Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Types of Bonds
advertisement

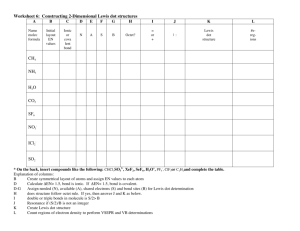
2/27/2012 Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Types of Bonds A. Electronegativity - The ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a bond 1. Periodic Trends (link to size) Metals – Low Electronegativity Non- Metals – High Electroneg The smaller the atom, the higher the electronegativity Lewis Dot Ionic vs. Molecular Compounds Ionic Compounds Metal + Non-Metal Stealing of Electrons Called Salts Clumps of Ions No prefixes, may need Roman # Lewis Dot Molecules Two Non-metals Sharing of electrons (Covalent or Polar Cov.) Separate Molecules Polar and Non-Polar Molecules (H2O vs CH4) Prefixes Types of Bonds 3. Types of bonds Electroneg. Difference Ionic >2 Polar Cov. 0.2 – 1.9 Covalent <0.2 Example: Li - F Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Which of the following form predominantly ionic, covalent, or polar covalent bonds? B-Cl Na-F C-Cl P-H P-Cl O-H 1 2/27/2012 Lewis Dot L. Dot for Ionic Compounds Lewis Dot Why do Ionics steal? To gain an Octet Draw Lewis Dot Pictures for: NaCl CaCl2 BaO Li2O Lattice Energy – Energy required to convert a mole of an ionic solid to its gaseous ions NaCl(s) Na+(g) + Cl-(g) • Increases as distance (d) decreases • Increases with increasing charge (Q) U = k Q1Q2 d Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Melting Point and Charge MgCl2 (778 oC) MgO (2800 oC) CaCl2 (772 oC) CaO (2528 oC) Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Which would have a higher lattice energy? Molecular Compounds CH4 CO2 a. NaCl or KCl b.CaBr2 or Ca3N2 c. NaCl or NaBr d.CaI2 or CaO H2O Old School Lewis Dots HCN C2H4 C2H2 2 2/27/2012 Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Michael Faraday's Benzene Sample (1825) Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Lewis Dots Rules The Lone Pear(Pair) rides again! Lewis Dot NH3 NCl3 SF6 CO2 HCN ClF5 Lewis Dots 1. Sum all valence electrons, including charges 2. Single Bonds 3. Outer atoms get an octet except H 4. Center gets rest even if it violates the octet 5. Double/triple bonds if center atom still does not have an octet Lewis Dot Lewis Dots You try: SF4 H2SO4 KrF4 Cl2O NH2CH3 3 2/27/2012 CH3CH2CHCH2 Lewis Dots Lewis Dots CNICl4BrO3NO+ CHCCH2NCl2 Lewis Dot Lewis Dots Lewis Dot Warm-Up: You try: CO32IBr4BF4SO42- Examples NO2- Lewis Dot Resonance Structures O3 Definition – When a molecule can exist in more than one arrangement of electrons 1. Atoms remain static 2. Only the electrons move Resonance Structures - CHO2 Benzene HNO3 Which needs resonance, SO3 or SO32Order the species in the previous problem from shortest to longest bond length. Resonance Structures SO2 SO22- 4 2/27/2012 Lewis Dot Less Than an Octet • Hydrogen Only gets 2 • Beryllium, Boron, and Aluminum BeCl2 BF3 AlF3 Lewis Dot Lewis Dot More Than an Octet • Just follow the rules and you will be able to draw these • Ex: AsF6- Lewis Dot Strengths of Covalent Bonds Single < Double < Triple Bond C-C C=C C=C N=N Lewis Dot Calculating Enthalpies of Reaction Hrxn = Hbroken – made Calculate the heat of reaction for the following reaction. CH4(g) + Cl2(g) CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g) Strength (kJ/mole) 348 614 839 941 Bond Length (Å) 1.54 1.34 1.20 1.10 Lewis Dot Let’s look at bonds broken and made H-CH3 + Cl-Cl Cl-CH3 + H-Cl Bonds broken: One mol C-H, One mol Cl-Cl Bonds made: One mol C-Cl, One mol H-Cl 5 2/27/2012 Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Hrxn = Hbroken – made Hrxn = [1(C-H) + 1(Cl-Cl)] – [1(C-Cl) + 1(H-Cl)] Hrxn = [413 kJ + 242 kJ] – [328 kJ + 431 kJ] Hrxn = -104 kJ (Exothermic reaction) Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Calculate the H for the following reaction: Bonds Broken 6 C-H 1 C-C 7/2 O2 Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Hrxn = Hbroken – made Hrxn = [6C-H + 1C-C + 7/2O2] – [4C=O + 6O-H] Hrxn = [6(413) + 1(348) + 7/2(495)] – [4(799) + 6(463)] Bonds Made 4 C=O 6 O-H Calculate the H for the following reaction: Hrxn = -1416 kJ (Exothermic reaction) 6 2/27/2012 Lewis Dot Lewis Dot Double Bonds Bonds Broken Bonds Made 4 N-H 1 N=N 1 N-N 2 H-H Hrxn = Hbroken – made Hrxn = [4N-H + 1 N-N] – [1 N=N + 2 H-H] Hrxn = [4(391) + 1(163)] – [1(941) + 2(436)] Hrxn = -86 kJ (Exothermic reaction) Lewis Dot Calculate the enthalpy change for the following reaction. Be sure to always break the multiple bond and remake a single C-C bond. Br Br | | H-C=C-H + Br2 H-C-C-H | | | | H H H H (ANS: -93 kJ) Lewis Dot Double Bonds Calculate the enthalpy change for the following reaction. If the enthalpy change for the following reaction is 0 kJ, calculate the C-Cl bond energy. H H | | H-C=C-H + 2H2 H-C-C-H | | H H (ANS: -289 kJ) CH3Cl(g) + H2O(g) CH3OH(g) + HCl(g) Bond energy H-Cl 430 kJ/mol C- O 360 kJ/mol O-H 460 kJ/mol (ANS: 330 kJ/mol) Lewis Dot If the enthalpy change for the following reaction is -1995 kJ, calculate the bond energy of C=O. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) Bond energy C-C 345 kJ/mol C-H 415 kJ/mol O2 495 kJ/mol O-H 460 kJ/mol (800 kJ) Organic Naming Suffix Suffix Class Characteristic -ane Alkane All single bonds -ene Alkene Double bond(s) -yne Alkynes Triple bond(s) 7 2/27/2012 IUPAC Names of Alkanes Name the following and write the chemical formula Suffix = -ane # of C atoms Name & Formula # of C atoms Name & Formula 1 Methane CH4 6 Hexane C6H14 2 Ethane C2H6 7 Heptane C7H16 3 Propane C3H8 8 Octane C8H18 4 Butane C4H10 9 Nonane C9H20 5 Pentane C5H12 10 Decane C10H22 Lewis Dot 16. BaF CsCl 14. [Ca]2+2[F]- (8 ve- around F) Li3N Al2O3 2 20 a) KF has a larger LE because F- is much smaller than Clb) Na – Cl ~ 2.8 A K-F ~ 2.7A 22. a) (i) Increases with charge (ii) decreases with d b) KBr < NaF < MgO < ScN 24 a) Ca2+ is smaller than Ba2+, higher LE b) NaCl is smallest pair, highest LE c) BaO has highest charges, highest LE 2 Lewis Dot 2 2 b) O has a double bond, shorter bond length 34. a) Draw LD of H O and O 2 38. a) O b) Al c) Cl d) F 40. a) O-F < C-F < Be-F b) S-Br < C-P < O-Cl c) C-S < N-O < B-F 50.Bond Length SO2 < SO3 < SO3 Lewis Dot 2- 52. CO2 (no resonance needed) 54. Bond Length NO+ < NO2- <NO366. a) -104 kJ b) 20 kJ c) 5 kJ 68. a) -2023 kJ b) -1255 kJ c) -192 kJ 70. a) -124 kJ b) -137 kJ 1. a) C2H3Cl3O2 b) Same 8 2/27/2012 62. Lewis Dot Lewis Dot 100. In2S (I) [Kr]5s24d10 InS (II) [Kr]5s14d10 In2S3 (III) [Kr]4d10 In(III) is smallest (least mutual electron repul) In(III) has the highest lattice energy 102.a) C2H3Cl3O2 b) C2H3Cl3O2 c) Structure CCl3CH(OH)2 9