Nematode notes
advertisement

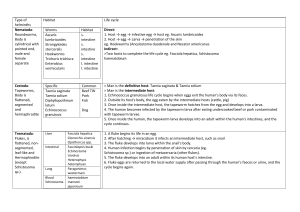
Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) • Bilateral symmetry • Acoelomate – Lack a body cavity(coelom) • 3 Layers : endoderm,ectoderm,mesoderm • Gastrovascular cavity • Mouth – one opening • Cephalization-nerves and sense organs at anterior end Class Turbellaria Includes marine worms & planarians *Most free living • PLANARIAN • Movement: cilia on ventral surface/ muscle contractions • Digestive System: • Feeding: suction of pharynx (middle of body) • Gastrovascular cavity • No Respiratory/ Circulatory system: diffusion • Nervous System: • Ganglia (simple brain) , 2 Nerve cords. Eyespot(senses light) • Excretory System: • Flame cells- remove fluid waste • Reproduction: • Sexual- hermaphrodite, cross fertilize • Asexual- regeneration Class Trematoda -flukes (parasitic) • Leaf-shaped • Sucks blood, cell fluids • Sheep liver fluke: – 2 hosts: sheep, snail – Larva develop inside snail – Sheep eats grass with larva Blood fluke Schistosoma causes disease Schistosomiasis • Class Cestoda • Tapeworm • Parasite • Body: absorbs nutrients; tegument/cuticle prevents parasite from being digested by host • Scolex- hooks and suckers that attach to intestinal wall (no mouth) • Proglottid- segment containing reproductive organs Life cycle of beef tapeworm Life cycle of beef tapeworm • Cow eats grass contaminated with eggs • Larva hatch and bore into intestine and enters bloodvessel • Burrow into muscle and form a cyst • Human eats beef that has not been cooked properly with cyst in it • Adult tapeworm forms in human’s intestine • Takes nutrients • Proglottid breaks off and eliminated in waste Prevention: Worm livestock USDA inspection Cook meat Dog/Cat Tapeworm • The tapeworm is transmitted to dogs and cats that ingest fleas (fleas eat tapeworm eggs) or eat wildlife / rodents infested with tapeworms or fleas. Proglottids in fur below tail Tapeworm in fish/ heron http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dy4cQO N7-JU&list=PLBA01CF012057626A Phylum Nematoda (roundworms) • Pseudocoelom (false cavity): located between endoderm and mesoderm • Fluid filled • O2, CO2, nutrients diffuse into fluid) • Two openings : mouth and anus (tube in a tube) • Free living (most) : • live in all types of soil ( handful contains thousands): Most numerous animal on earth. • Feed on bacteria, fungi, other nematodes, organic matter • Parasitic • Beneficial as a natural pest control • worm enters insect larva > worm releases bacteria > bacteria multiply/poison > larva dies Infected root Harmful Reduce plant vigor Ascaris life cycle • Immature worms hatch • from eggs in stomach > • Intestine(larva) > to lungs • Coughed up, • swallowed, return to intestine(mature to adult) • Eggs exit through feces Tremors movie trailer http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=liJfZvX diTE Ascaris dissection http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7RAoJ_2 W5ghttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7RA oJ_2W5g