Print › AP Biology- Cell Communication | Quizlet | Quizlet
advertisement
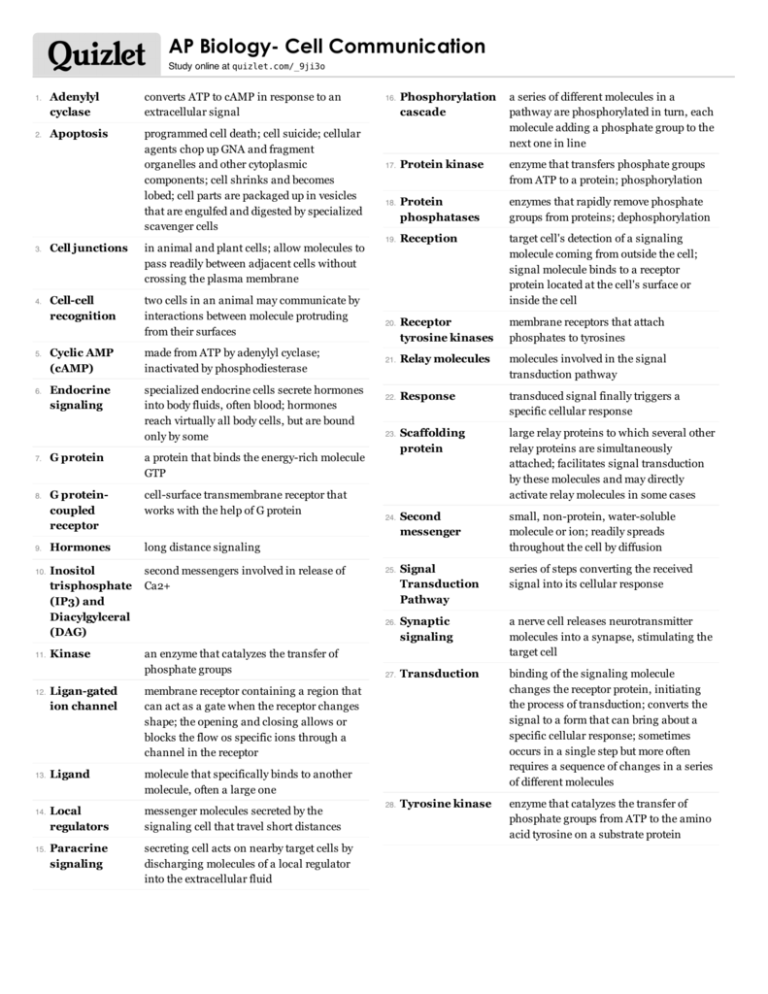
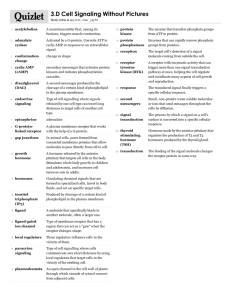
AP Biology- Cell Communication Study online at quizlet.com/_9ji3o 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP in response to an extracellular signal Apoptosis programmed cell death; cell suicide; cellular agents chop up GNA and fragment organelles and other cytoplasmic components; cell shrinks and becomes lobed; cell parts are packaged up in vesicles that are engulfed and digested by specialized scavenger cells Cell junctions in animal and plant cells; allow molecules to pass readily between adjacent cells without crossing the plasma membrane Cell-cell recognition two cells in an animal may communicate by interactions between molecule protruding from their surfaces Cyclic AMP (cAMP) made from ATP by adenylyl cyclase; inactivated by phosphodiesterase Endocrine signaling specialized endocrine cells secrete hormones into body fluids, often blood; hormones reach virtually all body cells, but are bound only by some G protein a protein that binds the energy-rich molecule GTP G proteincoupled receptor cell-surface transmembrane receptor that works with the help of G protein Hormones long distance signaling Inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and Diacylgylceral (DAG) second messengers involved in release of Ca2+ Kinase an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups Ligan-gated ion channel membrane receptor containing a region that can act as a gate when the receptor changes shape; the opening and closing allows or blocks the flow os specific ions through a channel in the receptor Ligand molecule that specifically binds to another molecule, often a large one Local regulators messenger molecules secreted by the signaling cell that travel short distances Paracrine signaling secreting cell acts on nearby target cells by discharging molecules of a local regulator into the extracellular fluid Phosphorylation cascade a series of different molecules in a pathway are phosphorylated in turn, each molecule adding a phosphate group to the next one in line Protein kinase enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein; phosphorylation Protein phosphatases enzymes that rapidly remove phosphate groups from proteins; dephosphorylation Reception target cell's detection of a signaling molecule coming from outside the cell; signal molecule binds to a receptor protein located at the cell's surface or inside the cell Receptor tyrosine kinases membrane receptors that attach phosphates to tyrosines 21. Relay molecules molecules involved in the signal transduction pathway 22. Response transduced signal finally triggers a specific cellular response Scaffolding protein large relay proteins to which several other relay proteins are simultaneously attached; facilitates signal transduction by these molecules and may directly activate relay molecules in some cases Second messenger small, non-protein, water-soluble molecule or ion; readily spreads throughout the cell by diffusion Signal Transduction Pathway series of steps converting the received signal into its cellular response Synaptic signaling a nerve cell releases neurotransmitter molecules into a synapse, stimulating the target cell 27. Transduction binding of the signaling molecule changes the receptor protein, initiating the process of transduction; converts the signal to a form that can bring about a specific cellular response; sometimes occurs in a single step but more often requires a sequence of changes in a series of different molecules 28. Tyrosine kinase enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to the amino acid tyrosine on a substrate protein 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 23. 24. 25. 26.