ACOELOMATES and PSUEDOCOELOMATES Be sure you know
advertisement

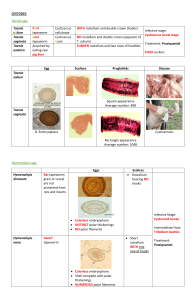
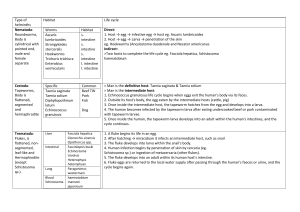
BIO 165 General Zoology R. Walter, Instructor Summer 2004 ACOELOMATES and PSUEDOCOELOMATES Be sure you know the classification, habitat, important structures, and key concepts for these organisms Resources o Lab book Exercises 9 (pgs. 135-152) and 10 (pgs. 157-166) o Textbook Chapters 14 and 15 Taxonomy Acoelomates Kingdom Animalia Phylum Platyhelminthes Class Turbellaria (free-living flatworms) Example: Dugesia (planaria) Class Trematoda (flukes) Examples: Clonorcus (live fluke), Schistosoma (blood fluke) Class Cestoda (tapeworms) Example: Taenia (dog tapeworm) Psuedocoelomates Kingdom Animalia Phylum Nematoda (free-living nematodes) Examples: Ascaris (intestinal roundworm), Trichinella, Tubatrix Phylum Rotifera Example: Philodina Key Concepts: proboscis, scolex, pharynx, rostellum, stobila, proglottids, corona, parthenogenesis Structures to Identify for Practical Acoelomates o Dugesia (Live specimens, slide, model) Whole mount slide: Eyespot, auricle, anterior & posterior trunk of intestine, and the pharynx (use Figure 9-1 as a guide) Cross section slide: ventral nerve cord, diverticula of intestines, ciliated epidermis, anterior trunk of the intestines, parenchyma cells, area of the body the cross section was taken from. (use Figure 9-2 in your lab book as a guide) o Clonorcus ( slide, model) Whole mount slide: oral sucker, mouth, pharynx, intestine, uterus, anterior and posterior testes. (use Figure 9-3 in your lab book as a guide). o Taenia ( slides, model) Slide: Rostellum with hooks, sucker, and the neck. (use Figure 9-7 in your lab book as a guide) Psuedocoelomates o Ascaris ( preserved specimens, model) Model: mouth, pharynx, pseudocoel, intestine, oviducts, vas deferens, spicule, and anus (Use Figure 10-1 as a guide). Cross section slide: intestine, cuticle, pseudocoel, longitudinal muscles, uterus with eggs. Make sure you can tell male verses female cross sections Study Lab Book Figures: 9-1, 9-2, 9-3, 10-2, 10-5, 10-7, pie-charts exercises 9 and 10. Learning Activities Acoelomates Dugesia (Planarians) Read pages 136-140 in your lab book 1. Observe the live specimen using your dissecting scope. Observe the feeding behavior and movement of the Planarian. *Make notes concerning its movement and speed. Compare to the Protozans you observed in lab #5. 2. Observe the whole mount slides of the Planarian using your dissecting microscope and/or your compound microscope. Draw the specimen and label the important structures (Eyespot, auricle, anterior & posterior trunk of intestine, and the pharynx) View the Dugesia slides (cross sections) using your compound light microscope. Draw the three cross sections and label the important structures. (ventral nerve cord, diverticula of intestines, ciliated epidermis, anterior trunk of the intestines, parenchyma cells, area of the body the cross section was taken from) Clonorcus (liver fluke) Read page 144 in your lab book. 1. Observe the whole mount slide using your compound light microscope and the model of the liver fluke on the back table. 2. Draw the specimen and label the important structures. (oral sucker, mouth, pharynx, intestine, uterus, anterior and posterior testes) Taenia (Tapeworm) Read pages 148-152 in your lab book. 1. Observe the model of the tapeworm on the back table. Observe the slides of the Taenia scolex. Observe the preserved specimens. 2. Draw a picture of the tapeworm scolex. Label the important features. (rostellum with hooks, sucker, and the neck) 3. Answer the following questions. 1. What is the difference between a proglottid and a strobila? 2. How long is the preserved specimen? 3. Where do you find gravid proglottids? 4. Is a tapeworm monoecious or dioecious? Psuedocoelomates Ascaris (Roundworms) Read pages 157-160 in your lab book. 1. Observe the preserved specimens and the model located on the back table. 2. Observe slides containing cross sections of male and female Ascaris. 3. Draw the cross sections and label important structures. (intestine, cuticle, pseudocoel, longitudinal muscles, uterus with eggs. Make sure you can tell male verses female cross sections) Identify the Unknowns on the back table 2