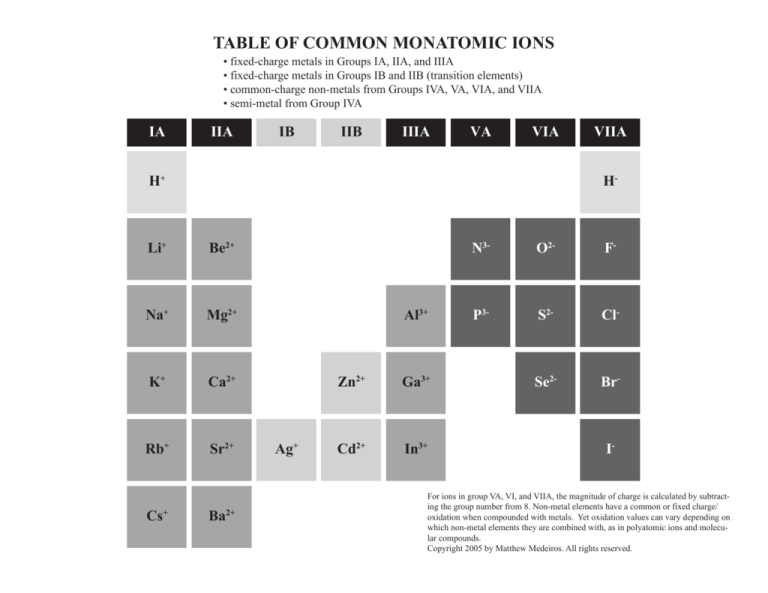
TABLE OF COMMON MONATOMIC IONS
• fixed-charge metals in Groups IA, IIA, and IIIA
• fixed-charge metals in Groups IB and IIB (transition elements)
• common-charge non-metals from Groups IVA, VA, VIA, and VIIA
• semi-metal from Group IVA
IA
IIA
IB
IIB
IIIA
VA
VIA
H+
H-
Li+
Be2+
Na+
Mg2+
K+
Ca2+
Rb +
Sr2+
Cs+
VIIA
Ba2+
Al3+
Ag+
Zn2+
Ga3+
Cd2+
In3+
N3-
O2-
F-
P3-
S2-
Cl-
Se2-
Br-
I-
For ions in group VA, VI, and VIIA, the magnitude of charge is calculated by subtracting the group number from 8. Non-metal elements have a common or fixed charge/
oxidation when compounded with metals. Yet oxidation values can vary depending on
which non-metal elements they are combined with, as in polyatomic ions and molecular compounds.
Copyright 2005 by Matthew Medeiros. All rights reserved.
TABLE OF COMMON VARIABLE-CHARGE METALS
• variable-charge transisiton metals
• variable-charge metals from groups IIIA and IVA
IVB
VB
2+
2+
Ti
Ti3+
V
V3+
VIB
VIIB
Cr2+
Cr3+
Cr6+
Mn2+
Mn3+
Mn7+
VIIIB
Fe2+
Fe3+
Co2+
Co3+
IB
Ni2+
Ni3+
IIB
IIIA
Cu+
Cu2+
Ge2+
Ge4+
Pd2+
Pd3+
Pt2+
Pt3+
IVA
Sn2+
Sn4+
Au+
Au3+
Hg+
Hg2+
Tl+
Tl3+
Pb2+
Pb4+
Comment: The variable-charge nature of certain metals presents a unique outcome in compound formation. Since these metals can form multiple
charges they will compound with nonmetals (or polyatomic ions) in differing ratios. Therefore, the Roman numeral designation is required in
the nomenclature to specify the correct compound. For example, there are several types of manganese oxides, each with characteristic chemical
and physical properties. Manganese (III) oxide, Mn2O3, is a black mineral insoluble in water. Whereas, manganese (VII) oxide, Mn2O7, is a
dark reddish mineral which is soluble in water. Manganese will also form two other oxides each with differing colors and solubilities.
Copyright 2005 by Matthew Medeiros. All rights reserved.
LIST OF COMMON POLYATOMIC IONS
(Monatomic ions are listed first in the family.)
Copyright 2005 by Matthew Medeiros. All rights reserved.
NITROGEN
N3NO2NO3NH4+
nitride
nitrite
nitrate
ammonium
ORGANIC (CARBON CONT.)
NOTES
HCOO-
formate (derived
from formic acid,
also written HCO2-)
-ate ................ used to designate
the oxyanion with
the higher number
of oxygen atoms
H3C2O2-
acetate (derived
from acetic acid,
also commonly
written CH3COO-)
PHOSPHORUS
P3PO33HPO32PO43HPO42H2PO4
-
phosphide
phosphite
hydrogen phosphite
phosphate
hydrogren phosphate
dihydrogen phosphate
SULFUR
S2SO32HSO3SO42HSO4S2O32S2O72-
sulfide
sulfite
hydrogen sulfite
sulfate
hydrogen sulfate
thiosulfate
disulfate
CARBON
C4CO32HCO3CN-
C2O42-
oxalate (derived
from oxalic acid)
thio- ............... add one sulfur,
remove one oxygen
OXYGEN
2-
O
O22OH-
oxide
peroxide
hydroxide
CHLORINE
ClClO4ClO3ClO2ClO-
chloride
perchlorate
chlorate
chlorite
hypochlorite
METALS/SEMI-METALS
carbide
carbonate
hydrogen carbonate
(or bicarbonate)
cyanide
-ite ................. used to designate
the oxyanion with
the lower number of
oxygen atoms
MnO4CrO42Cr2O72AsO43SiO44-
permanganate
chromate
dichromate
arsenate
silicate
per- ................ one additional
oxygen
hypo- ............. one less oxygen
-ide ................ although this suffix
is reserved for the
monatomic anion,
the exceptions are
cyanide, hydroxide,
and peroxide
di- .................. two or double (i.e.,
as with dichromate,
double the numeric
subscripts on the
chromate ion and
reduce the oxygen
by one; retain
charge)
OTHER COMMON ANIONS
SOME COMBINED IONS
BO33BrO3IO3IO4OCNSCN-
HSNH4PO42-
borate
bromate
iodate
periodate
cyanate
thiocyanate
HC2O4Fe(CN)63-
hydrogen sulfide
ammonium phosphate
hydrogen oxalate
hexacyanoferrate