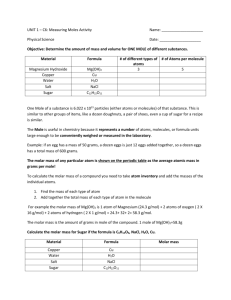
1. How many grams of KCl would you need to weight out to prepare
advertisement

1. How many grams of KCl would you need to weight out to prepare 0.25 L of a 2 M KCl solution ? (Mol masas of KCl = 74.5 g/mole) (37.25 g) 2. Calculate the molarity (molar concentration) of a solution made by dissolving 5 g of glucose (C6H12O6) in sufficient water to form exactly 100 ml of solution (mol. mass of glucose is 180 g/mole). (0.27 moles/L) 3. What is solubility? What does it mean, that solubility of NaCl at a certain temperature is 36 ? 4. Glucose concentration in blood is 100 mg/100 ml (mg%). Transfer this concentration into molar concentration. (0.0056 M = 0.0056 moles/L) 5. A physiological saline solution contains 154 mM (0.154 moles/L) each of Na+ and Cl−. How many grams of Na+ and Cl− are in 1.0 liter of saline solution ? (m. mass of Na = 23, Cl = 35.5 g/mole) (3.54 g Na+; 5.467 g Cl-) 6. 10 ml of 0.1 M HCl and 990 ml of water were mixed. What is pH of the solution ? (pH = 3) 7. How many grams of NaOH should be added to 2 L of 1 M solution of acetic acid in order to have equal values for [H+] and dissociation constant of acetic acid ? ([H+] = Kacetic acid). Kacetic acid = 1.8 × 10-5. (40 g) 8. How many ml of 1 M H2SO4 do you need to neutralize 0.02 moles of KOH ? (10 ml) 9. Two solutions: 1 % glucose (m/v) and 1 % urea (m/v) were separated by semipermeable membrane. Are these solutions isotonic ? If not which one exerts higher osmotic pressure on semipermeable membrane and why ? Write toward which solution water molecules will penetrate through semipermeable membrane. (Urea solution is hypertonic in comparison with glucose solution) 10. Calculate the freezing point of the water solution of nonelectrolyte that boils at 101.53oC. (-5.58oC) 11. What will be percent concentration of saccharose solution, isotonic to 2 % solution of glucose. Molar mass of glucose is 180 g/mole, for saccharose is 342 g/mole. (3.76 %) 12. What will be the freezing and boiling point of the solution composed of 55.5 g of CaCl2 and 1 L of water (molecular mass of CaCl2 is 111 g/mole). (f.p. = -2.79 oC; b.p. = 100.76 oC) 13. There are two water solutions: 0.9 % (m/v) NaCl and 0.9 % (m/v) KCl. Are these solutions isotonic ? If not, what will be percent concentration of KCl solution, isotonic to 0.9 % NaCl ? Molar mass of NaCl is 58.5 g/mole; molar mass of KCl is 74.5 g/mole. (1.14 %) 14. The solubility of NaCl at 20 oC is 36g/100g of water. Calculate whether all NaCl will be dissolved after mixing 30 g of NaCl with 80 g of water at 20oC. (not all NaCl will dissolve) 15. What volume of 0.2 M H2SO4 is needed to neutralize of 0.16 g NaOH ? (Molar mass of NaOH = 40 g/mole) (10 ml) 16. How many grams of HCl are there in 100 ml of the solution if during titration of 15 ml of this solution, 12 ml of 0.09 M NaOH were used (Mol. Mass of HCl = 36.5 g/mole)? (0.263 g) 17. What is the mole fraction of saccharose in the solution composed of 3 moles of saccharose and 2 L of water. (0.026) 18. 0.11 moles/L of NaCl penetrated to the dialyzing bag containing 0.02 moles/L of NaPr (Na+Pr-). Calculate concentration of NaCl outside the bag as: a. initial concentration (before dialysis) b. concentration at equilibrium state (at Donnan equilibrium). (Initial concentration of NaCl = 0.229 moles/L; at equilibrium state = 0.119 moles/L) 1. What will be the freezing and boiling point of the solution composed of 117 g of NaCl and 1 L of water (molecular mass of NaCl is 58.5 g/mole). (f.p = -7.44oC; b.p. = 102.04oC) 2. Two solutions: 1 % glucose (m/v) and 1 % urea (m/v) were separated by semipermeable membrane. Are these solutions isotonic ? If not which one exerts higher osmotic pressure on semipermeable membrane and why ? Write toward which solution water molecules will penetrate through semipermeable membrane. (Urea solution is hypertonic in comparison with glucose solution) 3. Calculate the freezing point of the water solution of nonelectrolyte that boils at 101.53oC. (-5.58oC) 4. What will be percent concentration of saccharose solution, isotonic to 2 % solution of glucose. Molar mass of glucose is 180 g/mole, for saccharose is 342 g/mole. (3.76 %) 5. What will be the freezing and boiling point of the solution composed of 55.5 g of CaCl2 and 1 L of water (molecular mass of CaCl2 is 111 g/mole). (f.p. = -2.79 oC; b.p. = 100.76 o C) 6. There are two water solutions: 0.9 % (m/v) NaCl and 0.9 % (m/v) KCl. Are these solutions isotonic ? If not, what will be percent concentration of KCl solution, isotonic to 0.9 % NaCl ? Molar mass of NaCl is 58.5 g/mole; molar mass of KCl is 74.5 g/mole. (1.14 %)