2014 ap biology summer quiz
advertisement

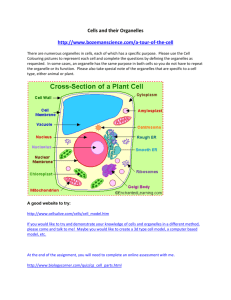
Name:____________________________________________________ AP Biology Summer Quiz ‐ 2014 Instructions: You are receiving this packet because you signed up for AP Biology in the 2014‐2015 school year. You are to complete this quiz and turn it on the first class of AP Bio in August. The idea of this quiz is to jumpstart your thinking on the subject of Biology. I expect you to know all this information before you start AP Bio. If you do not wish to take AP Biology next year, please contact your counselor and have your schedule changed. If your friends did want to take AP Biology and did not receive one of these quizzes, have them contact their counselor to get on the list and come to me for the quiz. If you lose this packet, it has been shared with you in GoogleDocs. If you have any questions, email me at lbowers1@aisd.net Biochemistry 1. Fill in the table with either the missing information of each type of biomolecule Biomolecule type Monomer name Polymer name Function Protein Nucleic acid Lipid Carbohydrate Osmosis 2. If an animal cell is placed into a hypotonic solution. The cell will a. Swell until it bursts b. Shrivel up and die c. Swell until it reaches the maximum capacity allowed by its cell wall d. Activate its aquaporin pumps to maintain homeostasis Cellular Respiration 3. Name the three phases (a.k.a. parts or steps) of cellular respiration. Hint: one of them takes place in the cytoplasm and the other two take place in the mitochondria. 4. Which phase can occur in the absence of oxygen? 5. Which phase produces the most ATP? 6. Draw a molecule of ATP. Indicate which is the high energy bond that is broken when ATP is used. Cells & Organelles 7. Identify the indicated organelles in the following pictures of a plant cell, an animal cell and a bacterial cell. The organelles may be repeated from picture to picture. Animal Cell – you only need to name the organelles that have lines next to them. Ignore the letters. Plant Cell – name the organelles indicated with an arrow and a letter (or two). Bacterium cell – name all the organelles that have a line pointing to them. Name:____________________________________________________ Photosynthesis 8. What are the two phases (a.k.a. parts or steps) of photosynthesis? 9. Water is necessary for the functioning of photosynthesis. Where and how is it used? 10. Carbon dioxide is necessary for the functioning of photosynthesis. Where and how is it used? 11. What is the name of the structure on a leaf through which the plant takes in carbon dioxide and releases oxygen? Genetics 12. Using the following DNA strand and genetic code, write a) the mRNA strand that would be transcribed from this DNA and b) the polypeptide chain that would be translated from the mRNA. You may use either the three letter or one letter abbreviations for the amino acids. DNA: sense (or coding) strand: 3’ – ATGCTTGCCATAAAATTCCCGTAGCAT – 5’ anti‐sense (or non‐coding)strand: 5’ – TACGAACGGTATTTTAAGGGCATCGTA – 3’ a) b) Population Genetics 13. In unicorns, the allele for straight horns (H) is dominant over the allele for curved horns (h). Two heterozygous unicorns mate. Fill in this Punnett square for the offspring of this couple. a) List the possible genotypes of the offspring and the ratio of these genotypes. b) List the possible phenotypes of the offspring and the ratio of these phenotypes. 14. In dragons, smooth‐edged wings (E) are dominant over ragged‐edged wings (e). Also, fire‐breathing (F) is dominant over non‐fire‐breathing (f). Two dragons that are heterozygous for both traits mate. Fill in this Punnett square for the offspring of this couple. a) List the possible phenotypes of the offspring and the ratio of these phenotypes. Evolution 15. Put the following events into chronological order according to the most widely accepted hypothesis in the theory of evolution. a. Plants colonize the land. b. Organic molecules assemble into self‐replicating RNA molecules. c. The precursor to the eukaryotic cell acquires an aerobic bacterium which eventually becomes a mitochondrion. d. Lipids form a micelle (a.k.a. protocell or protobiont) which encapsulates ribozymes. e. A eukaryotic cell acquires a photosynthetic bacterium which eventually becomes a chloroplast. f. Energy sources such as lightning and thermal vents catalyze the formation of small, organic molecules from inorganic molecules. g. Cyanobacteria develop the ability to capture light energy and turn it into glucose. h. Animals colonize the land. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th Cell Cycle 16. In three to four sentences, outline the process of mitosis. Do NOT name any of the phases (prophase, anaphase, etc.), only discuss what happens in mitosis. 17. The following diagram illustrates a process that occurs in meiosis, but not mitosis. In two to three sentences, identify the process, describe what is happening, and explain its significance for genetic diversity. Plants 18. Identify the following parts of a leaf. 19. Classify the following statements as being more accurate of xylem (X) or phloem (P). Write the appropriate letter to the left of the statement. a. Carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the shoots. b. Transports dissolved sugars. c. Comprised of living cells. d. Comprised of non‐living cells. e. Cell types include: vessel elements and tracheids f. Cell types include: sieve‐tube members and companion cells. Ecology 20. Put the following phrases in the order of primary succession. a. Grasses b. Climax community c. Bare rock d. Herbs, weeds e. Shrubs f. Lichens g. Fast‐growing trees h. Mosses ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 21. In one to two sentences, compare and contrast primary and secondary succession. Body Systems 22. What type of cell is depicted below? 23. Label the indicated parts of the cell. 24. Identify the following statements as most accurate for B‐cells (B), T‐cells (T), or both (BT). Write the appropriate letter to the left of the statement. a. Makes antibodies. b. Is activated by contact with an antigen. c. Is infected by HIV. d. Makes memory cells. e. Kills infected cells by releasing chemicals that induce apoptosis. f. This family of cells includes names like: helper, cytotoxic and suppressor.