Chapter 21-Mosses and Ferns

Date:___________________________ Period:______Name:_________________________
PLANT BIOLOGY: Mosses and Ferns
Ch. 21.1: Plants Invade the Land
I. Demands of Life on Land
The demands…. What land plants must do…
Provide cells with a constant
______________
___________________________________. a. find water b. _____________ _____________ to all cells. c. protect against __________________
_________________ by evaporation.
Expose food-making parts to ____________. Need ______________ __________________ to hold up and ___________________ leaves.
Need a transport system: Different tasks performed in distant plant parts: a. _______________ take up water/nutrients. b. _______________ make food. a. water/nutrients _______________________. b. sugars made by ______________________
downward.
For reproduction, gametes must find each other.
Need a mechanism to deliver sperm that
DOESN’T involve having them.
Questions:
1. What are the names of the two main phyla of land plants? Give an example of each.
Ch. 21.2: The Mosses, Liverworts and Hornworts
I. Introduction
A.
Need __________________ for reproduction to occur.
B.
Thrive only in wet areas: ____________________________.
C.
All less than a few ________________ tall.
D.
Mosses:
1. Each plant has:
>a thin upright ___________ like a stem with tiny __________ called the gametophyte.
>from base of the shoot grow ___________ that anchor the plant.
>shoots may be topped with a brown flag-like structure called a __________________.
2. Copy and label the diagram in 21.5:
II. Physical Characteristics of Bryophytes
A.
Water Conduction:
1. Lack tubes
2. Water passes between cells by _____________ and ______________________________.
3. These methods work: _____________ only; can’t grow ____________________________.
4. Lack a protective surface covering to prevent evaporation.
5. “Leaves” only _________________ thick; dry out ____________________.
6. Lack true roots: ________________ anchor, but don’t ________________ and
_____________ water and minerals.
B.
Reproduction:
1. Sperm must _______________ to the egg, using _______________ to propel themselves.
2. Moss environment must be wet for: _______________________.
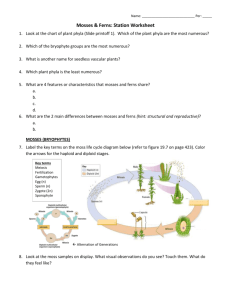
III. Alternation of Generations in Mosses
A.
Life Cycle Stages:
1. At the tips of the gametophyte: a) ____________________: makes sperm b) ____________________: makes eggs
2. Fertilization: a) Sperm swims to _____________________. b) Plants must be covered with __________________ or ______________________. c) Gamete fusion produces a ______________________ (diploid, or “2n”).
3. Growth of 2n Generation: a) Zygote grows into ____________________. b) Its ________________ and ______________ are supplied by female gametophyte. c) Sporophytes cannot live _________________. d)______________ at end of stalk makes haploid (“1n”) __________ by ___________.
4. Spore Release a) When ________________, capsule opens and shakes out spores. b) Spores _______________ off by ______________ and ___________________.
5. Growth of 1n Generation: a) Spores that land in moist places germinate into a ___________________________. b) Protonema = mass of __________________ (looks like algae!) c) This grows _________________ into soil and _______________ into the air that
develop into moss. d) The cycle begins again!
B.
Summary:
1. Gametophyte (haploid) is the ________________________, obvious stage.
2. Fertilization requires __________________________________________.
3. Sporophyte is dependent upon __________________________________.
Ch. 21.3: The Ferns and the First Vascular Plants
I. Introduction to Tracheophyta
A.
“True” land plants because they:
1. Vascular tissues – two types: a) ____________________: moves water from roots to rest of the plant. b) Phloem: ___________________________________________________________.
2. ______________ cells in xylem have thick, strong walls. a) Help plants __________________
3. True roots have transport tissue in a central _____________________________________.
4. True leaves have: a) Veins: _____________________________________________________________. b) Cuticle: ___________________________________________________________.
II. Club Mosses and Horsetails
A.
The only living descendants of ______________________.
B.
Some grew up to _____m tall!
C.
Some fossilized into _________________________.
D.
Sketch a horsetail: label its stem and leaves
III. Physical Characteristics of Ferns
A.
Organs:
1. Have true ________________________________.
2. True roots
3. Underground stems called _____________________________.
4. Large leaves called _______________________.
B.
Size and habitat:
1. Up to ____________ tall in North America.
2. Found in _______________, or ______________________ places (e.g. rainforests of
_________________________________).
IV: Alternation of Generations in Ferns
A.
Life Cycle Stages:
1. Spore production/release: a) Adult sporophytes produce haploid ______________ on ______________ of fronds. b) Formed in tiny containers called __________________________. c) Sporangia cluster together in groups called _____________________________. d) When _________, spores released; carried by ______________ and___________.
2. Growth: a) Spores develop into _______________ (1n) ________________. b) Grow into small, heart shaped _____________________________. c) ________________ and ______________ on underside of prothallium.
3. Fertilization: a) Antheridia release _____________________. b) Sperm must swim through ___________________ to an __________________. c) Each archegonium contains one _______________________________. d) Fusion of gametes produce a ________________ (2n) ____________________.
4. Growth: a) New sporophyte puts out _________________, ________________. b) Gametophyte: _________________________________
B.
Summary:
1. Dominant, obvious stage is the ________________________.
2. Sporophyte is a ______________ with true _________________________________.
3. Gametophyte can only grow in ___________________________________________.
4. Sex still requires ________________________.
Ch 21.4: Where Mosses and Ferns Fit into the World
I. Mosses: Ecological Role
A.
Common in ______________________________
II. Mosses: Uses by Humans
A.
Gardening – used as plants and peat moss added to soil to improve it.
B.
Burning sphagnum:
1. Flavours: ______________________________________
2. Peat is used as : ________________
III. Ferns: Ecological Role
A.
Common in the shadows of ___________________________, because they:
IV. Ferns: Uses by Humans
A.
Gardening – used as plants.
B.
Food:
1. Some species eaten when young; fronds called ____________________________.