Respiration
advertisement

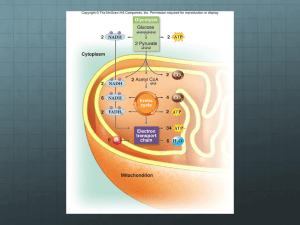
PRACTICE EXAM QUESTIONS 1 The diagram below shows some of the stages in anaerobic respiration in a muscle. Hexose (b). i. Name the process shown by stages A to C. [1] ii. State where in a cell this process occurs. [1] (c). i. Give two uses of ATP in cells. [2] ii. At which of the stages shown in the diagram is ATP used? [1] (d). NADH + H is a reduced coenzyme which is involved in anaerobic respiration At which of the stages shown is NADH + H+ oxidised? [1]Total 6 marks LONDON Stage A Hexose bisphosphate Stage B Glycerate 3-phosphate Stage C Pyruvate + 2 Stage D Lactic acid (a). The inner membrane of a mitochondrion is folded to form cristae. Suggest how this folding is a adaptation to the function of a mitochondrion.[2] (b). The equation represents oxidation of a lipid. C57H104O6 + 80O2 → 57CO2 + 52H2O + Energy Use the equation to calculate the Respiratory. Quotient (R.Q.) of this lipid. Show your working [1] (c). Suggest an explain for each of the following: i. the R.Q. of germinating maize grains is 1; [1] ii. the R.Q. of a normal, healthy person varies over a 24 hour period. [1] [Total 5 marks] 3 Copy and complete the table with a tick if the statement is true about the particular stage of respiration. Statement Stage of respiration ATP produced Carbon dioxide produced Reduced NAD converted to NAD Glucose → pyruvate Pyruvate→ acetylcoenzyme Krebs cycle Electron carrier chain [4] (b). The graph shows the volume of oxygen consumed and the volume of carbon dioxide released by a small animal over a 15 minute period. Showing your working in each case, use the graph to calculate: i. the rate of oxygen consumptions; ii. the respiratory quotient (R.Q). of this animal over the 15 minute period. 4 [1] [2] Mitochondria are organelles that are thought to have entered into a mutualistic existence with cells many millions of years ago. They are surrounded by a double membrane system and are usually 0.5 µm – 1.0 µm in length. The inner membrane is folded into structures called cristae and the space inside is called the matrix. Mitochondria possess proteins called cytochromes. They also contain small circle of DNA which code for a few of the mitochondrial proteins. Mitochondria have the biochemical machinery needed for carrying out some protein synthesis. Liver cells have between 1000 and 2000 mitochondria which can occupy up to 20% of the cell volume. a)Use information in the passage to answer the following. i. Outline two pieces of evidence suggesting that mitochondria originally existed outside eukaryotic cells as free living organisms.[2] ii. Suggest why mitochondria can no longer exist as free living organisms.[1] iii. Suggest why liver has so many mitochondria.[1] iv. Explain the significance of the folding of the inner mitochondrial membrane.[2] (b). The figure below represents the main stages of aerobic respiration. State precisely where the reactions in boxes A, B and C occur in the cell. [3] c)iWhat substance is X?[1] ii)A total of 38 molecules of ATP is formed during the complete breakdown of one molecule of glucose. State how many molecules are formed at each of the stages A, B and C.[2]`````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````` ````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````````` iii)If glucose is burned, the energy transferred as heat and light is 2881 kJ mol-1. In the reactions described above, some of the energy is retained in the form of ATP. The energy ‘trapped’ in ATP is 50 kJ mol – 1. Calculate the percentage of the energy made available from the breakdown of one molecule of glucose which is retained for biological reactions in the cell. Show your working [3] 5 (a). The diagram below shows a section through electron microscope i. ii. a mitochondrion as seen using an Name the parts labelled A, B and C. [3] On the diagram, by means of an arrows, show the location of the electron transport system. [1] iii. The magnification of this diagram is ×70 000. Calculate the actual length of the mitochondrion, giving your answer in suitable units. Show your working [2] (b). Active mitochondria can be isolated from liver cells. If these mitochondria are than incubated in a buffer solution containing a substrate, such as succinate, dissolved oxygen will be used by the mitochondria. The concentration of dissolved oxygen in the buffer solution can be measured using the electrode. An experiment was carried out in which a suspension of active mitochondria was incubated in a buffer solution containing succinate, an intermediate of the Krebs cycle. The concentration of dissolved oxygen was measured every minute for five minutes. A solution containing sodium azide was then added to this preparation and the concentration of dissolved oxygen was measured for a further five minutes. Sodium azide combines with cytochromes and prevents electron transport. The results are shown in the graph below. i. ii. Explain why the concentration of oxygen decreased during the first five minutes.[2] Suggest what effect the addition of sodium azide will have on the production of ATP and give an explanation for your answer. [3] [Total 11 marks]