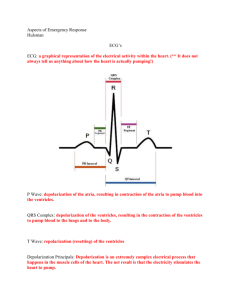
Atrial Dysrhythmias. -Problems with the S.A. Node and Atria. Normal
advertisement

Atrial Dysrhythmias. -Problems with the S.A. Node and Atria. Normal Sinus Rhythm: Sinus Dysrhythmia: Definition: S.A. Node firing at random. Look For: 1) Tachycardic if sympathetic (decreased vagal tone) origin, bradycardic if parasympathetic (increased vagal tone) origin, or normal rate. 2) Irregular rhythm. 3) Normal QRS as long as no bundle branch block. 4) Normal similar P waves. 5) Normal PR Interval duration as long as no A.V. block. Caused by: Fluctuation in Vagal Tone, heart disease, drug treatment, deep breathing. Sinus Pause and Arrest: Definition: S.A. Node forgets to fire but comes back (pause), or A.V. Node takes over (arrest). Look For: 1) Regular Rate. 2) Regular rhythm with one or more beats missing. 3) Regular QRS Complexes. 4) Regular P Waves with marriage to QRS. 5) Normal PR Interval. Causes: Increased vagal tone, hypoxia, ischemia, excess digitalis (foxglove) or propanolol (β blockers, β1), Hyperkalemia, Damaged S.A. Node. Note: Sinus arrest is arrest of S.A. node only, not necessarily cardiac arrest. Wandering Atrial Pacemaker: Definition: QRS complexes are caused by ectopic pulses from throughout the atria. Look For: 1) Regular Rate. 2) Regular Rhythm. 3) Regular QRS Complexes. 4) Irregular P Waves with marriage to QRS. 5) Regular PR Interval. Causes: Transfer of pacemaker sitters from S.A. Node to other atrial pacemaker or A.V. Junction. Premature Atrial Complexes (PACs) Definition: Ectopic site causes single or multiple beats before full repolarization. Look For: 1) Regular Rate. 2) Regular Rhythm with one or a couple beats too soon. 3) Normal QRS Complexes. 4) P Wave present and Marriage with QRS Complex (since P Wave is present problem is Atrial not Junctional). 5) PR Interval is normal. Causes: Increased sympathetic tone, stimulant use, drugs (epi, ventolin, digitalis), electrolyte imbalances, hypoxia, cardiac disease. Supraventricular Tachycardia and Paroxysmal Superventricular Tachycardia Definition: Rapid atrial or junctional depolarization which takes over the S.A. Node often due to re-entry mechanism. (PAT if atrial, PJT if junctional) Look For: 1) Tachycardic rate. 2) Regular sinus rhythm then sudden tachycardia (PSVT) or regular rhythm, just fast (SVT). 3) Normal QRS Complexes. 4) Change in P Wave at time of sudden tachycardia 5) Regular PR Interval. Causes: Stress, overexertion, tobacco, caffeine, Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome. Atrial Flutter: Definition: Look For: Causes: Atrial Fibrillation: Definition: Look For: Causes: Rapid atrial re-entry causing loss of atrial kick. May decrease perfusion. ECGs have a sawtooth or picket fence appearance. A.V. Node is regulating which impulses are allowed through. Picket-fence appearance, QRS every 5 P waves (ex) 1) Regular rate. 2) Regular Rhythm 3) Narrow QRS Complexes. 4) Regular P Waves with No Marriage to QRS waves. 5) PR Interval normal when QRS occurs. Cardiomyopathy, Cardiac hypertrophy, digitalis toxicity, hypoxia, CHF, pericarditis, myocarditis. Multiple areas of re-entry in atria or ectopic atrial pacemakers. Chaotic impulses to numerous to be conducted by A.V. Node in an orderly fashion. 1) Usually tachycardic rate (unless patient is on medications to slow down heart rate). 2) Irregular-Irregular Rhythm 3) Narrow QRS Complexes. 4) P Waves Absent. F waves Present. 5) No PR interval as P waves are absent. “Holiday Heart” syndrome, Rheumatic heart disease, CHF, Cardiac disease, Chest Trauma. *May lead to stroke A.V. Junctional Dysrhythmias: -Problems with the A.V. Junction, or problems above and A.V. has taken over Premature Junctional Complex (PJCs) Definition: Single electrical pulse in A.V. junction. Look for: 1) Normal Rate 2) Normal Rhythm with one premature beat 3) Narrow QRS complexes. 4) Normal P-Waves with abnormal, inverted or absent P-Wave before, during or after premature QRS complex. 5) Normal PR Interval with a narrow PRI of premature beat. Causes: Medications, increased vagal tone, hypoxia, congestive heart failure, A.V. Junction Damage. Junctional Escape Complex or Rhythm Definition: Isolated impulse or rhythm. The rate of primary pacemaker falls below A.V. Junction or there is an S.A. or A.V. block. Look For: 1) Bradycardia 40-60bpm 2) Regular Rhythm 3) Narrow QRS complexes 4) Uniform but Abnormal, absent, or inverted P-Waves occur before, during, or after QRS 5) PRI < 0.16 sec. Causes: Increased vagal tone, slow S.A. discharge, A.V. block. Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Definition: Increased A.V. node automaticity due to re-entry. Look for: 1) Rate of 60-99bpm 2) Regular rhythm 3) Narrow QRS 4) abnormal, absent, inverted P-Waves before, after, or during QRS 5) Normal PRI Causes: Re-entry **Note: Top 1/3 of A.V. Node is the gatekeeper. Bottom 2/3 can transmit pulses up towards atria and down towards ventricles. This is why P-Waves may be inverted: pulse is going backwards into atria. Ventricular Dysrhythmias: -Problems with the Ventricles, or Problems above and Ventricles have taken over. Look for -bizarre looking wide (>0.12s) QRS complexes -hidden or superimposed P-Waves -ST deviated from baseline -Often life threatening -Associated with myocardial ischemia or infarction -Causes: -failure of S.A., Atria, A.V., and A.V. junction, enhanced automaticity, reentry. Ventricular Escape Rhythm Definition: Isolated impulse or rhythm occurs when impulses from higher pacemakers: fail, don’t reach the ventricles, or have a slower rate of discharge than the ventricles. Body’s compensatory mechanism preventing cardiac standstill. Look For: 1) Extreme Bradycardia: 20-40 bpm 2) Regular rate 3) Wide QRS complexes 4) Absent or superimposed P-Waves 5) Absent P-Waves. Causes: Hypotension, decreased cardiac output, decreased perfusion to brain, syncope, shock. “Dying Heart” or Agonal Rhythm Definition: Ectopic pacemaker very low in the ventricles trying to keep the whole thing a-running but not doing a great job. Look for: 1) Extreme Bradycardia <20bpm 2) Regular Rate 3) Wide Bizarre QRS complexes 4) Absent P-Waves 5) Absent P-Waves Causes: Everything giving up. Premature Ventricular Complexes (PVCs) Definition: Single ectopic pulse causing an earlier than expected sinus beat. Extremely common. Look for: 1) Regular Rate 2) Regular Rhythm with one premature 3) Narrow QRS with one wide 4) P-Waves regular and married with one absent 5) PRI normal. Causes: Enhanced automaticity/re-entry, stress, caffeine, stimulants. **Note: Compensatory Pause: S.A. Node compensates for premature beats by skipping an impulse to avoid R on T phenomenon. Interpolated PVCs Definition: What happens when the S.A. node does not compensate for premature beat but it is okay. The beat becomes interposed in a normal cycle. Only works with slow rhythms. Look For: 1) Bradycardia 2) Regular Rhythm 3) Narrow QRS complexes with one wide bizarre 4) normal P-waves with one absent 5) Normal PRI when present Causes: Bradycardia, tissue attempts to enhance blood flow. Uniform/Unifocal PVCs Definition: Multiple PVCs originating from single site within the ventricles Look For: Multiple PVCs which look identical to each other. Multiform/Multifocal PVCs: Definition: Multiple PVCs originating from different ventricular sites. Look For: Multiple PVCs which occur in various shapes and sizes. Fusion Beats: Definition: PVC occurring at the same time as QRS of underlying rhythm. Look For: Characteristics of PVC and QRS complex. Grouped Beatings: -PVCs in a pattern. Bigeminy: Definition: Multiple PVCs occurring in an every other pattern. Look for: Normal, PVC, Normal, PVC, etc. Trigeminy: Definition: Multiple PVCs occurring in an every third pattern. Look for: Normal, Normal, PVC, Normal, etc. Quadrigeminy: Definition: Multiple PVCs occurring in an every 4th pattern. Couplet: Definition: 2 PVCs not separated by normal rhythm. Look for: Normal rhythm with 2 sequential PVCs. Run of Ventricular Tachycardia: Definition: 3 or more sequential PVCs. Look for: 3 or more sequential PVCs, rate greater than 100bpm. R on T Phenomena: Definition: QRS complex on top of T wave Extremely Dangerous: LOAD AND GO, even if patient’s rhythm returns to normal. Ventricular Tachycardia: -Shockable Definition: More than 3 consecutive ventricular complexes Look for: 1) Tachycardic Rate 100+ 2) normal rhythm 3) QRS complexes on acid 4) no P-Waves 5) no PR interval. Causes: Triggered by a PVC, atria and ventricles are asynchronous -Cardiac disease, electrolyte imbalance, CHF, increased catecholamines, stimulants, drugs, long QT interval. Torsades de Pointes/Polymorphic V-Tach Definition: 2 or 3+ ventricular sites in close proximity firing ventricular complexes. Look for: 1) Tachycardia 100+ 2) Regular rhythm 3) Undulating QRS complexes 4) No P-Waves 5) No PRI *prolonged QT interval Causes: Drugs Caution: Rapidly goes F-Fib. Ventricular Fibrillation: -Shockable Definition: Chaotic ventricular rhythm caused by multiple reentry foci in ventricles. Patient has no pulse, ventricles are just quivering. Look for: 1) Tachycardia 100+ 2) Irregular chaotic rhythm 3) WTF is happening is that a QRS? 4) Maybe its a P-wave… 5) I give up. Causes: MI, AMI, 3rd degree AV block, cardiomyopathy, digitalis toxicity, acidosis, electrolyte imbalance, electrical injury, drug toxicity, hypoxia. Types: Course and Fine: Ventricular Asystole. Definition: Absence of electrical activity Look for: Straight line Causes: death.