Dr Bobby Tsang,
Specialist Paediatrician
North Shore Hospital
Let’s Get Going
Managing Childhood Constipation
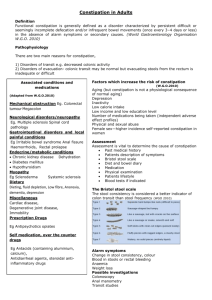
Childhood constipation
Common 10-30%
Associated incontinence
Essential aim - prevent pain with defecation
Invasive investigations not routinely needed
Refer if organic disease or review treatment
Behavioural and social consequences
Long term managment
Epidemiology
“Normal” relates to culture and diet
Majority pass 1 motion per day
1% < 3 per week or > 3 per day
3-5% Paediatric outpatients
Bimodal
Infancy (soon after birth) and around 2yrs
M:F 2:1
65-70% better after 2y
Persists post puberty >30%
Rome III criteria >2 for >2m
Developmental age > 4 y
<3 stools pw 75%
Fecal incontinence >1 pw 75-90%
Retentive posturing or XS volitional stool
retention 35-45%
Painful or hard bowel movements 70%
Large fecal mass in the rectum 30-50%
Large-diameter stools that obstruct toilet 75%
Other symptoms
Lack of energy, “not well”
Poor appetite 25%; Vomit 10%
Abdominal distension 20-40%
Fissures or haemorrhoids 5-25%
Rectal bleeding 7% Anal prolapse 3%
Enuresis or UTI 30%
Excessive foul flatus and stool
Scybalous stool
Psychological / Social 20%
Poorly organised family environments
Less expressive
Poor social competence
Poor scholastic performance, learning
disabilities, ADHD
Anxiety / depression
Unhappy, angry, irritable, moody
Disobedient, disruptive behaviour
Incontinence
Barrier to independence
Education, work, financial, social, relationships
Emotional
Low self-esteem, worry, embarrassment, guilt, fear,
isolation, sadness, frustration
Psych probs - Joinson 2006
Adult OR=2
OAB, LUT dysfn, UTI, obesity, sexual dysfn, mood
disorders
Fitzgerald 2006, Minassian 2006
Colon
Highly efficient complex organ
Absorbs
400ml/day (up to 3 litres)
Homeostasis of electrolytes
Stores faeces
Tone
Rhythmic segmentation 5-40 mmHg 60/day
Discharges faeces
Secretes mucus
Peristalsis
Mass movements 100 mmHg, on waking and PC
HAPC High amplitude propogating contractions
Paraplegia
Hyperactive irregular segmentation
interstitial cells of Cajal
Refinement of concept first proposed by Cajal and later Daniel and Posey-Daniel
Neurotransmitter released from enteric motor neurones binds primarily to receptors expressed
by (ICCs). Ward S M Gut 2000;47:iv40-iv43
Copyright © BMJ Publishing Group Ltd & British Society of Gastroenterology. All rights reserved.
Molecular level
5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) <-gut distension
Substance P excitatory
CF constipation. Channel activators for treatment.
Increased mast cells
?XS NO inhibits colonic motility in STC?
Chloride drives fluid secretion into colon
Lower substance P nerve fibre density in children
with IND
Nitric Oxide NO inhibitory
->local Ach -> muscle contraction upstream
->NO muscle relaxation downstream
? Primary or secondary to injury
Progesterone reduces excittory Ach and 5HT
Receptors overexpressed in women with STC
Symptoms vary with menstrual cycle
Ano-Rectum
Stores faeces temporarily
Continence maintained by
Valves of Houston – rectum
Freq of contraction distally
Levator floor tone
Rectopubalis sling – lifts weight of faeces
Anus
Internal sphincter relax w rectal distension
External sphincter reflex contraction and voluntary
relaxation
Sensation touch, pin prick, temperature
Defaecation
Pressure threshold in sigmoid/descending colon
Haustrations disappear
Rectal filling and anal sampling
Reduced angulation of ano-rectal canal (squat)
Bolus moves lubricated by rectal mucus
Reflex relaxation Internal anal sphincter
Voluntary relaxation of ext anal sphincter
Valsalva increases intra-abdominal intrarectal
pressure
Peristaltic cleaning wave follows bolus
Dys-synergia
Factors affecting activity
Posture - CP
Physical exercise – hypotonia
Eating
Psychological stimulus
Osmotic material in duodenum
Gastrocolic response – mass movt
Emotion pain/stress – inconsistent
handling/caregivers?
Drugs
Codeine, antacids, anticholinergics
(oxybutinin)
antipsychotics/antidepressants
Bristol stool form chart
Red flags
Symptoms @birth - few weeks
Meconium > 48 h after birth
'Ribbon' stool (usly <1 y)
Abdominal distension with vomiting
Weak legs or locomotor delay (falls > 1 y)
Lower limb deformity or neurology vDTR
Anus
Fistula; bruising; fissures; tight or patulous;
anteriorly placed; absent wink)
Lumbosacral
Asymmetric glutei, sacral agenesis, scoliosis,
skin abnormality, sinus, central pit)
Amber flags
Faltering growth and well-being
Possible maltreatment
Causes - infants and toddlers
History
Genetic predisposition
Breast feeding to cows’ milk formula
Cows’ milk protein allergy
Lack of fibre
Stool withholding
Retentive posturing
Coeliac disease
Examination
Anal fissure
Spina bifida
Anorectal malformations
Hirschsprung disease
Causes – School and adolescent
History
Poor intake
Toilet training coerced
Attention-deficit disorders
Developmental handicaps
Toilet phobia, school bathroom avoidance
Excessive anal interventions
Examination
Anorexia nervosa
Depression
Slow transit constipation
Psycho-social history
Family attitude and motivation
Toilet training
High stress environments
Socioeconomic level
Development
Temperament
Peer relations
Physical environments
School / home
Sexual abuse
Non-functional
Hirschsprung Disease
Drugs
Cow's milk intolerance
Celiac disease
Intestinal neuronal dysplasia
Anorectal malformations
Megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome
MMIHS (Berdon syndrome)
Chronic dysmolity / pseudo obstruction
Autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy
Acetylcholine receptor AChR dysmotility
Neuromuscular conditions
Hypertonia CP
Hypotonia
Hypothyroidism
Spinal dysraphism, tethered cord
Prune-belly syndrome
HypoK hyperCa
Neuropathic/ Myopathic / mitochondrial
Hirschprungs History
50% delayed meconium >36 hr
Constipation week 1 of life
Vomiting – bile
Alternating constipation & diarrhoea
Soiling rare
Severe abdominal distension
Failure to thrive
Tight anus
Explosive response to rectal exam
Family history 1:5000
Short segment M5:F1
Long segment M=F
Acute
Infants change in diet
Following bed rest
Anal tears and fissures
Rectal prolapse
Treatment
Increase fluids
Chronic Constipation
Soiling 70%
Faecal loading
Indentable masses
Huge motions
Lax anus
Anal fissures
Associated wetting
Recurrent abdominal pain
Retentive posturing
Painful defecation
Poor appetite & irritability
Physical Examination
Abdominal faeces
Perineum
location of anus
halfway betw posterior fourchette (base of
the scrotum) and tip of coccyx
fissures, fistulae, or haemorrhoids
anal wink and tone
Lumbar Spine and lower limb
neurology
Rectal examination
Neurogenic Bowel
Spinal dysraphism
Tethered cord
Sacral Agenesis
Vertebral deformities
Spinal cord tumour
Cord or nerve injury
Franco 2008
Investigations
None if thriving, eating and symptoms
confined to anorectum
Abdominal xray
Lumbar spine
Thyroid function
Calcium
Biopsy - rectal / large bowel
Transit study for IND
Running on Empty
Explanation/education
Empty Bowel
Keep bowel empty
Stool softener
Stimulants
Scheduled toileting
Fibre fluids exercise
Support
Maintenance
General Issues
Develop relationship
Reassure Encourage Support
Empower
Demystify diagnosis and causes
They are not alone
Develop treatment plan with child
Be positive - spontaneous cure 15% pa
Assess motivation
Long term maintenance
Toilet Routine
Scheduled
after meals
Comfortable
Footstool
School toilets
Positive
Reinforcements – star chart, praise++, rewards
No fuss/ nag / threat/ scold/ force/ tease/ leave in
soiled pants
Transfer responsibility
Sneaky poo
Regular evacuation
Establish Daily routine < 24 h
Avoid and treat constipation
Empty bowel
Praise & reinforcement with assistance
Outreach nursing support
Schedule with meals, baths, physical activities, time
Potty 10-15 minutes, 20-30 minutes after a meal
Knees higher than buttocks - footrest
Cough or grunt for abdominal activity
Digital stimulation, Wipe anus
Levator lift with fingers to each side of anus
Manage stool consistency – fibre H2O + laxatives
Suppository / enema for routine
To soften stool
Chocolate / malt
Kool-aid , fruit juice
Candy
Citrus fruit, tomato,
passionfruit, pineapple
Corn (fresh or tinned)
Baked beans
Pizza
Nuts/dried fruit
Disimpaction
Prescriptions
Bulk forming laxatives
benefibre metamucil konsyl mucilax isogel etc
Stool softeners and lubricants
lactulose paraffin coloxyl
Hyperosmotic cathartics
Picoprep, Golytely, Movicol
Magnesium Hydroxide 8% 1ml/kg (max 60ml)
Stimulants
Senna, Castor, bisacodyl (dulcolax), danthron (codalax)
5HT4 agonist
Tegaserod
(J Liem et al J Pediatr Gastro and Nutrition 46:54–58 # 2008 by
European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,)
Per Rectum
Suppository
Glycerol
Fleet glycerine (glycerol)
Fleet laxative (bisacodyl)
Coloxyl sup (bisacodyl;docusate)
Enema
Microlax (Na citrate; Na lauryl sulfoacetate; sorbic acid; sorbitol)
Fleet phosphate enema (Na phosphate)
Coloxyl enema conc (docusate Na)
Fleet micro- enema (Na citrate; Na lauryl sulfoacetate; sorbitol)
Fleet phospho-soda buffered saline mixture (Na Phosphate)
Colonic washouts
Clean bowel 2–3 days
Volume and hydrostatic
pressure
Saline/water; soap/water;
other
Reduce soiling
Latex precautions
Can contribute to
dependency
Retrograde
30 ml balloon catheter
w large syringe
Shandling catheter
Peristeen anal
irrigation kit
Mic Bowel
management Kit
Antegrade continent enema (ACE)
High degrees of satisfaction
Improves independence esp for
wheelchair dependent
Sterile bowel – no smell
Chait cecostomy button
Malone (MACE) – continent
appendicostomy
Monti technique - donut of
ileum/colon cecum or splenic
flexure
Anal plugs
Prevents rectal leakage up 12 h
Porous foam Lubricated with Vaseline
Expands with moisture 30 sec
Mushroom shape
Removed with attached string
Changed after toilet visit
Increase independence
Additional resources
For healthcare professionals
NICE Diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in
primary and secondary care. 2010.
http://publications.nice.org.uk/constipation-in-children-and-young-peoplecg99 and www.nice.org.uk/CG99
NHS Evidence. Constipation in children. Management.
www.cks.nhs.uk/constipation_in_children/management/scenario_diagnosis_
and_assessment_younger_than_1_year/view_full_scenario#467016006
For Families
www.kidshealth.org.nz/constipation
Continence Association NZ http://www.continence.org.nz
ERIC http://www.eric.org.uk/Constipation/constipation_and_soiling
One Step at a time for children with disability
http://www.continencevictoria.org.au/sites/default/files/Booklet.pdf
NHS choices www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Constipation/Pages/Treatment.aspx —
Advice for families on constipation and treatment, incl lifestyle
NICE http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG99/PublicInfo/doc/English —Guideline
for familiy on NICE guidance CG99
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse UShttp://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/constipationchild/
Childhood constipation
Common 10-30%
Associated incontinence 70%
Essential aim - prevent pain with defecation
Invasive investigations not routinely needed
Refer if organic disease or review treatment
Behavioural and social consequences
Empty bowel and keep empty
Maintain good habits