MOBNAS?
advertisement

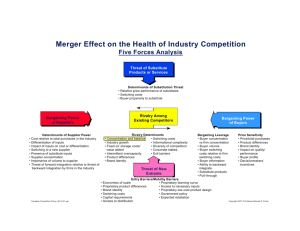
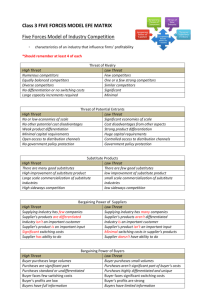
MOBNAS? Achadiat A. Suhadi Solo, 10 Desember 2011 INDONESIA : MARKET OF OPPORTUNITY •Indonesia, a very potential market with total population of 228.5 millions people in 2008 •58% of the population live in Java, although Java is only 7% of total land area in Indonesia. •Average GNP per capita is USD 3,000 per yr •The main driver for Indonesian economy is domestic consumption. •Growth at 6% for the last couple of years •Car Ownership : 121 people per car (2008) GROWTH 1,000,000 CAR SALES 900 800 2010 2011 2012 MARKET SHARE DOMINATION OF JAPANESE BRANDS TRANSPORT EQUIPMENT & MACHINERIES IMPORT VALUE 77% OF THE PARTS IS SUPPLIED BY LOCAL SUPPLIER GOVERNMENT POLICY “LOW PRICED CAR (Rp. 60,000,000/unit)” - Encourage indigene new entrant to invest - Especially in part manufacturing business PORTER”S FIVE FORCESS ON AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY •Fixed (or storage) costs/value added THE THREAT OF ENTRY (Entry Barriers) •Absolute cost advantages •Proprietary learning curve •Access to necessary inputs •Proprietary low-cost product design •Government policy •Economies of scale •Capital requirements •Proprietary product differences •Brand identity •Switching costs •Access to distribution •Expected retaliation •Intermittent overcapacity •Industry growthTHE DEGREE OF RIVALRY SUPPLIER POWER •Product differences •Supplier concentration •Concentration and balance •Importance of volume to supplier •Fixed (or storage) costs/value added •Brand identity •Differentiation of inputs •Intermittent overcapacity •Switching costs -> •Impact of inputs on cost or differentiation •Industry growth •Switching costs of supliers and firms in industry •Product differences •Informational complexity •Presence of substitute inputs •Brand identity •Threat of forward integration relative to•Diversity threat •Switching costs -> of competitors of backward integration by firms in industry •Informational complexity •Cost relative to total purchases in industry •Diversity of competitors •Corporate stakes •Corporate stakes •Exit barriers THE THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES •Relative price performance of substitutes •Switching costs •Buyer propensity to substitute BUYER POWER •Bargaining leverage •Buyer concentration vs. firm concentration •Buyer volume •Buyer information •Buyer switching costs relative to firm switching costs •Pull-through •Substitute products •Ability to backward integrate •Price sensitivity •Price/total purchases •Impact on quality/ performance •Product differences •Brand identity •Buyer profits •Decision makers’ • incentives ENTRY BARRIER Absolute cost advantages Proprietary learning curve X Access to necessary inputs X Proprietary low-cost product design X Government policy X Economies of scale X Capital requirements Proprietary product differences Brand identity Switching costs Access to distribution Expected retaliation Industry Attractiveness Force Internal rivalry Entry Substitutes/C omplements Supplier power Buyer power High Threat to profits High Low to Medium Medium to High Medium Medium STRATEGY TO ENTRY MARKET SITUATION SOCIAL Lower buying power, need for motorcycle substitution, Social empowerment for economics recovery Reinforce confidence for local added value TECHNOLOGY Shorter life time, lower production volume, multi variant Appropriate technology for low volume production, Extended enterprise by managing team work across supply chain of logistics & production Flexible manufacturing, multi resources-multi facilities Concurrent Engineering to speed up time to market STRATEGY TO ENTRY MARKET SITUATION ECONOMICS Foreign exchange saving, import substitution Ride on rebound wave of economics recovery Increase domestic turn over and spin off effect ENVIRONMENT Increase recycle-able material Environment friendly of product and production facility POLITICS Stimulate power of middle level community Nationalism dignity STRATEGY TO ENTRY INITIAL SWOT UTILIZATION STRENGTH -Emotional nationality sentiment driving force -New concept in business, technology & investment -Best utilization of access & relation of relationship with academician, industry & government WEAKNESS -New comer: image, market, supply & distribution network -Production facility -Financial strength STRATEGY TO ENTRY OPPORTUNITY -Low priced car program with opportunity market -Brand new investment (focus & accuracy) develop extended company chain network. -Government policy on industrial and economics growth THREATS -Slump down of global economics -Global automotive industry excessive capacity -New player & new product in the same segment TECHNICALLY………………………………. Ready to enter the industry with assumptions: 1. Make use proximity to market. 2. Pull , not Push process. 3. Priority on profit cashflow turnover 4. Smart, Accurate and Necessity investment 5. Proper technical step for competitive and sustainable profitability. 6. QCDSMT based supply and distribution chain development 7. Strong technopreneur support with long term commitment. Typical Ramp Up Steps Typical Initial Cost Necessary Items 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Product Development Market Proofing Production Tooling Production Facility Marketing & After Sales Raw material, WIP & Finish unit stock TOTAL: Amount Rp. 2,000,000,000.1,000,000.000,30,000,000,000,5,000,000,000,10,000,000,000.152,000,000,000.________________ 200,000,000,000