ACOELOMATE EUTROCHOZOA 1.a. "Planaria" really is a common
advertisement

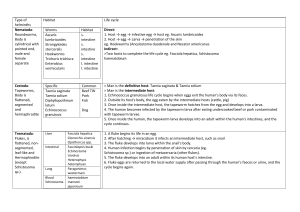
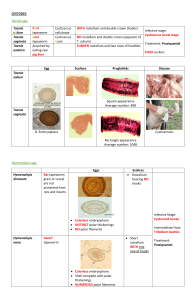
ACOELOMATE EUTROCHOZOA 1.a. "Planaria" really is a common name for a group of flat worms. Students generally examine a member of the genus, Dugesia, when studying planarians. Examine the living culture of planarians. What differences can you see between them? Use the bright light from a dissecting microscope and direct it laterally into a Petri dish with a living planarian. Describe its behavior. If you have enough time, introduce a small piece if liver into the dish. Watch the animal feed. 1.b. Look at a whole mount slide of Dugesia. Find the auricles, ocelli, proboscis, intestinal branches, epidermis, nerve cord. Add and/or label these into the drawing below. 1.c. Fine the same structures in a cross section slide of Dugesia. 2.a. Find the Sheep Liver Fluke, Fasciola hepatica, on a whole mount slide. Add a ventral sucker, an oral sucker, a mouth, pharynx, ovary, uterus, and testes to the drawing below. 2.b. Now locate slides of other parts of the Fasciola life cycle: • Eggs • Miricidia • Sporocysts • Cercariae • Metacercariae How does each one function in the life cycle? 2.c. Examine living cercariae as they emerge from snails in a finger bowl. Describe the behavior. 3.a. Find a slide of Schistosoma (male and female). How do they differ? Find the mouth, oral sucker, ventral sucker and gynecophoral groove. 3.b. How does the life cycle of Schistosoma differ from that of Fasciola? 4.a. Taenia is a common tapeworm. Add a scolex, rostellum, hooks, and suckers to the drawing below. 4.b. Sketch a gravid proglottid in the space below. 4.c. Outline the life cycle of Taenia and similar tapeworms like Dipylidium below. 5. Now look at Echinococcus. How does this one differ from .Taenia and Dipylidium? 6.a. Examine a preserved nemertine. How does this animal resemble a platyhelminth? 6.b. In what important way(s) does a nemertine differ from a platyhelminth?