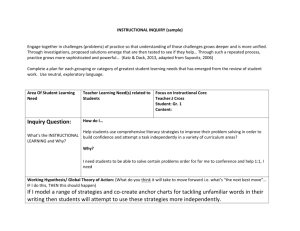
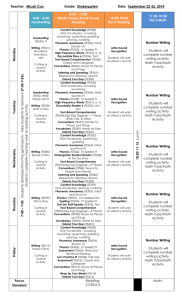
“To begin with the end in mind means to start with a clear
advertisement

“To begin with the end in mind means to start with a clear understanding of your destination. It means to know where you’re going so that you better understand where you are now so that the steps you take are always in the right direction.” Stephen Covey The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People 1 Understanding by Design An approach to develop curricula and assessments with a focus on developing and deepening students’ understanding of important ideas. It is a backward design approach. 2 Six Facets of Understanding Explanation– How does this function or operate? Interpretation– What does it mean? Why does it matter? What makes sense? Application– Use knowledge in new situations Perspective– Critical / Insightful points of view Empathy– Ability to get inside another person’s feelings and world view Self-Knowledge– The wisdom to know one’s ignorance and how one’s pattern of thought and action inform as well as prejudice understanding 3 Backward Design WHY? – To eliminate instruction that is activity oriented or coverage oriented WHAT? – Start with the end in mind and work backwards. Identify desired results Determine acceptable evidence Plan learning experiences/instruction 4 Stage 1 Identify Desired Results What should students know, understand, and be able to do? What is the big picture/enduring understandings? What are thought-provoking questions to get students thinking? What knowledge and skills should students master? 5 Stage 2 Determine Acceptable Evidence How will we know students really understand what is being taught? What are the different methods of assessments? Performance benchmark assessments 6 Stage 3 Plan Learning Experiences and Instruction What needs to be taught? How should it be taught? How do we make learning both engaging and effective considering the goals? WHERE TO 7 WHERE TO W- What H- Hook/hold E- Experiences R- Rethink/revise E- Evaluate T- Tailor O- Organize 8 Reading Comprehension……………………..Stage 1 - Desired Results: Enduring Understanding: Good readers develop, select, and apply strategies to help them understand text. Readers employ strategies before, during, and after reading text to enhance their comprehension. Essential Question: What is a story? What can we learn from print? What do good readers do when they don’t understand text? How should I read different types of texts? New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards: Standard 3.1 (Reading)- All students will understand and apply the knowledge of sounds, letters, and words in written English to become independent and fluent readers and will read a variety of materials and texts with fluency and comprehension. 9 Stage 1- Desired Results Knowledge and Skills: Students will: Use prior knowledge to make sense of text Preview materials to make initial predictions about a text Change initial predictions while reading when appropriate Utilize self-questioning throughout the reading process Establish a purpose for reading Identify story elements: characters, setting, problem, action, and solution Use pictures and dialogue in text to make predictions Draw simple conclusions using pictures and print Read regularly in on-level independent materials Reread text when it doesn’t make sense Make simple inferences 10 Stage 1- Desired Results Make text to self connections Make text to text connections Visualize mental images while reading Practice retelling using key points and big ideas Sequence important events from a story in order Listen and respond to read alouds Use graphic organizers to extend Identify favorite books and authors Read for different purposes (to learn and to enjoy) Recognize the purpose of a paragraph Understand common antonyms and synonyms Identify figurative language (idiom, metaphor, simile, and onomatopoeia) Evaluate their progress as a reader 11 Stage 2 Evidence of Understanding Millstone Township Benchmark: Quizzes, Tests, and Prompts: -on-going assessments -beginning/end of year Informal Reading Inventory -one-on-one quarterly assessments -selected-response format quizzes -observations Other Evidence and Student Self-Assessment: -verbal responses -pictorial responses in reading logs -written responses in reading logs -reflective journals -portfolios -rubrics based on self assessment of reading behaviors and performance 12 Stage 3……The Learning Plan W: Students will know expectations of this unit through: -Enduring Understandings and Essential Questions will be posted, used as anticipatory sets, and discussed -Objectives will be posted in the room and verbally communicated -Teachers will model strategies during Read Alouds, Think Alouds, and Shared Reading -Multiple discussions of why reading different types of texts is important in students’ lives -Teachers will explain how learning to read connects to environmental print and other texts -Review reading behavior rubric with students prior to utilizing strategies 13 Stage 3……The Learning Plan H: This unit will hook and hold students’ attention by: -Students will respond both verbally and in writing to stories read aloud -Teachers will provide a variety of interesting literature to be read in whole class, small groups, and independently -Students will be given time for self-selected reading each day -Teachers will provide opportunities for students to make personal connections to texts -Students will explore new vocabulary related to texts -Students will be given the opportunity to role-play 14 Stage 3……The Learning Plan E: The following learning experiences will help students explore the big ideas and essential questions: -Participating in daily mini-lessons to focus student attention on goals indicated under knowledge and skills -Revisiting and reflection of the posted essential questions through class discussion -Responding to Shared Reading through journal writing -Making text to self-connections -Modeling comprehension strategies through Read Alouds, Shared Reading, and small group instruction -Introducing Super Six Monitoring strategy through Think Alouds -Listening to stories on tape during the Listening Post center -Utilizing the Four Blocks Guess the Covered Word game to introduce context clues 15 Stage 3……The Learning Plan -Dialoguing with student partner using Turn and Talk or Think/Pair/Share -Listening to teacher read aloud daily -Participating in Three Ring Circus (Read with teacher, partner, or independently) -Cooperating with peers to create skits -Acting in Readers’ Theater -Verbally retelling a story to partner or teacher -Responding to focus questions -Relating characters to each other with class Venn diagram -Illustrating a specific story element of a text (character, setting, problem, solution) in reading response journal or log -Creating class made books with pictures and simple text to retell stories from Shared Reading time -Participating in Self-Selected Reading with appropriate independent level materials on a daily basis to apply reading strategies 16 Stage 3……The Learning Plan -Complete quick sketches of specific elements in a story as teacher reads -Engaging in literacy centers such as Read the Room or Browsing Boxes as independent work - Using computers to listen and respond to fiction and non-fiction texts -Sequencing stories or poems in pocket charts after reading them in whole group -Reading the morning message as a class during routine -Partaking in picture walks as a group and then, independently -Completing a KWL chart as a class -Creating QAR charts for questioning -Developing a timeline as a class to map events in both fiction and non-fiction -Completing homework -Creating various art projects that connect to the text 17 Stage 3……The Learning Plan R: Students will reflect, rethink, revise, and refine by: -Students will regularly revisit and discuss/answer essential questions -Students will pair-share thoughts after listening to or reading a text -Students will revisit and reassess their predictions during and after reading -Students will reread when necessary if something does not make sense (self-correcting miscues) -Students will share/show work completed during literacy centers -Students will present skits or Readers’ Theater to audience -Students will discuss/evaluate self-selected reading materials with partner or class -Students will decipher strengths and weaknesses through self-assessment rubric -Students will conference with teacher to discuss reading strategy strengths and weaknesses - Students will assist in updating KWL chart - Students will read aloud to partner, small group, or whole class and talk about the story elements and their favorite parts -Students will use the Just Right rule when choosing appropriate books for self-selected reading time 18 Stage 3……The Learning Plan E: Students will exhibit understanding through: -Pair/share discussions -Teacher observation -Written responses before, during, and after reading -Homework -Give me 5! -3-2-1 discussions -Student self-assessments (rubrics, checklist reflections) -One-on-one quarterly assessments -Authentic performance assessments -Apply strategy to a new text 19 Stage 3……The Learning Plan T: Differentiation opportunities include: -Tiered graphic organizers -Various grouping for any/all activities (heterogeneous, homogeneous/skills based) -Offer option of books on tape -Use of computer software -Jigsaw activities -Center activities -Guided Reading groups -Varying picture walk and vocabulary given prior to reading -Tiered sequencing of events in stories -Leveling texts for small group work, browsing boxes, or self-selected reading -Contracts- teacher or student generated and then discussed -Varying amount of teacher support to read and discuss a text during Shared Reading -Implementation of Three Ring Circus during Shared Reading -Vary the amount/length of text to be read and discussed -Offer choice of text response after reading (written, verbal, drawing) -Cubing activities 20 Stage 3……The Learning Plan O: Organization and sequencing considerations include: Teachers should use a scaffolding model of approach to teaching, such as Don Holdaway’s Learning Model. Students should be taken through modeled, interactive, guided, and independent stages of reading. The sequence below states the steps for learning. -The teacher models the activities and skills for students. -The teacher partially participates with the students. -Students practice skill/activity with teacher support as needed. -Students can complete or perform the task independently. -There should be an ongoing cycle of model, practice, feedback, and adjustment while teaching any comprehension strategy. 21 Stage 3……The Learning Plan Time Allotment: Comprehension strategies will be taught during Language Arts and across content areas throughout the year. The length of time spent on specific strategies and skills will vary depending upon the class. Generally, teachers will spend two full periods each day implementing Shared Reading (whole class instruction), then Guided Practice (small group), and then independent study (one to one conferencing and assessing when necessary). 22 Stage 3……The Learning Plan Resources: Student Materials: -Children’s literature books and poetry -Rigby Guided Reading leveled books -Various Graphic Organizers -Reading journals/Response logs -Big books Technology: -computer lab Teaching Materials: -Rigby Guided Reading teaching manual -Teacher-created materials and models for reading and response -Resource books that contain ideas for teaching reading (Super Six, Four Blocks). -Literature pieces by accomplished authors 23 “Life can only be understood backwards; but it must be lived forwards.” Soren Kierdegarrd, 1843 24 Special Thanks To the Following Staff Members: Language Arts Literacy Nina Banerjee Trish Bogusz Rachael Bolen Stephanie Dunk Jen Gabler Bernadette Heine Jen McPartland Kelsey Plunkett Donna Romano Karen Shaffer Jill Tobey Michelle Uffer Michele Vigliotti Science Jessica Acinapura Alecia Binns Rachel Mueller Mary O’Rourke Ted Ostaszewski Irene Pearson Alison Pressey Stephanie Prudente Sara Stofik Gloria Tomasella Beth Topinka Dana Vogel Math Lisa Camposano Laura Czvornyek Cheryl Hoffmann Val Gunsalus Rhonda Joyce Lisa McManus Lisa Murin Peggy Musillo Marian Peck Lisa Schneider Karen Vitro Fern Zinkoski Karen Barry, Matt Howell, Brandy Krueger, Michelle Vella Technology Jeanne Biroc Linda Guzinski Phyllis Matseur Primary UbD Sue Cerulo Colleen Henkin Doreen Laskiewicz Karen Lucy Faith Miller Christine Smith Traci Soriano Susanne Malmos Linda Nuzzi Heather Philhower Christie Robinson Taline Toutounchi Nicole Vitiello Katie White John White Bob Williams Elementary UbD Nicole Ascione Jen Boms Laura Bryan Pat Prevosti Michelle Williams MS UbD Jaime Golizio Kerri Kapulsky 63 teachers and 4 administrators 25