diazotization/diazocoupling
advertisement

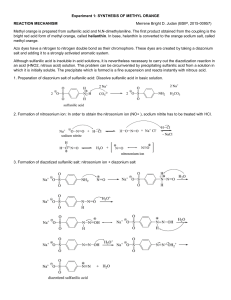
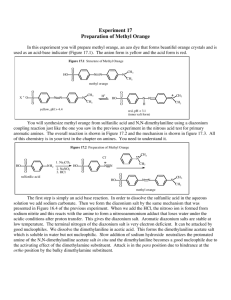
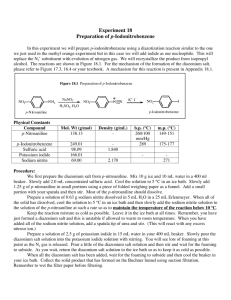
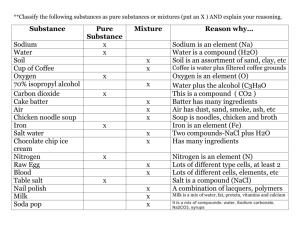
E X P E R I M E N T 2 9 DIAZOTIZATION/DIAZOCOUPLING: PREPARATION OF METHYL ORANGE Amines have numerous reactions with nitrous acid, HONO. These reactions involve attack by the nitrosonium ion, :N=0:+, as an electrophile, at the nitrogen atom's electon pair. They may be summarized as follows: N2 and alcohols 1 oaliphatic Ar-N=N:+ 1oaromatic 2 oaromatic N-nitrosoamines 3 oaliphatic no reaction 3 oaromatic p-nitrosoamines One of the more important synthetic tools in organic chemistry is the diazonium salt, ArN=N:+, which acts as an intermediate in the production of Ar-X, Ar-C=N, and Ar-OH. The diazonium salt reacts with various nucleophiles to form the substituted product and N 2 gas. This nucleophilic substitution reaction is thought to occur by a radical mechanism. Some examples of these reactions are shown below. Ar-N=N:+ reacts with: (1) KCN, CuCN → Ar-C=N (nitrile) + N2 (2) H+ , H2O → Ar-OH + N2 (3) H3PO2 → Ar-H + N2 (4) KI → Ar-I + N2 (5) CuBr (or CuCl) → Ar-Br (or Ar-Cl) + N2 (6) HBF4, Heat → Ar-F + N2 A diazonium salt is capable of reacting with highly activated aromatic compounds to form coupling products which have the formula Ar-N=N-Ar-G. These highly conjugated compounds are excellent dyes. Ar-N=N:+ + H-Ar’ –G Ar-N=N-Ar’-G + H+ Coupling Product In this experiment, a diazonium salt will be synthesized and then reacted with N,Ndimethylaniline in a coupling reaction. The process of diazotization is carried out by reacting a primal aromatic amine with the nitrosonium ion under slightly acidic conditions. In this case the compound to be diazotized is sulfanilic acid, p- SO 3 - -C 6 H 4 -NH 3 + . This difunctional compound normally exists as a "zwitter ion" which is indicated in the latter formula. This process is summarized as follows: (1) Reaction of sulfanilic acid with sodium carbonate. This creates the free -NH2 group. NH3+ 2 NH2 + Na2CO3 2 + H2O + CO2 - SO3 SO3Na 1 mole = 173.19 g (2) Diazotization: Reaction of sodium sulfanilate with sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and HCl. This reaction involves attack of NO+ at the aromatic nitrogen, followed by elimination of water. NH2 N N + NaNO2 + 2HCl + +2 H2O + 2 NaCl 0-5oC SO3Na SO3 - diazonium salt (3) Diazocoupling: The diazonium salt produced by this process is not purified but is reacted with the coupling reagent. In this case, the diazonium salt is reacted with N.Ndimethylaniline (1 mole = 121.18g) to yield methyl orange, an azo dye. This reaction is an example of electrophilic aromatic substitution by the very weak electrophile, the diazonium ion. N N+ NH(CH3)2Cl + SO3 + 2NaOH SO3Na N N N(CH3)2 +NaCl + 2H2O - diazonium salt Methyl Orange Thus, amines react with HONO to yield various products. A primary aromatic amine is converted to a diazonium salt which in turn leads to numerous substitution and coupling products. For this reason, diazonium salts are often used in many synthetic processes. PROCEDURE I.Diazotization 1. Place 200 mg of sulfanilic acid in a 50-mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add 60 mg of anhydrous Na2CO3 and 2-mLs of water. Warm this mixture gently on the sand bath to dissolve the solids. Then, cool the solution to room temperature. 2. Add 85 mg of NaONO (sodium nitrite). Stir to dissolve. 3. Place in an ice-water bath to cool. 4. While this solution is cooling, mix about 2 grams of ice with six drops of concentrated HC1 in a reaction tube. Pour this mixture into the Erlenmeyer flask. Stir thoroughly. 5. The diazonium salt should begin to form within 2-5 minutes. It will appear as a white suspended precipitate. Set this suspension aside in the ice-water bath in preparation for the coupling reaction. II.. Oiazocoupling: Preparation of Methyl Orange. 1. Tare a reaction tube in a small beaker. Add 130 mg dimethyl-aniline and 110 mg of glacial acetic acid to "this tared reaction tube. Mix well. [Note: dimethylaniline is the limiting reagent.] 2. Pour the dimethylaniline/acetic acid solution into the Erlenmeyer flask containing the suspended diazonium salt. Rinse the reaction tube with a little water to transfer the last traces of the dimethylaniline/acetic acid solution. 3. Stir the contents of the Erienmeyer flask for several minutes. A red, pasty mass of methyl orange should separate. 4. Add 2-mLs of 10% NaOH and mix. Check with Litmus paper to determine if the solution is alkaline. Add more NaOH if needed. 5. Add 1.2 grains of NaCI. The color of the crystals should become yellow as the acid form of methyl orange is converted to its sodium salt in its base form. NaCI is added to decrease the solubility of this sodium salt in water. 6. Warm the solution to nearly boiling in the sand bath. Allow the solution to cool to room temperature and then in an ice-water bath. The dye should separate as orangecolored crystals. 7. Suction filter the crystals. Press dry. Obtain the weight of the crystals and turn in the product in a properly labeled vial. EXPERIMENT 29: Report and Worksheet DIAZOTIZATION/ DIAZOCOOPLING: PREPARATION OF METHYL ORANGE Student Name:__________________ _______ Student Number: ____________________________ Day:_______________ Date:_________________ DATA Mass of sulfanilic acid used. .... _______ grams _____ moles Mass of dimethylaniline used. .... ________ grams ____ moles Theoretical yield of methyl orange: _________ grams (Show calculation.) Mass of methyl orange obtained:_____________ Percent Yield:_________ (Show calculation.) grams QUESTIONS 1. Draw TWO RESONANCE STRUCTURES for the nitrosonium ion, NO+. 2. What is the equation for generating NO+ in a dilute solution of HCl and NaNO2? 3. What is the BALANCED EQUATION for the reaction between sulfanilic acid and sodium carbonate ? 4.What is the BALANCED EQUATION for the reaction sodium sulfanilate (product of previous reaction) and NaNO2 and HCl ? 5. What is the BALANCED EQUATION for the reaction between the diazonium salt; (product of 6. What is the purpose of adding NaOH to the red crystals of methyl orange? 7. WHY is NaC1 added to the reaction mixture before final crystallization? 8. What is the general reaction that occurs between a diazonium salt and a nucleophile, Nu- ? 9. What product is formed when p-CH3-C6H4-N2+Cl- is reacted with each of the following compounds? (1) KI (2) HBF4, heat (3) CuCN, then, H2 catalyst (4) phenol (5) o-methylphenol (o-cresol) (6) H+, water