature at the suction to the compressor, and inlet to the expander are 27 °C. and 37°C, respectively. Isentropic efficiencies of the compressor and expander are 0.8 and 0.82, respectively. Determine the power input to the compressor, if the refrigerator, if the refrigerator produces cooling at the rate of 50TR. Take γ=1 .4, Cp=1 .004 KJ/kgK Q.19.What do you understand by Dry Air Rated Temperature (DART)? What are the limitations of Carnot cycle with a gas as the working fluid? What are advantages of an air cycle with regards to its application in aircraft refrigeration? Q20.What is the basic difference between open and closed air refrigeration cycle? Describe a Bell Coleman or reversed joule air refrigeration cycle with help of neat labelled sketch and also explain the basic difference between this cycle and a reversed Carnot air refrigeration cycle. Q21. A Simple aircraft refrigeration system has to undertake a load of 20TR. The ambient pressure and temperature are 0.9 bar and 22°C respectively. The pressure of air is increased to 1 bar due to isentropic ramming action. The air is further compressed in a compressor up to 3.5bar and then cooled in a heat exchanger up to 72°C. Finally the air is passed through a cooling turbine and then supplied to the cabin a pressure of 1.03 bars. The air leaves the cabin at 25°C. Calculate the power required and COP of the system Take γ=1.4, Cp=1.005 KJ/kgK Q.22.Describe the operation of a Bootstrap air cycle system for aircraft applications with the help of its block diagram and a temperature –entropy diagram Q.23. A plane moving with a speed of M/3 uses simple air refrigeration system with ambient conditions of 0.5 bars and -5°C. The pressure ratio in the main compressor is 0.85. The compressed air is cooled to a temperature which is 5°C above the rammed air temperature. The air is expended to cabin pressure of 1bar in the turbine having isentropic efficiency of 0.9. If the air leaves cabin at 25°C, find (1) COP (2) Mass flow rate of air for a system of 50TR capacity. Take γ=1.4, Cp=1.0 KJ/kgK Q.24.An air refrigeration system operating on bell-Coleman cycle draws air from a cold chamber at pressure of 1bar and temperature 10°C.it is then compressed in compressor up to a pressure of 5bar and after being cooled at constant pressure up to a temperature of 40°C,it enter the expander. Assuming both compression and expansion processes to be isentropic, calculate the COP of the system. Take Cp =1.005KJ/kgK and γ =1.4 Q25.In the air cooling system of a jet aircraft, air is bled from the engine compressor at 3 bars and it is cooled in a heat exchanger to 105°C. It is expanded to .69 bars in air turbine, isentropic efficiency of the process being 85%. The air is then delivered to cockpit and leaves the aircraft at 27°C. Calculate the temperature at which the air enters the cockpit and mass flow of air required for refrigerating effect of 4KW. If the air turbine is used to help to drive the auxiliaries, calculate its contribution in power.