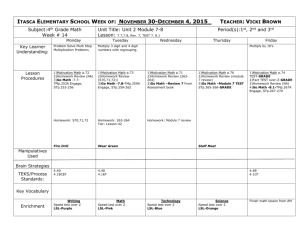
Acronyms and Definitions

Appendix J. Acronyms and Definitions
Active Transportation: Transportation which requires physical activity as part of the mode. Typically, active transportation refers to walking, bicycling and to transit, as transit trips begin and end with a walking or bicycling trip.
ADA ‐ Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990: Federal law that requires public facilities (including transportation services) to be accessible to persons with disabilities including those with mental disabilities, temporary disabilities, and the conditions related to substance abuse.
ADAAG – ADA Standards for Accessible Design Guidelines: Enforceable accessibility standards adopted by federal regulations.
ADT ‐ Average Daily Traffic: The number of vehicles passing a fixed point in a day, averaged over a number of days. The number of count days included in the average varies with the intended use of data.
ATRI – American Transportation Research Institute: A well‐known leader in transportation‐related research, is an organization whose hallmark is innovative thinking, critical analysis and uncompromised excellence. As part of the American Trucking
Associations (ATA) Federation, ATRI benefits from the broad support of the ATA and its members.
AVL – Automated Vehicle Locato r: A device that makes use of the Global Positioning System (GPS) to enable a business or agency to remotely track the location of its vehicle fleet by using the Internet.
AVO ‐ Average Vehicle Occupancy: The ratio of person trips to vehicle trips; often used as a criteria in judging the success of trip reduction programs.
BLOS – Bicycle Level of Service: A measure, expressed on a scale of A to F, of the general conditions of roadways for supporting bicycle travel. LOS indicates the level of comfort or perceived safety based on a combination of factors including the roadway’s vehicular speed limit, traffic volumes, shoulder widths, travel lane widths, and bicycle facilities.
BRT – Bus Rapid Transit (BRT‐Lite): A high speed bus system operated within an exclusive right‐of‐way. BRT incorporates exclusive transit ways, modern stations, on‐board fare collection, high‐tech vehicles and frequent service. BRT systems can be built incrementally and designed for vehicles ‐ rather than people ‐ transfer from local bus routes to the high speed lines. BRT‐
Lite typically refers to a bus service that includes some components of BRT, but not operating within a dedicated guideway.
CAAA ‐ Clean Air Act Amendments: 1990 amendments to the federal Clean Air Act which classify non‐attainment areas and provide for rules dealing with air pollution in such areas; specifically brought transportation decisions into the context of air quality control.
CBIS – Computer Based Information System
CCTV – Closed Circuit Television: The use of video cameras to transmit a signal to a specific place or limited set of monitor/displays. CCTV is used for video surveillance of traffic conditions.
CFR – Code of Federal Regulations: The codification of the general and permanent rules published in the Federal Register by the departments and agencies of the Federal Government. It is divided into 50 titles that represent broad areas subject to
Federal regulation. Federal transportation planning requirements pertaining to MPOs are generally provided in Titles 23 and 49.
CMAQ ‐ Congestion Mitigation and Air Quality Improvement Program: Provides a flexible funding source to State and local governments for transportation projects and programs to help meet the requirements of the Clean Air Act. Funding is available to reduce congestion and improve air quality for areas that do not meet the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for ozone, carbon monoxide, or particulate matter (nonattainment areas) and for former nonattainment areas that are now in compliance
(maintenance areas).
CMP ‐ Congestion Management Process (previously known as Congestion Management System): A systematic process required under SAFETEA‐LU for all TMAs that shall address congestion management through the metropolitan planning process that provides for effective management and operation, based on a cooperatively developed and implemented metropolitan‐ wide strategy of new and existing transportation facilities eligible for funding under title 23 and chapter 53 of title 49 through the use of travel demand reduction and operational management strategies. The CMP is required under 23 CFR 500.109 and shall include methods to monitor and evaluate the performance of the multi‐modal transportation system, identify causes of congestion, identify and evaluate alternative actions, provide information supporting the implementation of actions, and evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of implementation actions. The CMP is periodically reviewed for efficiency and effectiveness of the implemented strategies, the results of this evaluation shall be provided to decision‐makers to provide guidance on selection of effective strategies for future implementation purposes.
Complete Streets – Streets that offer transportation choices that are safe and convenient for all ages and ability levels. These choices may include transit, walking, bicycling and automobile travel.
J. Acronyms and Definitions 1
CO2 – Carbon Dioxide – A naturally occurring and important greenhouse gas. Burning of carbon‐based fuels since the industrial revolution has rapidly increased its concentration in the atmosphere, leading to global warming. Emissions from transportation vehicles is a contributor to this increase in concentration.
CONST – Construction (phase of a project): The phase of a project after the preliminary environmental and engineering work is completed, where the project is being built and the improvements are prepared for implementation.
CRT – Cumberland Region Tomorrow: A nonprofit organization comprised of private‐sector community leaders founded in
2000 to support quality growth planning across Middle Tennessee.
DMS – Dynamic Message Signs: An electronic roadway sign that allows for messages to be customized to travelers based on current conditions.
DMU – Diesel Multiple Unit: A type of propulsion technology for passenger trains requiring no separate locomotive. Instead, the engine is incorporated into one or more of the cars/carriages of a light rail, commuter rail, or street car system.
DOT ‐ Department of Transportation: Agency responsible for transportation at the local, state, or federal level. For title 23
U.S.C. federal‐aid highway actions, this would mean the Federal Highway Administration and for federal‐aid transit actions under title 49 U.S.C, this would mean the Federal Transit Administration.
E+C – Existing plus Committed Transportation Network: Also called a No‐Build network, this is a test of how a roadway network, consisting of an existing network plus currently funded future roadway projects, could withstand the demand of projected population and employment growth.
EA – Environmental Assessment: The process of identifying, predicting, evaluating and mitigating the biophysical, social, and other relevant effects of development proposals prior to major decisions being taken and commitments made. The purpose of the assessment is to ensure that decision‐makers consider environmental impacts before deciding whether to proceed with new projects.
EIS ‐ Environmental Impact Statement: A National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) document that explains the purpose and need for a project, presents project alternatives, analyzes the likely impact of each, explains the choice of a preferred alternative, and finally details measures to be taken in order to mitigate the impacts of the preferred alternative.
EJ ‐ Environmental Justice: Derived from Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, and established by Executive Order 12898, EJ requires federally funded plans and programs to assess their impact, either positive or negative, on traditionally underserved
(e.g., low‐income, minority, etc.) communities or segments of the population. The goal of EJ is to ensure public involvement of low income and minority groups in decision making to prevent disproportionately high and adverse impacts on low income and minority groups, and to ensure that these groups receive equal benefits from transportation improvements.
EPA – U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and with safeguarding the natural environment: air, water, and land.
E‐TRIMS – Enhanced Tennessee Roadway Information Management System: A database managed by the Tennessee
Department of Transportation that includes attribute information for various transportation assets.
Executive Board: A standing committee created for the purpose of serving as spokespersons for the citizens of the metropolitan area and is the designated MPO to prioritize and direct federal transportation funds to local projects. The Board is comprised of elected officials from the cities over 5,000 population and the counties of Davidson, Maury, Robertson,
Rutherford, Sumner, Williamson and Wilson. The Executive Board also has representatives from TDOT, representing the
Governor. The Board is responsible for creating policies regarding transportation planning issues. The Executive Board meetings are open to the public and where any member of the public can address the MPO on any transportation issue.
FHPP ‐ Federal High Priority Projects: Discretionary projects earmarked by the U.S. Congress as high priorities at the federal level during the Congressional appropriations and re‐authorization process.
FHWA ‐ Federal Highway Administration: Division of the U.S. Department of Transportation responsible for administrating federal highway transportation programs under title 23 U.S.C.
Fiscal Constraint: A requirement that the MPO regional transportation plan and TIP include sufficient financial information for demonstrating that projects in the metropolitan transportation plan, TIP, and STIP can be implemented using committed, available, or reasonably available revenue sources, with reasonable assurance that the federally supported transportation system is being adequately operated and maintained. For the TIP and the STIP, financial constraint/fiscal constraint applies to each program year.
FRA – Federal Railroad Administration: The modal administration of the United States Department of Transportation responsible for the safety and effectiveness of the nation’s railroad infrastructure.
J. Acronyms and Definitions 2
FTA ‐ Federal Transit Administration: The modal administration of the United States Department of Transportation responsible for federal transit planning and programs under title 49 U.S.C.
FTA ‐ Franklin Transit Authority: The local transit agency for Franklin, Tennessee, currently operated on behalf of the city by
The TMA Group.
Functional Classification: Functional classification is the process by which streets and highways are grouped into classes, or systems, according to the character of service they are intended to provide. Basic to this process is the recognition that individual roads and streets do not serve travel independently in any major way. Rather, most travel involves movement through a network of roads. It becomes necessary then to determine how this travel can be channelized within the network in a logical and efficient manner. Functional classification defines the nature of this channelization process by defining the part that any particular road or street should play in serving the flow of trips through a highway network.
FY ‐ Fiscal Year: A federal fiscal or budget year; runs from October 1 through September 30 for the MPO and the federal government. State and local governments operate on a fiscal year beginning July 1 and ending June 30.
HIA – Health Impact Assessment: An assessment conducted ideally in the planning phases of a built environment project which estimates any positive or negative impacts that a project may have on environmental or personal health. The assessment makes recommendations for improvements to the project to mitigate negative impacts such as reducing emissions or improving positive impacts such as increasing physical activity.
GIS – Geographic Information System: a system for capturing, storing, analyzing and managing data which is spatially referenced to the earth. GIS is a tool that allows users to create interactive queries (user created searches), analyze the spatial information, edit data, maps, and present the results of all these operations.
GNRC – Greater Nashville Regional Council: a regional organization created by State law to serve as the development district for 13 counties in northern Middle Tennessee. GNRC serves as the Area Agency on Aging and Disability, the Middle Tennessee
Tourism Council, and provides community planning and economic development assistance to its local government members.
GPS – Global Positioning System: a space‐based navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites.
HERS‐ST – Highway Economic Requirements System‐State Version: an engineering/economic analysis (EEA) tool that uses engineering standards to identify highway deficiencies, and then applies economic criteria to select the most cost‐effective mix of improvements for system‐wide implementation.
HOV ‐ High Occupancy Vehicle: In Tennessee, vehicles carrying two (2) or more people receive this designation and may travel on freeways, expressways and other large volume roads in lanes designated for high occupancy vehicles. Motorcycles are also authorized to use these lanes.
HPMS – Highway Performance Monitoring System: a national level highway information system that includes data on the extent, condition, performance, use and operating characteristics of the nation's highways.
HUD – United States Department of Housing and Urban Development: Federal agency charged with helping to create strong, sustainable, inclusive communities and quality, affordable homes.
HTS (or HHTS) – Household Travel Survey: A major survey effort conducted periodically to collect socio‐economic and travel behavior information from a random selection of households across the planning area. Data from the survey are used in travel demand modeling to predict future transportation trends.
IM – Interstate Maintenance: A funding category created by the Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991
(ISTEA), the IM authorizes funding for activities that include the reconstruction of bridges, interchanges, and over crossings along existing Interstate routes, including the acquisition of right‐of‐way where necessary, but shall not include the construction of new travel lanes other than high occupancy vehicle lanes or auxiliary lanes.
IMS ‐ Incident Management System: A systematic process required under SAFETEA‐LU to provide information on accidents and identify causes and improvements to the Transportation system to increase safety of all users.
ISTEA ‐ Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991: Federal law which restructured transportation planning and funding by requiring consideration of multimodal solutions, emphasis on the movement of people and goods as opposed to traditional highway investments, flexibility in the use of transportation funds, a greater role of MPOs, and a greater emphasis on public participation. ISTEA preceded TEA‐21 and SAFETEA‐LU.
ITE ‐ Institute of Transportation Engineers: An international society of professionals in transportation and traffic engineering; publishes Trip Generation (a manual of trip generation rates by land use type).
J. Acronyms and Definitions 3
ITS ‐ Intelligent Transportation System: Use of computer and communications technology to facilitate the flow of information between travelers and system operators to improve mobility and transportation productivity, enhance safety, maximize the use of existing transportation facilities, conserve energy resources and reduce adverse environmental effects; includes concepts such as “freeway management systems,” “automated fare collection” and “transit information kiosks.”
Intergovernmental Agreement: Legal instrument describing tasks to be accomplished and/or funds to be paid between government agencies.
LMT – Leadership Middle Tennessee: A leadership institute founded in 1999 to broaden the perspective of community leaders to include a greater understanding of regional issues and challenges.
LOS ‐ Level of Service: A qualitative assessment of a road’s operating condition, generally described using a scale of A (little congestion) to E/F (severe congestion).
LRT – Light Rail Transit: a particular class of urban and suburban passenger railway that utilizes equipment and infrastructure that is typically less massive than that used for rapid transit systems, with modern light rail vehicles usually running along the system.
LRTP – Long‐Range Transportation Plan : A document resulting from regional or statewide collaboration and consensus on a region or state's transportation system, and serving as the defining vision for the region's or state's transportation systems and services. In metropolitan areas, the plan indicates all of the transportation improvements scheduled for funding over the next
20 years. It is fiscally constrained, i.e., a given program or project can reasonably expect to receive funding within the time allotted for its implementation.
MAP‐21 – Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21 st Century Act: The federal transportation act passed by Congress and signed into law in 2012 that authorized federal surface transportation programs for FYs 2013 and 2014.
MG ‐ Minimum Guarantee: A funding category created in TEA‐21 that guarantees a 90 percent return of contributions on formula funds to every state.
MPO Activities: Are plans, programs and projects related to the MPO process.
MPW – Metro Public Works: The Metropolitan Government of Nashville‐Davidson County Department of Public Works.
MPO ‐ Metropolitan Planning Organization: The forum for cooperative transportation decision‐making; required for urbanized areas with populations over 50,000.
MTA – Metropolitan Transit Authority: The public transit agency serving Nashville/Davidson County.
NBI – National Bridge Inventory: A compilation of bridge data supplied by the States to the FHWA for bridges located on public roads.
NBIAS – National Bridge Investment Analysis System: A tool developed by the FHWA to help analyse the financial needs to keep bridges in a state of good repair.
NEPA – National Environmental Policy Act: Passed in 1970, NEPA requires federal agencies to integrate environmental values into their decision making processes by considering the environmental impacts of their proposed actions and reasonable alternatives to those actions.
NHPP – National Highway Performance Program: A federal transportation grant program administered through the FHWA to support for the condition and performance of the National Highway System (NHS), for the construction of new facilities on the
NHS, and to ensure that investments of Federal‐aid funds in highway construction are directed to support progress toward the achievement of performance targets established in a State's asset management plan for the NHS
NHS ‐ National Highway System: Consists of roadways important to the nation’s economy, defense, and mobility. The NHS includes the Interstate System, principal arterial highways in rural and urban areas, the Strategic Highway Networks and connectors for national defense purposes, and intermodal connectors that tie together the surface, air, water, and rail transportation systems.
NOx – Nitrogen Oxides or oxides of nitrogen: The third largest greenhouse gas. It attacks ozone in the stratosphere, aggravating the excess amount of UV light striking the earth's surface.
Obligated Funds: Funds that have been authorized by and committed to legally by a federal agency to pay for the federal share of the project cost.
Officials: Are people who have governmental decision‐making, planning or administrative responsibilities that relate to MPO activities.
J. Acronyms and Definitions 4
PE – Preliminary Engineering (phase of project): a process to begin developing the design of the facilities and system, to analyze the function and operation of the system, evaluation cost efficiencies and prepare for the final design of the project.
PLOS – Pedestrian Level of Service: A measure, expressed on a scale of A to F, of the general conditions of roadways for supporting pedestrian travel. LOS indicates the level of comfort or perceived safety based on a combination of factors including the roadway’s vehicular speed limit, traffic volumes, travel lane widths, and pedestrian facilities.
PMS ‐ Pavement Management System: A systematic process utilized by State agencies and MPOs to analyze and summarize pavement information for use in selecting and implementing cost‐effective pavement construction, rehabilitation, and maintenance programs; required for roads in the National Highway System as a part of ISTEA; the extent to which the remaining public roads are included in the process is left to the discretion of State and local officials.
PPP – Public Participation Plan: a federally‐required document that describes the MPO’s process for involving the public and interested stakeholders in the development and adoption of required plans and programs, and the formal procedures used to adopt or amend the Long‐Range Transportation Plan, the Transportation Improvement Program, and Unified Planning Work
Program.
Public: Includes citizens, public agencies, advocacy groups and the private sectors that have an interest in or may be affected by
MPO activities.
Public Participation: Is an integral part of a planning or major decision‐making process. It provides opportunities for the public to be involved with the MPO in an exchange of data and ideas. Public participation offers an open process in which the rights of the community, to be informed to provide comments to the Government and to receive a response from the Government, are met through a full opportunity to be involved and to express needs and goals.
ROW ‐ Right‐of‐Way: Real property that is used for transportation purposes; defines the extent of the corridor that can be used for the road and associated drainage.
RTA – Regional Transportation Authority: Nine‐county regional agency that plans and develops regional transit in the Nashville area.
RTDM ‐ Regional Travel Demand Model: This is a tool for simulating and forecasting regional travel patterns as well as testing various growth patterns or transportation investment scenarios to measure the impact to area traffic. The base year travel patterns are determined from periodic survey research of travel behaviors among Nashville area households and data provided by the US Census.
SAFETEA‐LU ‐ Safe, Accountable, Flexible, Efficient Transportation Equity Act: A Legacy for Users ‐ legislation enacted August
10, 2005, as Public Law 109‐59. SAFETEA‐LU authorizes the Federal surface transportation programs for highways, highway safety, and transit for the 5‐year period 2005‐2009. SAFETEA‐LU was preceded by ISTEA and TEA‐21.
School Siting: the process by which a community decides where to locate a new public school. The placement of schools and the zones of populations assigned to attend a school affect transportation patterns in the community as well as the modal types used to make a home to school trip.
SIP – State Implementation Plan (for air quality): the regulations and other materials for meeting clean air standards and associated Clean Air Act requirements.
SR – State Route: a roadway owned, financed and maintained by a state.
SRTS – Safe Routes to School: the name of a national movement and a component of SAFETEA‐LU by which communities provide infrastructure and education to enable and encourage children to walk and bicycle to school.
STA – State gas tax fund: Also called motor fuel excise tax, this is a tax charged by the gallon and collected as consumers pay at the pump. The tax goes primarily towards basic operating costs, highway maintenance contracts, resurfacing, bridges, major reconstruction, new construction, consultant contracts, right‐of‐way purchases, and to match federal funds.
STIP ‐ State Transportation Improvement Program: A priority list of transportation projects developed by the Tennessee
Department of Transportation that is to be carried out within the four (4) year period following its adoption; must include documentation of federal, State, and local funding sources for each project. Transportation projects in the state’s 11 metropolitan areas are determined through Metropolitan Planning Organization process.
STP – Surface Transportation Program (S‐STP, L‐STP, M‐STP, U‐STP, O‐STP): A federal grant program administered by the
Federal Highway Administration that provides flexible funding that may be used by States and localities for projects to preserve and improve the conditions and performance on any Federal‐aid highway, bridge and tunnel projects on any public road, pedestrian and bicycle infrastructure, and transit capital projects, including intercity bus terminals. S‐STP refers to STP funding provided to TDOT for statewide use. L‐STP refers to STP funding distributed to areas of 5,000 to 50,000 in population.
M‐STP
J. Acronyms and Definitions 5
refers to STP funding distributed to the Murfreesboro Urbanized Area. U‐STP refers to STP funding distributed to the Nashville‐
Davidson Urbanized Area. O‐STP refers to the sum of L‐STP, M‐STP, U‐STP funding allocated in the regional transportation plan between the years 2021 and 2040.
STRACNET – Strategic Rail Corridor Network: A network consisting of 38,800 miles of rail lines important to national defense and which provides service to 193 defense installations whose mission requires rail service.
STRAHNET – Strategic Highway Network: A network of highways that provides defense access, continuity, and emergency capabilities for movements of personnel and equipment in both peace and war.
TAZ – Traffic Analysis Zone: A unit of geography ‐ usually based on U.S. Census tracts, blockgroups, or blocks ‐ used in travel demand models which predict the number of trips expected to occur between zones.
TCA – Tennessee Code Annotated: The codification of Tennessee state laws.
TCC ‐ Technical Coordinating Committee: A standing committee of MPO area planners, engineers, and other transportation related agencies which provide advice on plans or actions of the MPO. TCC meetings are open to the public.
TDM – Transportation Demand Management: a method of planning for and implementing transportation improvement in a manner that reduces traffic congestion and pollution by influencing changes in travel behavior.
TDEC – Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation: State agency responsible for protecting the quality of the natural environment, conserving natural and historic resources, and providing quality outdoor recreational activities through the state park system.
TDOS – Tennessee Department of Safety and Homeland Security: State agency responsible for driver's licenses, vehicle titles, highway patrol, handgun permits, public safety, and homeland security
TDOT – Tennessee Department of Transportation: State agency responsible for the planning and implementation of
Tennessee’s multimodal transportation system including roads and bridges, aviation, public transit, waterways, and railroads.
TEA‐21 ‐ Transportation Equity Act for the 21st Century: Federal Legislation that authorized funds for all modes of transportation and guidelines on the use of those funds. Successor to ISTEA, the landmark legislation clarified the role of the
MPOs in the local priority setting process. TEA‐21emphasized increased public involvement, simplicity, flexibility, fairness, and higher funding levels for transportation. TEA‐21 preceded SAFETEA‐LU.
TITAN – Tennessee Integrated Traffic Analysis Network: A database of traffic incidents report to TDOS by local and state law enforcement agencies.
TIP ‐ Transportation Improvement Program: A priority list of transportation projects developed by a metropolitan planning organization that is to be carried out within the four (4) year period following its adoption; must include documentation of federal, state, and local funding sources for each project and be consistent with adopted MPO long range transportation plans and local government comprehensive plans.
TMA ‐ Transportation Management Area: An area designation by the U.S. Department of Transportation given to all urbanized areas with a population of 200,000 or more (or other area when requested by the Governor and MPO); these areas must comply with special transportation planning requirements regarding congestion management systems, project selection and certification; requirements identified in 23 CFR ‐ 450.300‐338.
The TMA Group: A local non‐profit organization headquartered in Williamson County responsible for carrying out certain transit services on behalf of the Regional Transportation Authority and the Franklin Transit Authority, and for the administration of the regional Clean Air Partnership of Middle Tennessee, under contract to Williamson County and the
Nashville Area MPO.
TOD ‐ Transit Oriented Development: a mixed‐use development that is anchored by a transit station. The transit mode may include bus or rail, and the development may include uses such as housing, office and retail.
TODD ‐ Transit on Demand: a type of flexible transit service offered by the Franklin Transit Authority that is available upon request from customers.
Transportation Disadvantaged: People who are unable to transport themselves or to purchase transportation due to disability, income status or age.
Transportation Enhancements: Specific activities which can be funded with Surface Transportation Program (STP) funds; activities include pedestrian/bicycle facilities, acquisition of scenic easements and scenic historic sites, scenic or historic highway programs, scenic beautification, historic preservation, rehabilitation/operation of historic transportation structures,
J. Acronyms and Definitions 6
railway corridor preservation, control/removal of outdoor advertising, archeological planning/research and mitigation of highway runoff water pollution.
TRIMS – Tennessee Roadway Information Management System: An Oracle database application which enables TDOT to capture, maintain, and view critical roadway data. The TRIMS application provides users with a view of roadway data, traffic, bridges, crashes, railroad grade crossings, pavement conditions and photolog digital images.
TSM ‐ Transportation Systems Management: Strategies to improve the efficiency of the transportation system through operational improvements such as the use of bus priority or reserved lanes, signalization, access management, turn restrictions, etc.
UGB – Urban Growth Boundary: A regional boundary, set in an attempt to control urban sprawl by mandating that the area inside the boundary be used for higher density urban development and the area outside be used for lower density development. In Tennessee, UGBs are defined through a public planning process involving a county and its municipalities.
UPWP ‐ Unified Planning Work Program: Developed by Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPOs); identifies all transportation and planning activities anticipated within the next one to two years, including a schedule for the completion of the identified tasks and activities.
U.S.C – United States Code: A consolidation and codification by subject matter of the general and permanent laws of the
United States. Titles 23 and 49 of the USC pertain to highways and transportation.
V/C Ratio Volume over Capacity Ratio: A roadway performance measure to show how a highway volume compares with a highway‘s capacity.
VMT ‐ Vehicle Miles Traveled: A measure calculated from observed traffic counts or from a travel demand model to convey the total distanced traveled by automobiles. May also be expressed on per capita basis.
VOC – Volatile Organic Compounds: Organic chemical compounds that have high enough vapor pressures under normal conditions to significantly vaporize and enter the atmosphere. Included among these compounds are dry‐cleaning solvents and some constituents of petroleum fuels.
J. Acronyms and Definitions 7