Cellular Respiration
advertisement

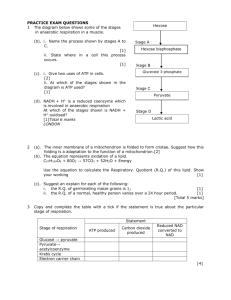
Cellular Respiration Zoom in: muscle tissue cell mitochondria cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria 3 body systems are needed to make the mitochondria work; digestion, circulation, and respiration Why digestion? through the digestive system the body acquires the food it needs to fuel all cells main food source needed are carbohydrates broken into glucose molecules the cell breaks the glucose into something smaller and sends it off to the mitochondria there the mitochondria uses these smaller pieces with oxygen to make energy for you Why circulation? the heart and vessels are responsible to pump and transport all nutrients to all parts of the body through tiny vessels called capillaries are things like glucose, oxygen and carbon dioxide able to enter or exit the tissue or vessel the only way to get glucose (from the intestine) and oxygen (from the lung) to the cells of your toes are though blood vessels the blood vessels are essential in removing waste products too, like carbon dioxide Ka Hana ‘Imi Na‘auao – A Science Careers Curriculum Resource Go to: www.cds.hawaii.edu/kahana 1 Why respiration? the lungs are necessary to get oxygen into the body in the lungs there are millions of little air sacs called alveoli that are surrounded by capillaries here the blood drops off carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen this oxygen will be taken directly to the cells when the oxygen gets to the cell, the mitochondria takes it and begins the process of cellular respiration What does the cell do with all this? cell needs to get glucose and oxygen molecules are taken in and a series of reactions begin step 1: Glycolysis the glucose molecule must break in half new molecule called pyruvate energy measured in ATP 2 ATP used at the beginning, but 4 gained at the end profit of 2 ATP 2 ADP 2 ATP 2 ATP 2 ADP Pyruvate Glucose Pyruvate 2 ADP 2 ATP Ka Hana ‘Imi Na‘auao – A Science Careers Curriculum Resource Go to: www.cds.hawaii.edu/kahana 2 step 2: Kreb’s Cycle pyruvate can enter mitochondria only if oxygen is present intermediary step before many ATP can be made reaction called the Kreb’s Cycle, and produces important electron carriers (2) called NADP(H) Pyruvate + oxygen NADPH Kreb’s Cycle NADPH step 3: Electron Transport Chain NADPH enters a chain reaction called the electron transport chain the “H” breaks off, and jumps around on certain proteins in doing so each “H” produces 17 ATP profit of 34 ATP (2 NADPH were made in the Kreb’s Cycle) NADP H H 17 ATP from 1 electron Ka Hana ‘Imi Na‘auao – A Science Careers Curriculum Resource Go to: www.cds.hawaii.edu/kahana 3 What if there’s no oxygen? then everything ends at step 1 there is an alternate route called fermentation the pyruvate molecule turns into lactic acid lactic acid is responsible for making your muscles ache after strenuous exercise Glucose Kreb’s Cycle Electron Transport Chain 36 ATP Pyruvate Fermentation Occurs when there isn’t oxygen to go to the Kreb’s Cycle. result of fermentation is lactic acid which is responsible for sore muscles after strenuous workouts ~ 6 ATP Ka Hana ‘Imi Na‘auao – A Science Careers Curriculum Resource Go to: www.cds.hawaii.edu/kahana 4 Teacher’s Notes: Cellular Respiration Zoom in: muscle tissue cell mitochondria cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria 3 body systems are needed to make the mitochondria work; digestion, circulation, and respiration Why digestion? through the digestive system the body acquires the food it needs to fuel all cells main food source needed are carbohydrates broken into glucose molecules the cell breaks the glucose into something smaller and sends it off to the mitochondria there the mitochondria uses these smaller pieces with oxygen to make energy for you Why circulation? the heart and vessels are responsible to pump and transport all nutrients to all parts of the body through tiny vessels called capillaries are things like glucose, oxygen and carbon dioxide able to enter or exit the tissue or vessel the only way to get glucose (from the intestine) and oxygen (from the lung) to the cells of your toes are though blood vessels the blood vessels are essential in removing waste products too, like carbon dioxide Why respiration? the lungs are necessary to get oxygen into the body in the lungs there are millions of little air sacs called alveoli that are surrounded by capillaries here the blood drops off carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen this oxygen will be taken directly to the cells when the oxygen gets to the cell, the mitochondria takes it and begins the process of cellular respiration What does the cell do with all this? cell needs to get glucose and oxygen molecules are taken in and a series of reactions begin Ka Hana ‘Imi Na‘auao – A Science Careers Curriculum Resource Go to: www.cds.hawaii.edu/kahana 5 step 1: Glycolysis the glucose molecule must break in half new molecule called pyruvate energy measured in ATP 2 ATP used at the beginning, but 4 gained at the end profit of 2 ATP step 2: Kreb’s Cycle pyruvate can enter mitochondria only if oxygen is present intermediary step before many ATP can be made reaction called the Kreb’s Cycle, and produces important electron carriers (2) called NADP(H) step 3: Electron Transport Chain NADPH enters a chain reaction called the electron transport chain the “H” breaks off, and jumps around on certain proteins in doing so each “H” produces 17 ATP profit of 34 ATP (2 NADPH were made in the Kreb’s Cycle) What if there’s no oxygen? then everything ends at step 1 there is an alternate route called fermentation the pyruvate molecule turns into lactic acid lactic acid is responsible for making your muscles ache after strenuous exercise Ka Hana ‘Imi Na‘auao – A Science Careers Curriculum Resource Go to: www.cds.hawaii.edu/kahana 6